Interaction of Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen Leader Protein (EBNA-LP) with HS1-Associated Protein X-1: Implication of Cytoplasmic Function of EBNA-LP
Full text
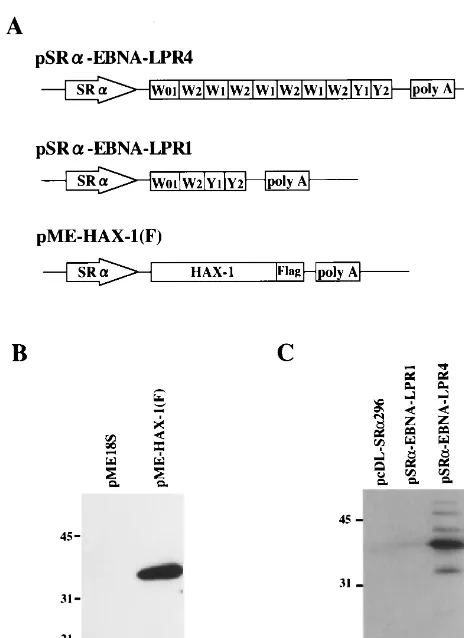
Figure



Related documents
Character- ization of protein-DNA complex formation with this region indicates that it contains binding sites for three series of com- plexes of PC12 cell nuclear proteins, that
The vacuoles containing virions fused with the outer plasma membrane and the particles appeared on the surface of the infected cell.. Late in infection, enveloped virions were
As indicated above, this amino acid substitution did not reduce the ability of the virus to grow in either MDBK cells or CEF but it did change the receptor-binding properties so
A. Specificity of HCMV binding to the 34- and 32-kDa receptor proteins. Cold competition analyses were performed to demonstrate the specificity of binding of HCMV to the 34- and
By using monospecific anti-nsP3 antibodies in combina- tion with immunofluorescence microscopy, we showed re- cently that SFV-specific nonstructural protein nsP3 is local- ized to
Eight nonoverlappimg regions of the hemagglutinin (HA) molecule of influenza virus A/PR/8/34 (PR8), which serve as recognition sites for class II-restricted T cells (TH) from
We have analyzed LCMV isolates derived from purified CD4+ T cells and macrophages of congenitally infected carrier mice and shown that three types of variants are present in
Infection of baby hamster kidney cells with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) results in the accumulation of immature Ul and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) that