Akt inhibitors as an HIV 1 infected macrophage specific anti viral therapy
Full text
Figure
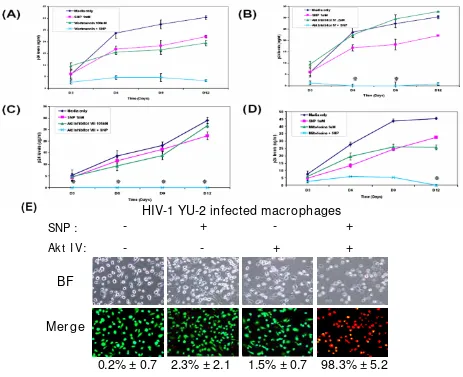
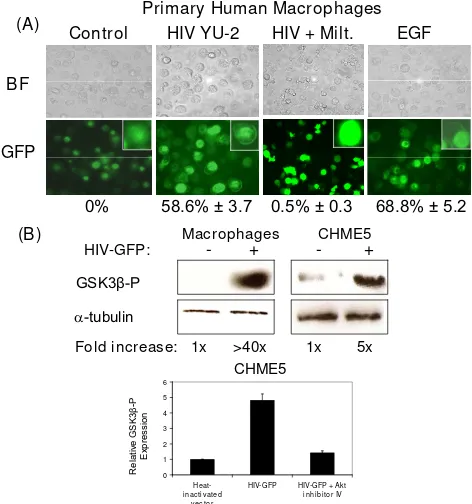
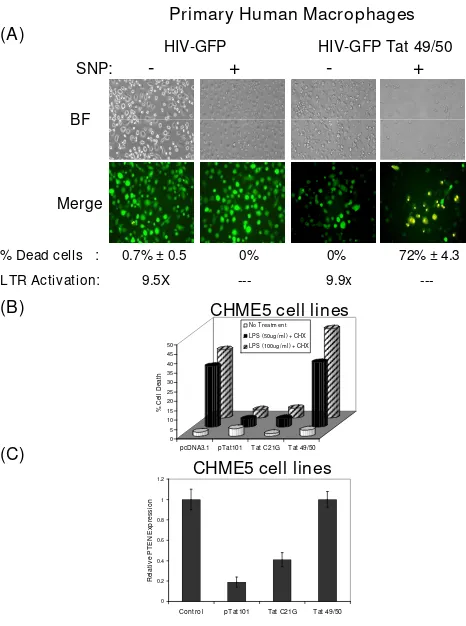

Related documents
In situ nucleic acid hybridization and immunohistochemistry were used to determine the histological local- ization of mouse adenovirus type 1 (MAV-1) during acute infection of
Levels of mRNA of IL-1, TNF- a , and musfiblp were greater and more persistent in BALB/cJ than in A/J macrophages, whereas the levels and kinetics of IL-1, TNF- a , and TF
We have identified two non-template-length RNAs gener- ated by in vitro transcription of minus-strand sat-RNA C with partially purified TCV RdRp: the hairpin-like S-RNA, com- posed
These results clearly indicate that HTLV-I virions, in the presence of PHA, are able to trigger immature thymocyte proliferation by upregulating the expression of IL-2 receptors and
In addition, two transcriptional activation domains located between amino acids 281 and 318 and amino acids 547 and 628 of the HNF1 polypeptide were shown to influence the in
We now provide support for this proposal from experiments involving in vitro translation of three separate mutations of an infectious DA cDNA clone: DA"l"-1, which contains
The human coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (hCAR) was detected by immunofluorescence selec- tively at the basolateral surfaces of freshly excised human airway epithelial
Korsmeyer-Peppas model of formulation C1F7, S1F7, X1F7 and G 1 F 7 dermal patches for mechanism of drug
