Role of gene 2 in bacteriophage T7 DNA synthesis.
Full text
Figure


![FIG. 4.preventedfractionsradioactivityscribedE.wereindicateswildcentrifugedterials0.3ityinfectionmintomultiplicityJ'H]thymidine 2 coli The fate of newly synthesized DNA in T7 type-infected cells](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/1571361.109725/4.498.250.436.385.546/preventedfractionsradioactivityscribede-wereindicateswildcentrifugedterials-ityinfectionmintomultiplicityj-thymidine-newly-synthesized-infected-cells.webp)
Related documents
When wild-type virus, mutant, or tsl201revl-infected cells were pulse-labeled with [35SJmethionine late in infection, at least three virus-specific polypeptides, ranging in
Infection of Escherichia coli with T7 gene 2 mutant phage was abortive;.. concatemeric phage DNA was synthesized but was not packaged into the phage head, resulting in an
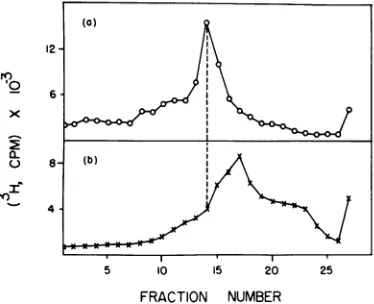
We have studied the DNA replicative interme- diates in cells infected with a dar mutant and a dar-amC5 (gene 59) mutant by velocity sedimentation in neutral and alkaline
[3H]thymidine-labeled DNA bound to '4Cloleic acid- labeled cell membrane (M-DNA) from position II of a CsCl gradient (cf. 2b) was dialyzed against DNA buffer and sedimented through
Like thymidine, labeled DHPU was not incorporated into the DNA (or RNA) of infected cells or
In an attempt to establish whether Escherichia coli B infected with N130 (an am- ber mutant defective in gene 46) is recombination-deficient, the postinfection fate of 14C-labeled
gradient, it was observed that DNA from 4)2-in- fected 168 sedimented slower than DNA isolated from 4)2-infected spoA cells (not shown). Figure 5 shows the sedimentation pattern of
degradation of bacterial DNA after infection with a gene 4 mutant (am H131) was studied by sedimentation analysis in sucrose gradients.. The breakdown of cellular DNA has been