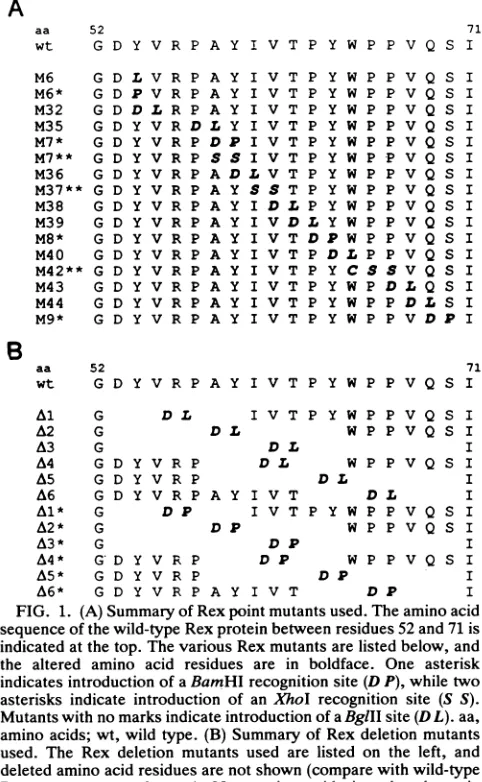
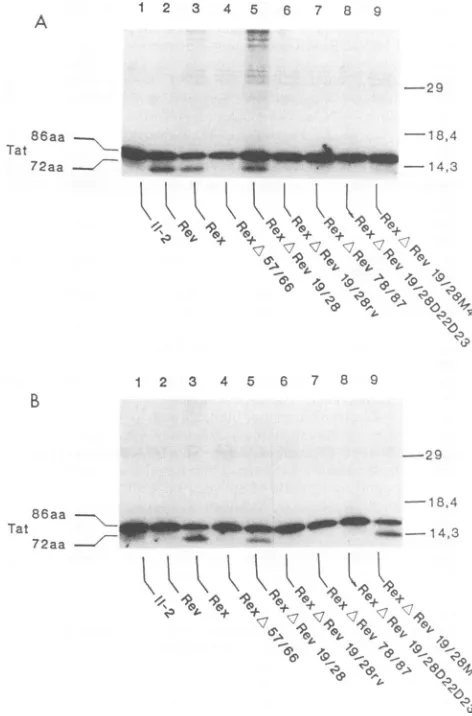
Dominant-negative mutants are clustered in a domain of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Rex protein: implications for trans dominance.
Full text
Figure

Related documents
Therefore, we proposed that a functional domain resides be- tween amino acids 2 and 21 and that this domain is related to the trans-dominant inhibitory function of LHDAg but is
An EcoRI fragment (bases 9862 to 15806 of the f 29 genome) containing the gene coding for upper collar protein gp11, appendage protein gp12, and non- structural protein gp13 of phage
We have constructed a cDNA library using poly(A) 1 RNA from the stably transformed Marek’s disease virus cell line MKT-1 and isolated cDNAs specific to the short internal repeat
Synthetic polymeric constructions (SPCs) including the consensus sequence of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) surface envelope glycoprotein gpl20 V3 loop (GPGRAF)
(B) 35S-labeled VZV-infected cell lysate was immunoprecipitated (Immppt) with antisera to ORF 62 and ORF 47 proteins under three conditions: lane 1, in the absence of a competing
Importantly, many of the poxviruses whose arachidonate metabolite profiles indicated that there was a functional 38-kDa protein expressed after infection of BS-C-1 cells form white
To examine the processing mechanism of the HCV precursor polyprotein, the amino-terminal region of the putative nonstructural protein region of the HCV genome, containing the
These results suggest that H13, the human equivalent of the murine ERR, can acquire the ability to function as the MuLV-E receptor if amino acid residues at positions 240 and 242 or