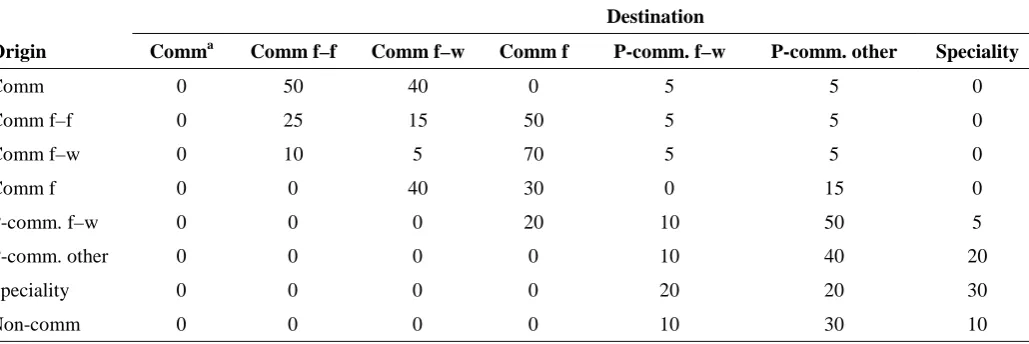
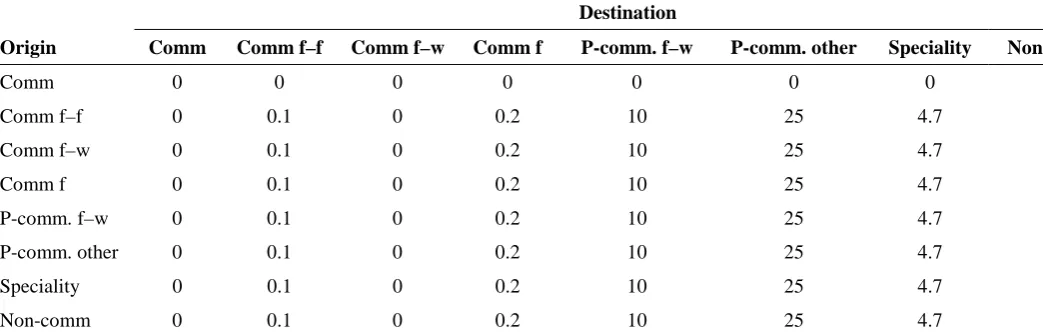
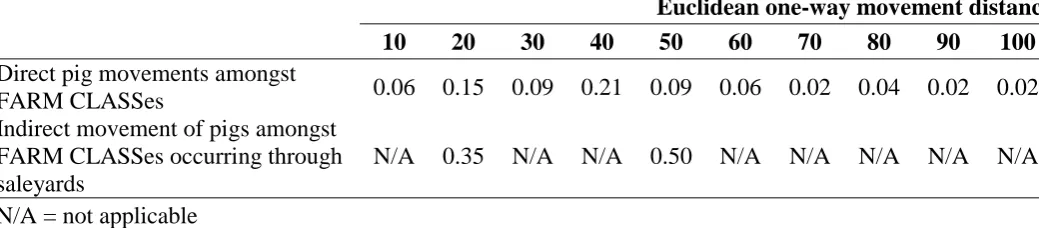
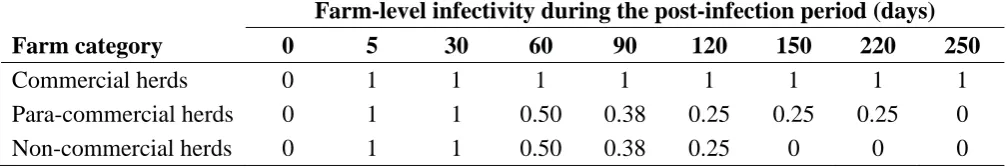
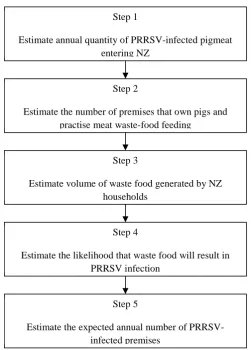
Biosecurity and exotic disease surveillance in the New Zealand pig industry : a thesis presented in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at Massey University, New Zealand
Full text
Figure

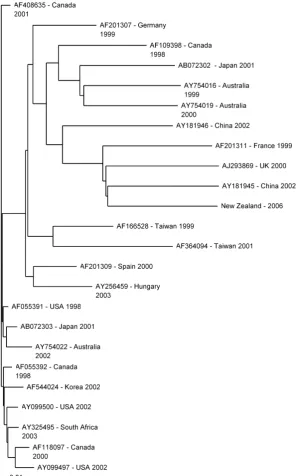

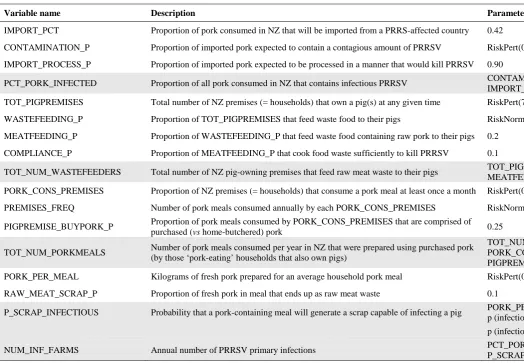
Related documents
To be included in the meta-analysis studies had to fulfill all of the following inclusion criteria: 1) Adult patients with chronic HCV genotype-1 and HIV coinfection. Stud- ies
Dairy calves are more likely than beef calves to experience welfare compromise through undernutrition or dehydration because of failure to suck or a delay between birth and
Ivermectin is indicated in Australia only for crusted scabies or cases of typical sca- bies when prior topical treatment has failed or has been contraindicated [29].. It is
The number of samples, and percentage of total samples n = 1 5 with urine protein to creatinine ratios that exceed varying cut-off limits as the level of blood contamination
To evaluate the Type I error rates of our four statistical tests with real learning algorithms, we needed to nd two learning algorithms that had identical performance when trained
In this work two strains of Candida guilliermondii were compared for their citric acid-producing capabilities, these being parent strain Candida guilliermondii NRRL
7.7: Cross-section diagrams of the step-by-step MEMS release process, a Initial CMOS chip with circuitry and unreleased MEMS capacitors, b Lithography with thick resist DWW
T cells, B cells, monocytes and granulocytes were removed from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) by the negative selection using magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS)