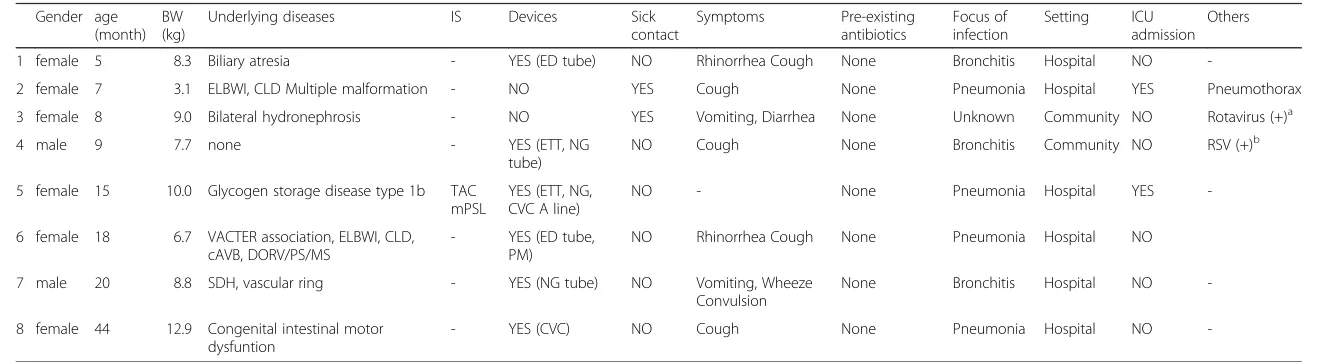
Clinical characteristics of the patients with bacteremia due to Moraxella catarrhalis in children: a case–control study
Full text
Figure



Related documents
Roe et al., (2000, cited in DeGeorges & Reilly, 2008), mention similar initiatives, such as the 1980 IUCN on “World Conservation Strategy,” which emphasizes linking the
According to the original study of the SIJ score, the score comprised the sum of the weighted points of the following six items: one-finger test, scored as 3 points; groin
So it seems that the plot is so well known that the need to parody it is as if encoded in the tale type, and what appears in the archives categorised as the fairy tale Little
Purposively, 400 government primary school girls were recruitedfor data collection (n = 200) from urban, and (n = 200) from rural. Data was collected from five tehsils of
This research seeks integration of multiple data sources into single Data Warehouse irrespective of number and types of sources, this is achieved by designing, implementing and
ABCA1: ATP-binding cassette transporter A-1; ABCA7: ATP-binding cassette transporter A-7; ADIPOR1: Adiponectin receptor 1; ALIENOR: Antioxydants, Lipids Essentiels, Nutrition
Our results suggest that pulmonary tuberculosis and NTM lung diseases can usually be distinguished by asses- sing the CT findings of nodules in patients with PTB as well
BSCTs: breast spindle cell tumors, SCL: spindle cell lipoma, MFB: myofibroblastoma, ME: myoepithelioma, MME: malignant myoepithelioma, SCC: spindle cell carci- noma, SFT: