DEVELOPMENT OF NEW THIRD LIGHT BRAKE SIGNAL ON MOTORCYCLE HELMET
AHMAD REZDUAN ZAINAL
This report was submitted in accordance with the partial requirements for honor of Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering (Automotive)
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka
ii
DECLARATION
“I hereby declare that the thesis is based on my original work except for quotations and citations which have been duly acknowledged”
Signature :………..
Author’s Name: AHMAD REZDUAN ZAINAL
iii
DEDICATION
My special dedication towards my beloved parents, family, Mr. Mohd Zakaria Mohd Nasir; my supervisor and all friends. May god bless them for all the help to complete
iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of ALLAH s.w.t; I would like to express my first and foremost thankfulness for giving me the optimum health, courage and strength along the period of completing this project.
To the most respectful supervisor, Mr. Mohd Zakaria Mohd Nasir, I would like to express my higher gratitude and thank you for the guidance, advices, ideas, moral support and also endless encouragement during the time of completing this thesis.
My sincere thank also to Mr. Mohd Nazim Abdul Rahman, all technicians and staffs in Automotive section in Faculty of Mechanical, UTEM; thank you so much for the co-operations, helps, patience and also friendship.
v
ABSTRACT
vi
ABSTRAK
vii
TABLE OF CONTENT
TOPIC PAGE
DECLARATION ii
DEDICATION iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT iv
ABSTRACT v
ABSTRAK vi
TABLE OF CONTENT vii
LIST OF TABLE x
LIST OF FIGURE xi
LIST OF SYMBOLS xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES xiv
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1Problem Statement 1.2 Objective 1.3 Scope 1 4 5 5
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Motorcycle Helmet Design 2.1.1 Outer Shell
2.1.2 Impact-Absorbing Liner 2.1.3 Comfort Padding
2.1.4 Retention System
2.1.5 Choose the Motorcycle Helmet 2.2 Overview of Wireless System
viii
2.2.1 Radio Frequency(RF) System 2.2.2 Bluetooth System
2.2.3 Infrared System 2.3 Simple Transmitter
2.4 Frequency Modulator(FM) 2.4.1 basic Block of RF
2.5 Overview Electrical Wiring of Motorcycle 2.6 Electronic Component in Circuit Fabrication 2.6.1 Light Emitting Diode(LED)
2.6.1.1 LED Characteristic 2.6.1.2 LED Function 2.6.2 Resistor
2.6.2.1 Resistor Characteristic 2.6.2.2 Resistor Function 2.6.2.3 Basic of Resistive Unit 2.6.3 Capacitor
2.6.3.1 Capacitor Characteristic 2.6.3.2 Capacitor Function
2.6.3.3 Basic Unit Of Capacitance 2.6.4 Transistor
2.6.4.1 Transistor Characteristic 2.6.4.2 Transistor Function 2.6.5 Integrated Circuit(IC) 2.6.5.1 IC characteristic 2.6.5.1 IC function 2.6.6 Relay
2.6.6.1 Relay Characteristic 2.6.6.2 Relay Function
10 12 12 13 17 19 20 22 23 23 24 24 24 24 25 26 26 26 27 28 28 28 29 29 30 30 31 31
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY 3.1 PSM Flow Chart
3.2 Wireless System Selection 3.3 System Attachment Prediction
ix
3.4 Block Diagram Of System
3.4.1 Block Diagram of Transmitter Unit 3.4.2 Block Diagram of Receiver Unit 3.5 System Design of Transmitter and Receiver 3.5.1 Circuit Design by MultiSim Software
38 39 39 39 40
CHAPTER 4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Fabrication of Transmitter and Receiver Circuit
4.2 Component of the System 4.2.1 Transmitter Unit 4.2.2 Receiver Unit
4.3 Specification for Circuit System Operating 4.4 Alignment of Tone Frequency
4.5 Alignment of RF Signal Frequency 4.6 The Distance Range Setup and Testing 4.7 System Unit Attachment
4.7.1 Transmitter Unit Attachment 4.7.2 Receiver Unit Attachment 4.8 Estimate Cost for Overall System Unit 4.9 Radio Frequency Radiation Effect on Human 4.9.1 Non-Ionization Radiation
4.9.2 Measurement of RF Radiation
4.9.3 Biological Effect Caused by RF Energy 4.9.4 Emission for radio and Television
Broadcast Antennas 47 47 49 49 51 53 53 55 56 57 57 58 63 64 64 65 65 66
