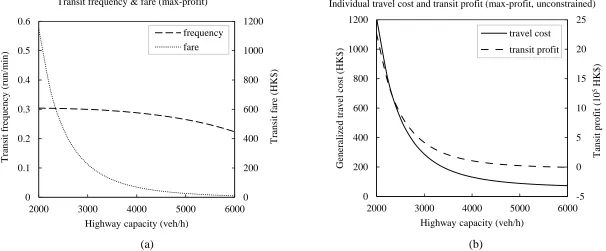
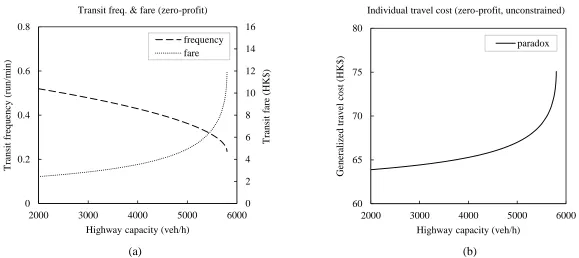
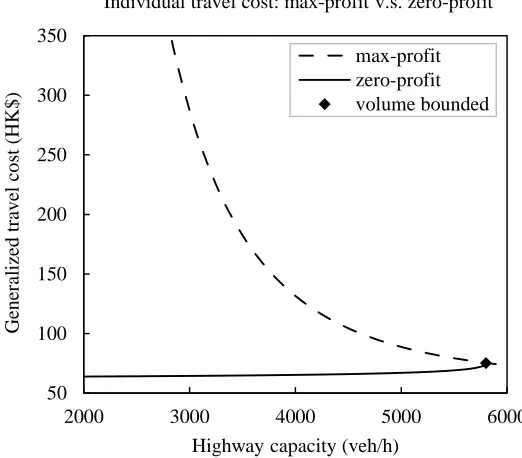
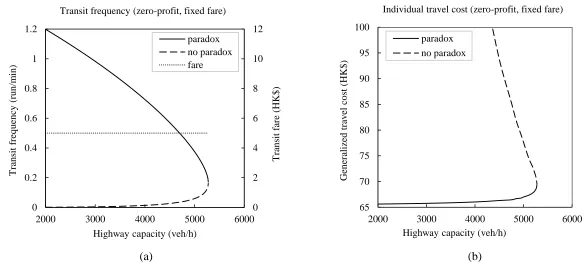
The Downs–Thomson Paradox with responsive transit service
Full text
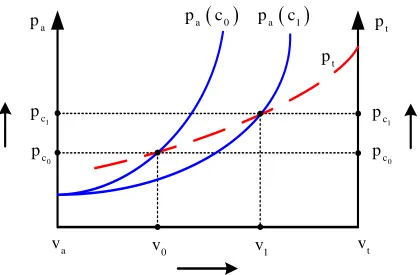
Figure



Related documents
Moreover, in PLS system this problem becomes more serious because part of the loss in case of project failure is borne by the lender too unlike the convectional model where
For the feature ranking and selection procedures, it is not surprising that CAD score is the most relevant fea- ture for the combined strategy, as it is a complete screening strategy
The qualitative research data provided context for the change in teacher self-assessment for all four of the TPACK framework constructs (TK, TPK, TCK, and TPACK). The
SP9 Change primary fi lter element (Racor) SP10 Change secondary fuel fi lter SP14 Check turbocharger boost pressure SP16 Check cooling system.. SP22 Check the state of
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the rela- tive performance of 26 public urban transportation organizations in India using various criteria.. We grouped these 19 criteria
Finally, the journal editors have an interest in making the data that support the studies they publish as openly accessible as possible, and this is greatly facilitated by
1) Because biological processes control all transformations of C and N, these elements will show strong correlations within and between compartments (plant, soil).. 2)