Biosynthesis of glycoproteins E and I of feline herpesvirus: gE-gI interaction is required for intracellular transport.
Full text
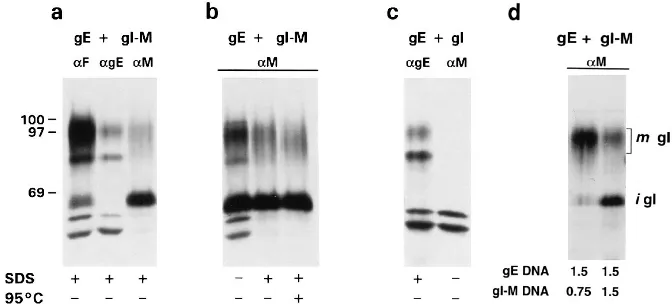
Figure


Related documents
Each domain contains a GTG core sequence and subsequent mutations targeting the GTG core in each of these domains also significantly reduced enhancer activity (see GTG core mutants
On the basis of the biological functions, conserved protein domains, and unique spatial arrangements of the homologous polypeptides (IE180 versus ICP4 and EPO versus ICPO)
We conclude therefore that SCMV EcoRI-D contains a sequence that can function as a replication origin, here designated oriLyt, in permissive cells and that its replication requires
The evolution of an 851-bp segment of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) genome encoding.. the nef open reading frame and U3/R elements of the long terminal repeat has
peptide (amino acids 228 to 241) corresponding to the cleavage region of the rotavirus SAil VP4 protein was able to induce neutralizing antibodies.. 5396 ARIAS
160 ,ul of the preparation of intracellular virus (lane 2) contains approximately 2 p.g of E protein, which corre- sponds to 12 x 1010 physical virus particles, each containing
Expression of this gene changes normally in response to the state of cellular differentiation; in infected cells the level of c-myc expression was correlated to the levels of
shown that the DNA-binding domain of the BPV-1 E2 protein contacts the conserved G nucleotides of the consen- sus sequence ACCN6GGT (Fig. This confirms the con- sensus sequence as