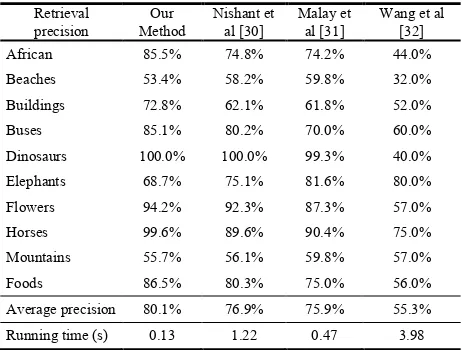
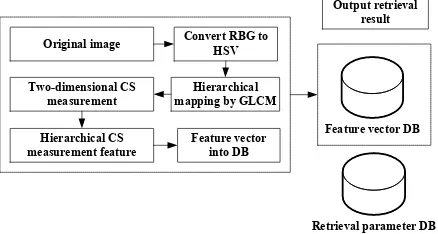
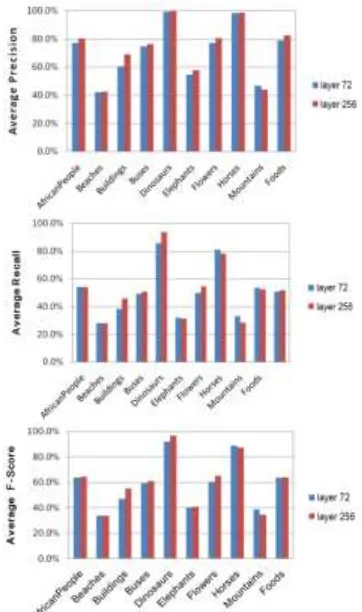
Hierarchical visual perception and two-dimensional compressive sensing for effective content-based color image retrieval
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Main objective of our study was to try to improve the performance of the query-by-example image retrieval system based on texture features – Gabor wavelet and wavelet transform – by
Approaches Time(sec) Centroid Distance 18 Tangential Approach 17 Quadrant Sector 11 Circle Sector 10 Retrieval Time for Clustered Contour Based Retrieval Approaches:..
Unlike the traditional approach of using keyword annotation as a method for searching images, a CBIR system performs retrieval based on the similarity of feature vectors such
In this paper, a novel image feature descriptor, namely texture structure histogram (TSH) for content-based image retrieval is proposed.. This method uses the color and
A multi feature model for the Content Based Image Retrieval System is proposed in [3] by combining the Color Histogram, color Moment, texture, and edge Histogram descriptor
Fig 3.4: shows the Performance analysis of CBIR using Color and texture features of Query image and corresponding retrieved similar images. Table II indicates the
They apply the algorithm to content-based image retrieval and compare its performance with that of the k-means clustering algorithm.Partitional clustering aims at
8 summarize the performance of proposed method (GCLBP) with different distance measures in terms of average retrieval rate... 7: Comparison of proposed method (GCLBP) with: