A low-loss reconfigurable frequency selective surface based antenna for direct antenna modulation
Full text
Figure
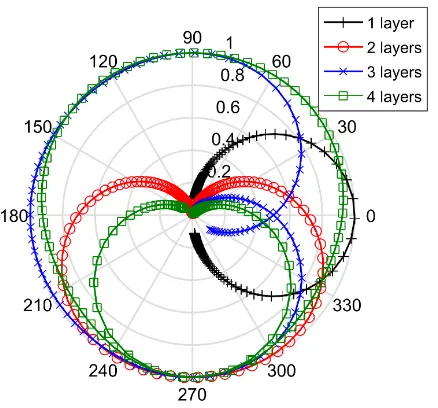
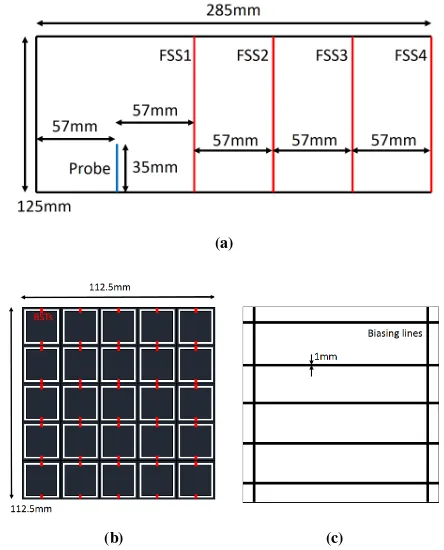
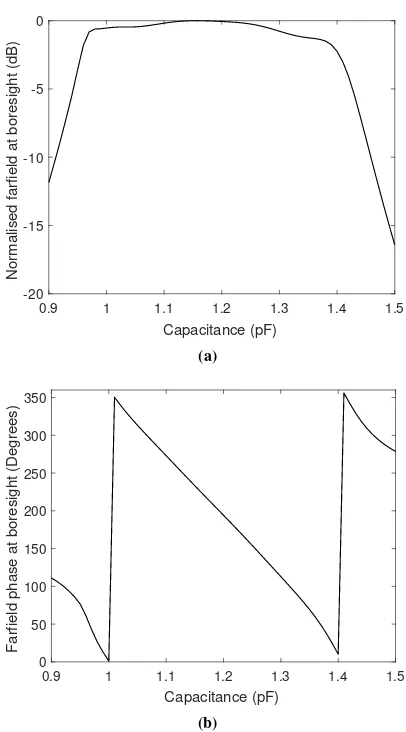
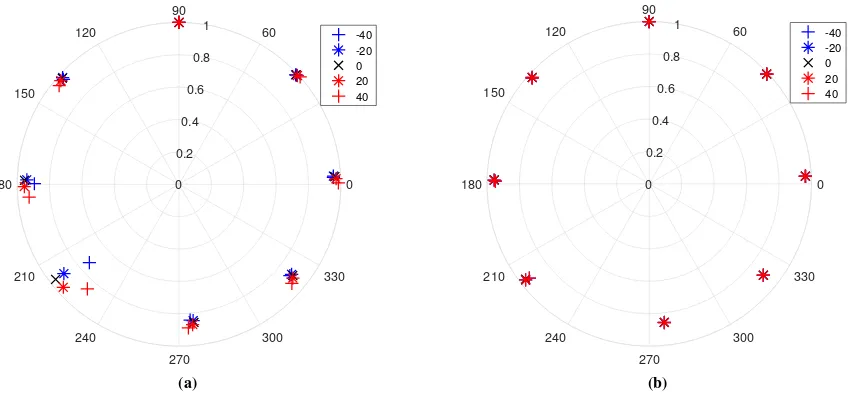
Related documents
Influence of motorcycle and operator characteristics on sound Influence of motorcycle and operator characteristics on sound pressure level measured at the ear of the
Site Upland-3 deep location groundwater constituent multivariate correlations and matrix .... Site Upland-2 shallow location groundwater constituent multivariate correlations
e concept of a coverage model for sensor systems is presented in a highly general form—simply a bounded function over an arbitrary stimulus space—and thus any optimization
In order to investigate the influence of moisture content of heated specimen on the progress of crystallization of concrete, pore structure measurement by mercury intrusion technique
in non-small cell lung tumor tissues, and may correlate with microvessel density and clinical outcomes [16]; the de- creased expression of miR-126 may be associated with
The studies of uptake and passage of IgG and BLG either by intestinal cells in vivo or Caco-2 cells in vitro have elucidated the complex journey of molecules from the luminal side of
Neural network [10] with Radial Basis Function will be applied to implement tumour cells segmentation and classification.. Decision should be made to classify
The crack propagation within a structure can be simulated using several different methods [2, 3 and 4]: (i) node release technique controlled by any fracture