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION 5.1 Conclusion
5.2 Recommendation
68 69
REFERENCE 69
x
LIST OF TABLE
NO TITLE PAGE
1.1 Registered vehicle according type of vehicle(1993-2007)
1
1.2 Statistic of Road Fatalities from June to July 2008 2
2.1 Requirements components for FM circuit 17
2.2 LED characteristics 23
2.3 Resistor characteristic 25
2.4 Value of the resistive according to the colour 26
2.5 Type of the capacitor 27
2.6 Functions of Transistor leg 28
2.7 Type and symbol of transistor 29
2.8 Types of the existing relay 32
3.1 Project specifications 35
4.1 Requirements components for Transmitter circuit 49 4.2 Requirements components for Receiver circuit 51 4.3 Result of distance range between transmitter and
receiver
57
xi
LIST OF FIGURE
NO TITLE PAGE
2.1 Basic components of helmet design 8
2.2 SIRIM standard sticker for motorcycle helmet 9
2.3 The peripheral vision of helmet 10
2.4 Electromagnetic spectrum 13
2.5 No deflection of compass 14
2.6 Deflection of compass 14
2.7 The appearence of voltage and current effect from electromagnetis field
14
2.8 The square wave produced 15
2.9 A sine wave fluctuated produces 15
2.10 The wave identification 16
2.11 Single Bulb with two filaments 21
2.12 The location of the contact switch at motorcycle 22
2.13 Red LED 23
2.14 Ordinary resistor 24
2.15 capacitor 26
2.16 Type of the transistor 28
2.17 IC in variable sizes 29
2.18 The cross section of IC 30
2.19 Single pole 2 way relay 30
2.20 The main part of relay 31
3.1 Helmet design selection 36
3.2 Major design modification of helmet 37
xii
3.4 12V Relay 40
3.5 Example listed of the variable component in MultiSim software
41
3.6 Example changing the value of the component 42
3.7 Other component setting 43
3.8 Grouping setup for new component 44
3.9 Example of Transmitter circuit drawing in MultiSim 45 3.10 Example of Receiver circuit drawing in MultiSim
Software
46
4.1 Printed circuit board for receiver and transmitter 47
4.2 Transmitter Circuit 50
4.3 Transmitter switch location at the front brake 50
4.4 Receiver circuit 52
4.5 Transmitter switch location at the rear brake 52
4.6 Adjusting trimmer potentiometer 54
4.7 The LED at the receiver board light up 54
4.8 Adjusting trimmer capacitor in variable distances 55 4.9 Distance between the transmitter and receiver units 56
4.10 Example for range test process 57
4.11 Full scale of motorcycle model 58
4.12 Combination of brake switch at the front and rear brake
59
4.13 Compressed of board circuit 59
4.14 The red LED in parallel arrangement 60
4.15 6V battery for receiver unit 60
4.16 Location of receiver circuit’s switch 61
4.17 Receiver unit attachments on air spoiler of the helmet 62 4.18 Condition of light brake before(a) and after(b)
operating
62
xiii
LIST OF SYMBOLS
Z = Impedance
R = Resistance
xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES
NO TITLE PAGE
1 PSM1 Chart 73
2 PSM2 Chart 74
3 Figure of new design of motorcycle helmet 75
1
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
[image:15.595.107.530.525.759.2]Motorcycle is the most popular transport and become the main mode used by commuters in Malaysia. In 2007, about 7943,364 vehicles were registered with Jabatan Pengangkutan Jalan (JPJ) which was motorcycle. Not surprisingly, motorcycle consumed the highest road accidents compared to other vehicle involved in accident. From the statistic recorded, almost every year begin from 1993 until 2007, motorcycle have recorded highest road accidents compared to cars, van, bus and other vehicle that involved in accidents.(source: www.panducermat.org.my)
Table 1.1: Registered vehicle according type of vehicle(1993-2007) (Source: JKJR (September 2008))
REGISTERED VEHICLE
Year
Private Car Private Motorcycle
Lorry/Van Bus Taxi
1993 2,255,420 3,703,838 466,871 33,358 36,458
1994 2,426,546 3,977,047 495,736 34,771 40,088
