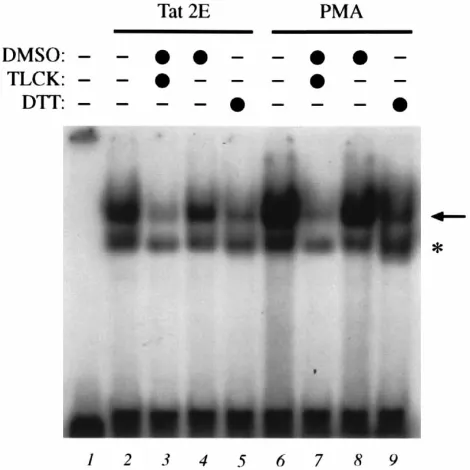
Activation of transcription factor NF-kappaB by the Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1.
Full text
Figure



Related documents
We show here that there is packaging of the endogenous Mtv-l virus, which is expressed at high levels in the lactating mammary glands of C3H/HeN mice, by the virions of exogenous
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) virions contain at least two regulatory proteins that modulate gene expression in infected cells: the transcriptional activator VP16 and the virion
(B) 35S-labeled VZV-infected cell lysate was immunoprecipitated (Immppt) with antisera to ORF 62 and ORF 47 proteins under three conditions: lane 1, in the absence of a competing
We have probed the structures of monomeric and oligomeric gpI20 glycoproteins from the LAI isolate of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) with a panel of monoclonal
The 40-kDa protein was initially eluted from protein A-Sepharose beads at 37°C because we had observed that the UL53 gene product translated in vitro aggregated upon.. boiling (47a),
precisely localize the N-MAb sites of neutralization on VP7, the amino acid sequences of rotavirus strains sensitive and resistant to each N-MAb were compared in antigenic regions A,
Two blocks in Moloney murine leukemia virus expression in undif- ferentiated F9 embryonal carcinoma cells as determined by transient expression assay. Delayed de novo methylation
They bound to receptor-positive but not to receptor-negative cells and fused with Raji cells but not with receptor-positive, fusion-incompetent Molt 4 cells; monoclonal antibodies
