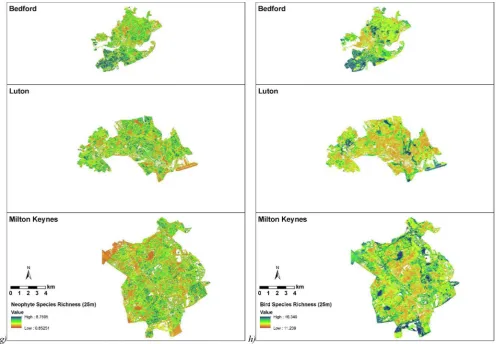
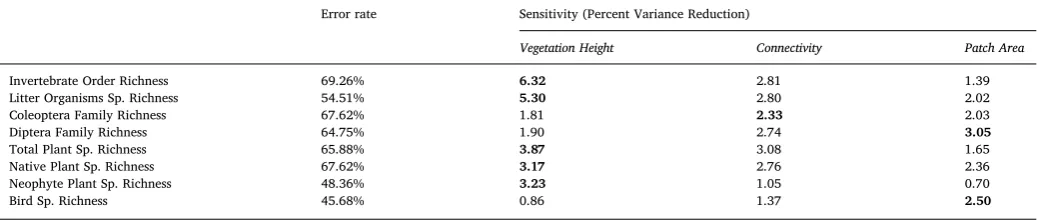
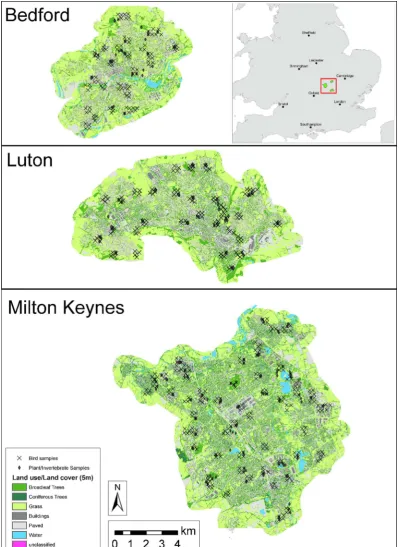
Using GIS-linked Bayesian Belief Networks as a tool for modelling urban biodiversity
Full text
Figure



Related documents
The plan also determines that the most favourable size, site and timing of solar PV installation from the planner’s point of view is 2771 MW capacity in the Ottawa zone (Fig. 1) and
Therefore, this study aims to quantify the concentrations of PFBS, per fl uorohexane sulfonate (PFHxS), PFOS, PFOA, per fl uorononanoic acid (PFNA), per fl uorodecanoic acid (PFDA),
Courses: Constitutional Law, Criminal Law, Criminal Procedure, Criminal Practice, Family Law; Comparative Law, Law and International Development, International Human Rights
In this paper, a crypto-biometric scheme, based on fuzzy extractors, by using iris templates, is proposed, i.e., we propose a new system in order to permit a user to retrieve a
This contentious debate over whether public lands should accommodate consumptive or non-consumptive uses is illustrated by such modern cases as the Bears Ears National Monument
In a multivariate model adjusted for age, race/ethnicity, education, food insecurity, inadequate fruit and vegetable consumption, physical inactivity, and perceived stress,
Having reviewed the academic literature on segmentation and segmenting mature markets, the secondary objective here is to investigate whether there is a gap between the theory
However, existing research has not: (a) provided a comprehensive coverage of mobile botnets and range of system calls, (b) considered systematically different detection scenarios