1995 2,532,396 3,564,756 430,716 35,224 27,276
1996 2,886,536 3,951,931 512,165 38,965 59,456
1997 3,271,304 4,328,117 572,720 43,444 51,293
1998 3,452,852 4,692,183 599,149 45,643 54,590
2
Year
Private Car Private Motorcycle
Lorry/Van Bus Taxi
2000 4,145,982 5,356,604 665,284 48,662 56,152
2001 4,557,992 5,609,351 689,668 49,771 56,579
2002 5,027,173 5,859,195 714,796 51,251 58,385
2003 5,428,774 6,164,953 740,462 52,846 60,723
2004 5,911,752 6,572,366 772,218 54,997 65,008
2005 6,473,261 7,008,051 805,157 57,370 67,451
2006 6,941,996 7,458,128 836,579 59,991 70,409
2007 7,419,643 7,943,364 871,234 62,308 72,374
[image:16.595.109.528.69.289.2]According to the road statistic which reported by PDRM, motorcyclist and pillions have involved at the highest road fatalities which consumed about 304 in Jun 2008 and 300 for the next month. (Source: www.panducermat.org.my (September 2008))
Table 1.2: Statistic of Road Fatalities from June to July 2008 Source: JKJR (September 2008)
2008 2008
Category of road user JUNE JULY
Car driver and passenger 143 102
Motorcyclist and pillions 304 300
Pedestrians 47 47
Cyclist 13 21
Bus driver and passenger 10 1
Lorry diver 13 14
Van driver 5 12
Four wheel vehicle driver 11 11
Others 9 1
3
In year 2005, from 6188 road fatalities, about 58% which consumed 3584 death involved motorcyclist and pillion. About 68% of the read fatalities recorded caused by the head injuries among the motorcyclist and pillion. Even the small accident can caused body injuries especially head and other important of body parts. (Source: www.panducermat.org.my (August 2008))
The usage of the motorcycle helmet was the effective way in order to protect and reduced head injuries. However, the usage of motorcycle helmet needs to fulfill the standard specifications which stated from Jabatan Keselamatan Jalan Raya(JKJR). The standards are related to the design of the helmet in reducing the impact to the head when the accident happens.
The Center of the Road Safety in Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) reported of suggestion of using the right helmet and the application of each type of helmet. The right application of helmet need to subjected because of the success of helmet used which can reduced almost 50% head injuries caused by road accidents.
In order to reduce the road accident among motorcyclists and pillions, a lot of method have been developed and derived. One of the way is by exposed the motorcyclist to used the recommended and standard which stated from JKJR.
4
1.1 Problem Statement
There is a lot of problem facing in order to minimize the risk of motorcyclist and pillions involved in accidents especially at night and during heavy rain where the other vehicle hard to detect the appearance of motorcyclist. This is because the bad weather will interrupt other road user to see clearly towards the motorcyclist and pillions.
5
1.2 Objective
1. Development light brake at the back of motorcycle helmet via wireless system.
2. Development of wireless system for flexibility and safety features for motorcyclist.
1.3 Scope
1. Literature review on wireless system and electrical system of motorcycle. 2. Literature review on the existing helmet design.
3. Fabrication of the motorcycle and helmet model for the light brake system. 4. Analytical study of the components for prototype fabrication.
5. Combination of existing design of helmet with the attachment of the wireless unit.
6
CHAPTER 2
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Motorcycle Helmet Design
Different helmets operated with different application of used such as hard hats on construction and heavy-industry heads and Kevlar caps on military heads. The compositions of the type material and design will not interchangeable. Motorcycle helmets are very sophisticated and specialized for the activity. They've been developed carefully and scientifically over the years.
