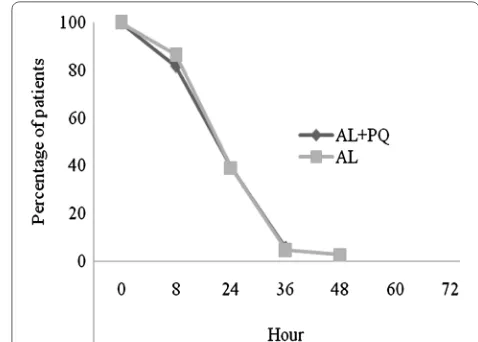
Adding a single low dose of primaquine (0 25 mg/kg) to artemether lumefantrine did not compromise treatment outcome of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Tanzania: a randomized, single blinded clinical trial
Full text
Figure


Related documents
It is exhibited that proposed approach can fundamentally lessen the ideal opportunity for error identification and area in big data indexes produced by expansive scale
Rekonstruktionen mit einem überlegeneren klinischen Outcome als nicht- anatomische.. VKB Rekonstruktionen in der LP-
1) Fcj1 ist mit einer Transmembrandomäne in der Innenmembran verankert. Für die Funktion von Fcj1 ist das Vorhandensein einer Transmembrandomäne wichtig. Allerdings ist
– REHAB, a group setting was selected for the telephone aftercare. With telephone-based aftercare in a small, professionally moderated group, a higher intensity of.. care can
IC50 values for antiproliferative effect of ( a ) vistusertib for several endocrine sensitive and resistant cell line models both in the presence or absence of 0.01 nM E2, ( b
Main text: In this article, a multidisciplinary group of clinicians and health service researchers present a pragmatic guide to help clinicians and clinical researchers understand
Specifically, we hypothesise that a clus- ter-randomised intervention using a facilitation approach targeting primary healthcare staff and key community members reduces the risk
In patients still taking ETN (group 1), the state of disease activity at cross-sectional visit was assessed through the following criteria: 1) criteria for inactive disease (ID) in