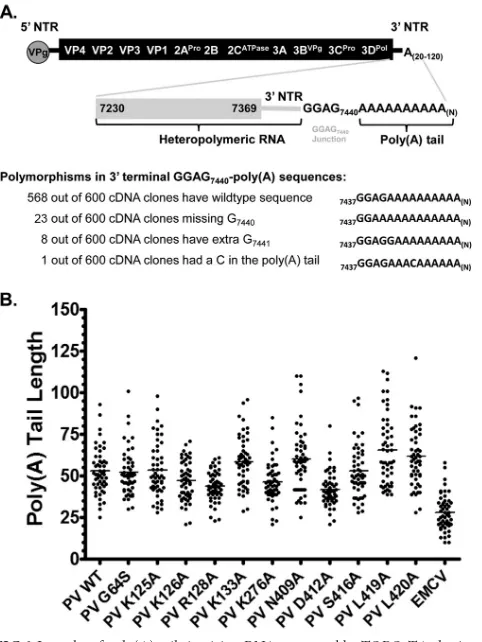
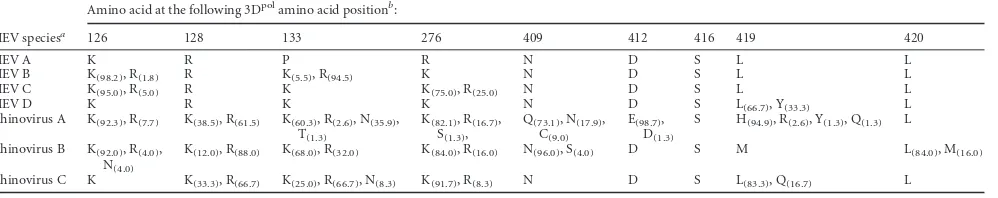
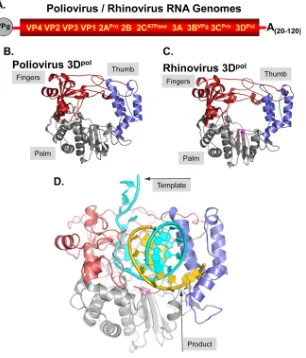
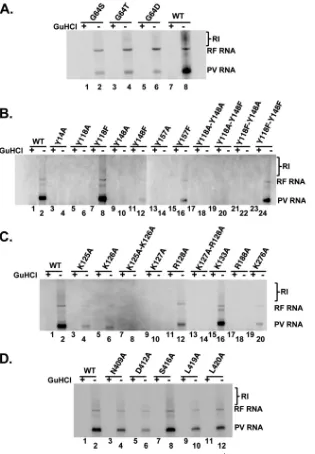
Structural Features of a Picornavirus Polymerase Involved in the Polyadenylation of Viral RNA
Full text
Figure


Related documents
This work adopts the perspective of value orientation and life course position which implies a recursive nature of attitudes and behaviour whereby behaviour
Distribution model factors are suitable for distribution fitting tasks. To extend the applicability of this type of factors, different types of known distributions could be
The release of fatty acid-containing material due to phage alone was calculated by sub- tracting the fatty acid content of material released by uninfected cells at zero time from
Below we suggest that, rather than looking at business models as a naturalistic feature of organizations, they should be seen as a performative representation used in business
translation of Uukuniemi virus-specific RNAs: identification of a nonstructural protein and a precursor to membrane glycopro- teins. Semliki Forest virus capsid protein associates
Rather than report the rape, the survivors constructed narratives that direct blame and accountability toward the ‘old self.’ This less visible, yet still agentic strategy, allows
We propose an alternating iteration algorithm for solving the split equality common fixed point problem with L-Lipschitz and quasi-pseudo-contractive mappings and prove that the