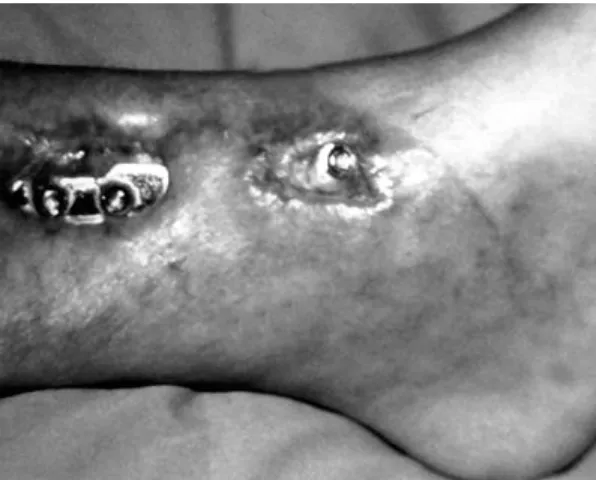
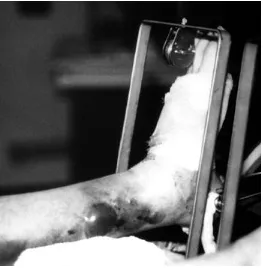
A case study of distal tibial fractures managed with locking compression plate using MIPO technique
Full text
Figure
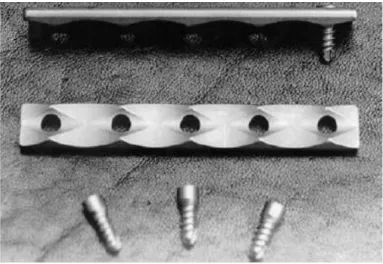



Outline
Related documents
Babst, Locking Compression Plate with Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibia fracture: A retrospective study of 32 patients, Injury; 38(3): 365-370
Urochordate βγ βγ βγ βγ -crystallin and the evolutionary origin of the vertebrate eye lens. Department of Zoology, University of Oxford, The Tinbergen Building, South Parks
The reaction of autohydrogen transfer was first reported in the 19 th century using nickel as a catalyst for alkylation of aliphatic amines with primary
A survey of preferences for product attributes for wooden outdoor furniture using different product bundles based on price and warranty for the furniture, and
Part (a) was well done. Many candidates correctly recalled formulae U= -GMmR -1 and Ek = GMm/ 2R. The difficulty here was the determination of R. Very well done by most
A prospective study to analyse the outcome of locking compression plating by minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis technique in proximal
Our study comprised of 20 patients with distal femur fractures who were treated by locking compression plate (LCP) using open reduction (ORIF), and minimally invasive
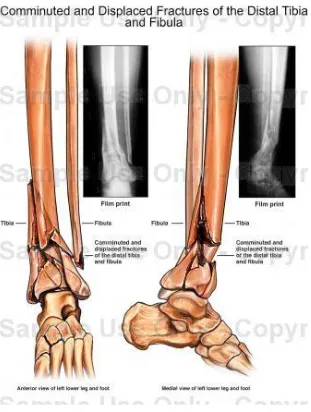
32 patients with fractures of the distal tibia treated using Locking compression plate with MIPO technique were included in the study.. All patients with distal tibial