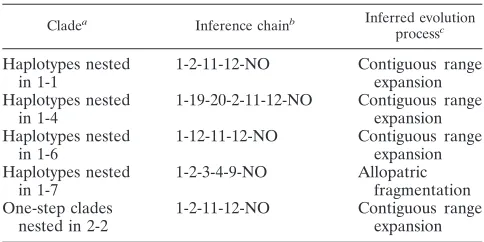
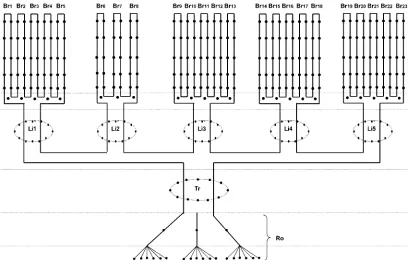
Distinct Viral Populations Differentiate and Evolve Independently in a Single Perennial Host Plant
Full text
Figure



Related documents
And the fish species richness, total abundance, total biomass and total abundance and total biomass dominant fish species were significantly changed in seasons in
19% serve a county. Fourteen per cent of the centers provide service for adjoining states in addition to the states in which they are located; usually these adjoining states have
Anti-inflammatory effects of the preparation were studied according to the below methods: S.Salamon– burn induced inflammation of the skin, caused by hot water (80 0 C) in white
The objective of this study was to develop Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy in combination with multivariate calibration of partial least square (PLS) and
Appendix 2: Letter VII – Executive Education Programs from the Collective Agreement between the Faculty association and the Board of Governors of the University of Windsor (2014
In addition, during the IMRT planning process, the deliberate placement of areas of steep dose gradient in patient tissue where Planning Target Volumes and Organs at Risk are in
Experiments were designed with different ecological conditions like prey density, volume of water, container shape, presence of vegetation, predator density and time of
Regressions between monocyte maximal uncoupled respiration and reserve capacity with respiratory control ratio and maximal uncoupled respiration from isolated mitochondria from