Definition of the viral targets of protective HIV 1 specific T cell responses
Full text
Figure




Related documents
We found that with the increased expression level of FBP in the cells, the expression level of NS5A was significantly decreased (Fig. 6, lane 4) compared to that in untransfected
The perception that asset managers where in the best position to increase the positive impact of the investor setting on microfinance was not only indicated by the stakeholder
The leading thinkers interviewed as part of this study broadly agreed that external support provides an affordable and ‘high leverage’ strategy for improving the leadership capacity
tein A self-interaction, we tested whether FRET was produced upon the coexpression of protein A-CFP (A-CFP) and protein A-YFP (A-YFP) fusion proteins in yeast cells (Fig..
Items in associatively related lists are better recalled in serial order task than items in unrelated lists on both immediate and delayed conditions and this is true of all
Firstly a literature review was undertaken to help better understand the theory behind fibre composites and secondly a series of small scale (coupons) and large scale
To evaluate whether HIPK2 interaction with the US11 protein could account for this unusual behavior, the intracel- lular distribution of EGFP-HIPK2b was determined after co-
Alignment of all completely sequenced BDV p24 coding regions derived from the brains of diseased horses and sheep revealed that most nucleotide exchanges in both animal species
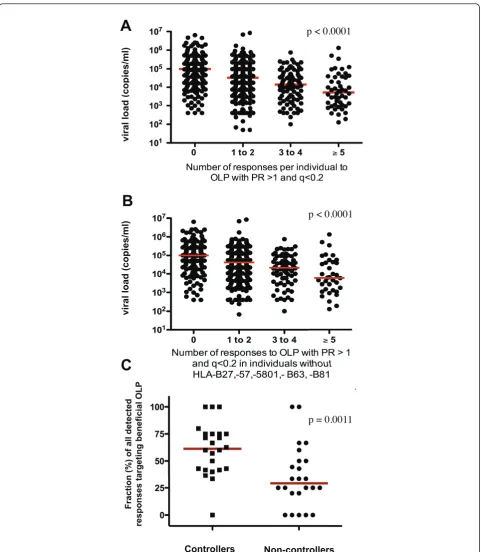



![Figure 4 Responses to OLP identified in multi-variate analysis are associated with reduced viral loadsgenetics in the clade B cohort in Lima and clade C cohort in Durban were subjected to FASS multivariat analysis [41-43]](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/8313792.293890/14.595.58.548.88.638/responses-identified-analysis-associated-loadsgenetics-subjected-multivariat-analysis.webp)