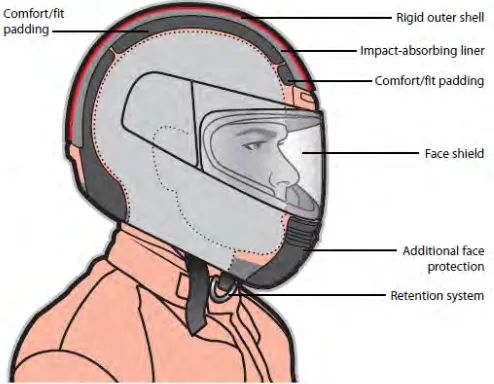
There are four basic components which work together to provide protection in the motorcycle helmet. The components refer to an outer shell, an impact-absorbing liner, the comfort padding, and a good retention system.
2.1.1 Outer Shell
7
2.1.2 Impact-Absorbing Liner
Inside the outer shell there are components that equally important which referred to impact-absorbing liner. This impact-absorbing liner usually made of expanded polystyrene or commonly said as Styrofoam. This component will dense layer cushions and absorbs the shock as the helmet stops and motorcyclist head wants to keep on moving because of the inertia.
Both the shell and the liner compress if hit hard, spreading the forces of impact throughout the helmet material. The more impact-energy deflected or absorbed, the less there is of it to reach the head and do damage. Some helmet shells delaminate on impact. Others may crack and break if forced to take a severe hit; this is one way a helmet acts to absorb shock. (Source: www.msf-usa.org)
2.1.3 Comfort Padding
The comfort padding is the soft foam-and-cloth layer that sits next to motorcyclist head. It helps keep motorcyclist in comfortable and the helmet fitting snugly. In some helmets, this padding can be taken out for cleaning.
2.1.4 Retention System
8
Figure 2.1: Basic components of helmet design (source:www.msf-usa.org)
2.1.5 Choosing the Motorcycle Helmet
A full-face helmet gives the most protection since it covers more of motorcyclist face. Full face helmet usually has a moveable face shield that protects the eyes when it is closed. Racers prefer full-face helmets for the added protection and comfort.
A three-quarter, open-face helmet is also a choice of some motorcyclist. This type of motorcycle helmet is constructed with the same basic components, but this type does not offer the face and chin protection of full-face helmets. The use an open-face helmet should have a snap-on face shield in place during ride that can withstand the impact of stone or other debris.
A half-helmet protects even less of motorcyclists head. It is more likely to come off from head upon impact. Therefore, half-shell helmets are not recommended. (Source:www.msf-usa.org)
9
accessories. Manufacturers are working to make them less expensive, stronger and more comfortable.
Every single unit of helmet must meet minimum safety standards which recommended. The way to find reliable helmet is by look at the Standard and Industrial Research of Malaysia (SIRIM) sticker outside of the helmet. The sticker means the helmet meets the safety test standards of the JKJR recommendations
[image:23.595.215.531.235.396.2].
Figure 2.2: SIRIM standard sticker for motorcycle helmet
The SIRIM sticker was mention that the motorcycle helmets have meet their specification in terms of safety features and testing. The SIRIM departments have these responsibilities in testing the helmet before it can meet the user. The principle and testing of Snell Memorial Foundation which used in West Country are close with the testing that be done in Malaysia in way of conceptuality and practically.
Each organization has rigid procedures for testing:
• Impact – the shock-absorbing capacity of the helmet.
• Penetration – the helmet's ability to withstand a blow from a sharp object. • Retention – the chin strap's ability to stay fastened without stretching or
breaking.
• Peripheral vision – the helmet must provide a minimum side vision of 105 degrees to each side.
10
Figure 2.3: The peripheral vision of helmet (Source: www.smf.org)
2.2 Overview of Wireless System
There is a lot of wireless system which used widely in this modern country including Malaysia. Most of the wireless system which recently use was Radio Frequency (RF), Bluetooth and Infrared (IR). In this project, one of the wireless system will adapted through objective and flexibility of the application of the system. There is a lot of factor should be in consider to choose either each of the wireless system are suitable with application of the project. In order to find out the most flexibility of the system, the system of RF, Bluetooth and IR advantages and disadvantages will be listed for comparison.
2.2.1 Radio Frequency(RF) System