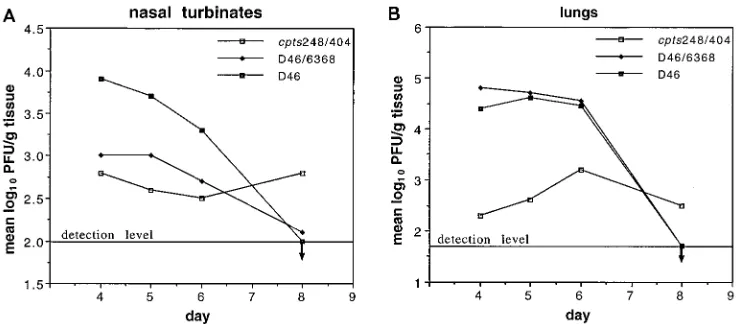
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus from which the entire SH gene has been deleted grows efficiently in cell culture and exhibits site-specific attenuation in the respiratory tract of the mouse.
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Perioperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel versus fluorouracil or capecitabine plus cisplatin and epirubicin for locally
Rogers (2008), suggest that for an effective monitoring and evaluation structure, for result based management, the structure for M&E should incorporate the position of a
Purposes of this research are (1) to explain the competence of human resources, which consists of knowledge, skills, and abilities, (2) to explain the influence
We aimed to examine the effects of liraglutide on gly- cemic control, body weight, and QOL score in obese Japanese patients with T2DM in patient’s psychologi- cal attitude and
Nachdem wir in den vorherigen Experimenten ( siehe Kapitel 4.2. ) zeigen konnten, dass die Sialyltransferase ST3Gal-IV wesentlich für eine suffiziente Adhäsion eosinophiler
A recent study showed that regression of microal- buminuria in patients with T1DM is associated with lower levels of urinary tubular injury biomarkers (kidney injury