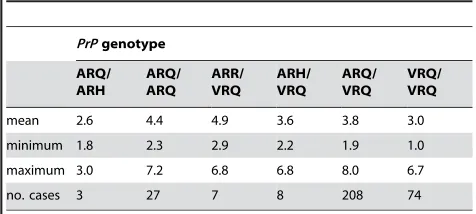
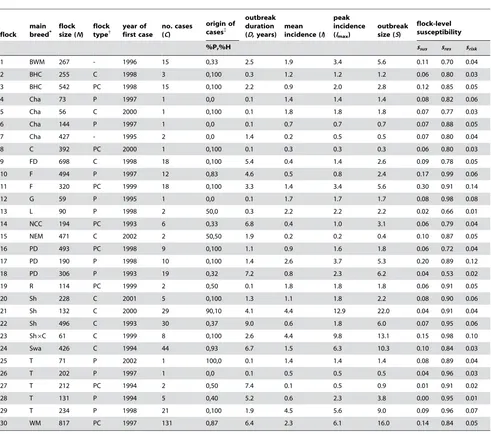
Epidemiological Characteristics of Classical Scrapie Outbreaks in 30 Sheep Flocks in the United Kingdom
Full text
Figure



Related documents
Relative Superior Mandelbrot sets for the hyperbolic transcendental function cosh(z) appear like beautiful flowers having the symmetry of 2n-1 petals/leaves while
Results clearly demonstrate that the EMP- 2 project provided support in terms of financial capital, human capital, physical capital, social capital and natural capital and
Above Table 4 represents that, homologous series 1, X and Y are: A homologous novel series - 1 and A are enantiotropically smectic plus nematic and series-B is
Conference on Higher Education (2009) emphasizes “higher education must pursue the goals of equity, relevance and quality simultaneously.” This is particularly true in today’s..
To what extent these findings can be applied to those declin- ing participation in PA programmes outside a trial setting is not certain; while it seems logical that some of the
A simulation study is employed to (a) compare the pre- dictive ability of different link functions (the odds, logit and cloglog functions) in the proposed Bayesian model when PPV
It shows that originality and creativity are equally distributed between superior intelligent students and low intelligent students (ii) It was found that there is
Here we show that vIL-10 expression by MHV-76 enhances spleen cell prolif- eration and viral titers in the lung during acute infection, but does not affect splenic latency