Impact of the free healthcare initiative on wealth related inequity in the utilization of maternal & child health services in Sierra Leone
Full text
Figure

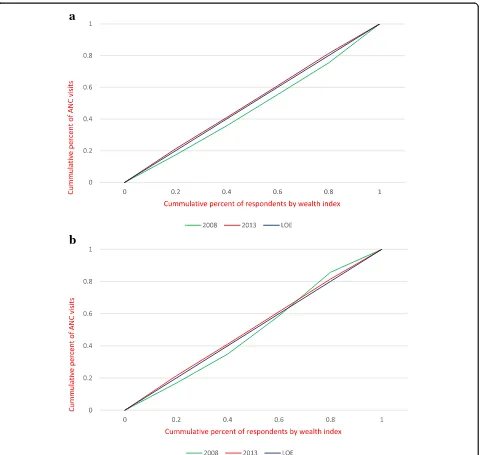
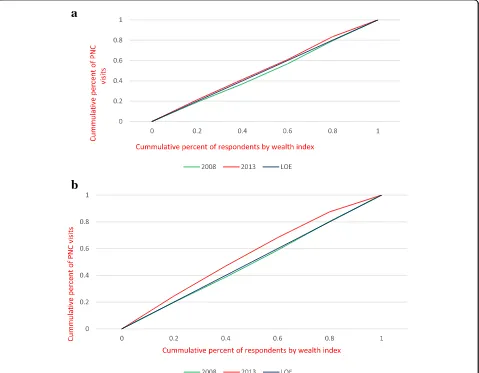

Related documents
In this study, we investigate if the need for IVF treatment is higher among women with ASD, as well as the associated infertility diagnosis, using the unique Danish registries
In this research the study of compressive and flexural strength of concrete with replacement of ordinary Portland cement by 10% Rice Husk Ash with the addition of 0.5% and 1.0%
Results of epidemiologic studies provide strong evidence that exposure of children to environmen- tal tobacco smoke is associated with increased rates of lower respiratory illness
Keywords: C1q deficiency, Systemic lupus erythematosus, Hypocomplementemia, Novel mutation, Fresh frozen
Many critics have discussed the burden, or the lightness, of Joyce's advice in "Station Island" XII, and have examined the importance for Heaney of the tundish episode
Orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) is an effective treatment of liver failure caused by EPP, but it does not ameliorate the underlying protoporphyrin overproduc- tion in the
Salivary Cortisol and Mood and Pain Profiles During Skin-to-Skin Care for an Unselected Group of Mothers and Infants in Neonatal
Cardiac abnormalities were found in both the older (Group I) as well as the neonatal cohort (Group II); (whose HIV infection status was un- known before enrollment) thereby



