Hepatitis C Virus Causes Uncoupling of Mitotic Checkpoint and Chromosomal Polyploidy through the Rb Pathway
Full text
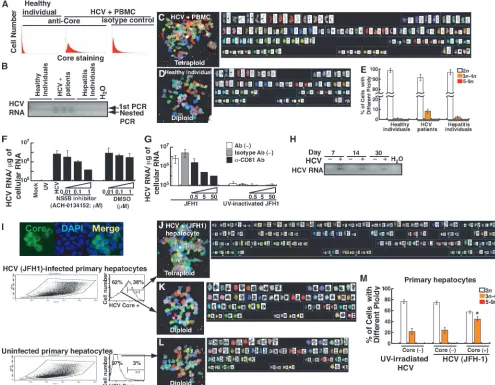
Figure



Related documents
In this paper, new α-order trigonometric and inverse trigonometric fuzzy entropies are proposed and the fuzzy entropy axiomatic requirements are satisfied for the new fuzzy
The architecture of the proposed system contains different hardware like GLCD; it is a Graphical LCD has a format for displaying of 128x64 dots, Joystick; which is used to control
Comparing the transmission coefficient S 21 (dB) in the parallel and mirror configurations (see Figures 10(a), and 10(b)) with offsets in the range [0; 160] mm, we remark that
In the proposed scheme, only one passcode is used for extracting the frame and internally second frame number is selected to select second cover frame to hide MSB and LSB bits
In conclusion, EGCG could inhibit eNOS uncoupling and alleviates endothelial dysfunction and apoptosis of HG-treated HUVECs by activating the
Interestingly, our study showed that miR-770-5p could be upregulated in podocytes by MEG8, and the upregulation of miR-770-5p by MEG8 is at least partially achieved through the role
The purpose of the work here is to directly measure the orientation and strain in individual collagen fi brils during uncon fi ned compression of meniscal fi brocartilage by
To assess the impact of change in the regularity of bedtimes through child- hood we performed a difference in differences analysis, 20 using data on behavioral dif fi culties as