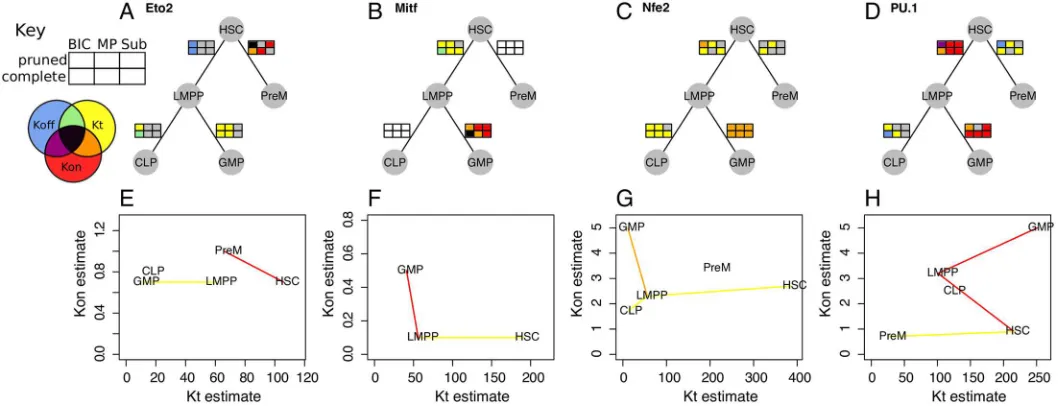
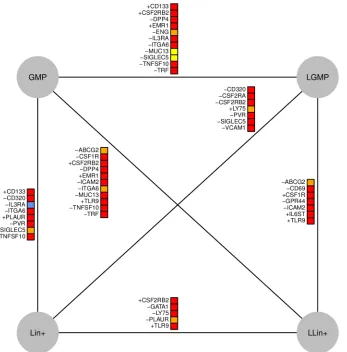
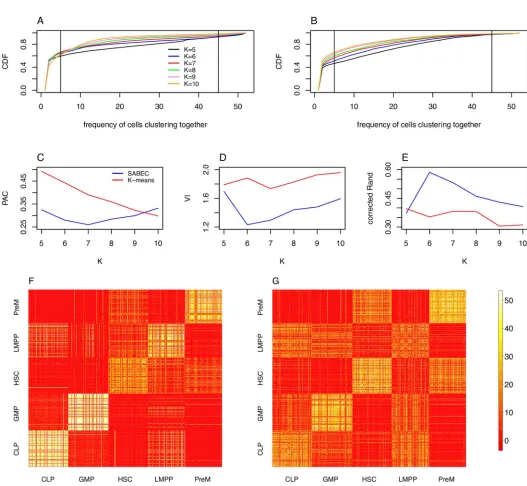
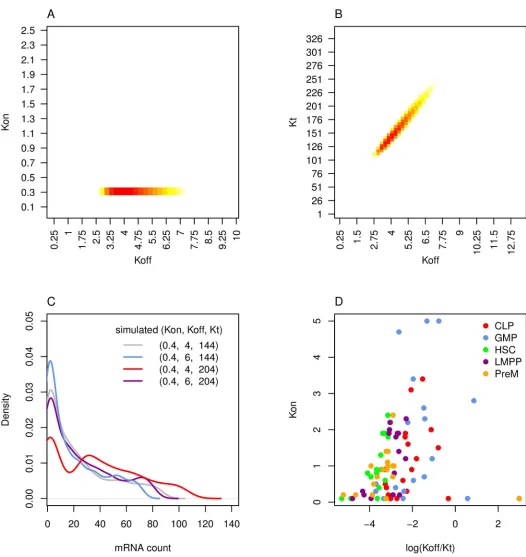
Determining Physical Mechanisms of Gene Expression Regulation from Single Cell Gene Expression Data
Full text
Figure
Related documents
The present study showed that the combined regimen of topical TXA and rivaroxaban significantly reduces post- operative blood loss, the transfusion rate, and wound
The yearly random general urinalysis results for each prison—included in Appendix A Figure A1—show that the Melbourne Assessment Prison, the Dame Phyllis Frost Centre (DPFC), and
Their report involved over 3000 queries and 12 million user interactions with a popular web search engine, the results of this study show the accuracy of entering end user
This work demonstrates the use of a simple synthetic method using cheap precursors of Aloe vera plant extract provides high – yield nanosized ferrites with well crystalline
important, however, based on our searches, a similar study to the present study investigating the effect of a midwife-based group discussion education on sexual dysfunction beliefs
International Journal of Mechanical & Mechatronics Engineering IJMME-IJENS Vol:18 No:05 70 The other type of disturbance is applied from the body.. coordinate as
In this paper we proposed a novel volumetric approach to surface modeling from unorganized sets of points, which is able to overcome the typical problems of computational