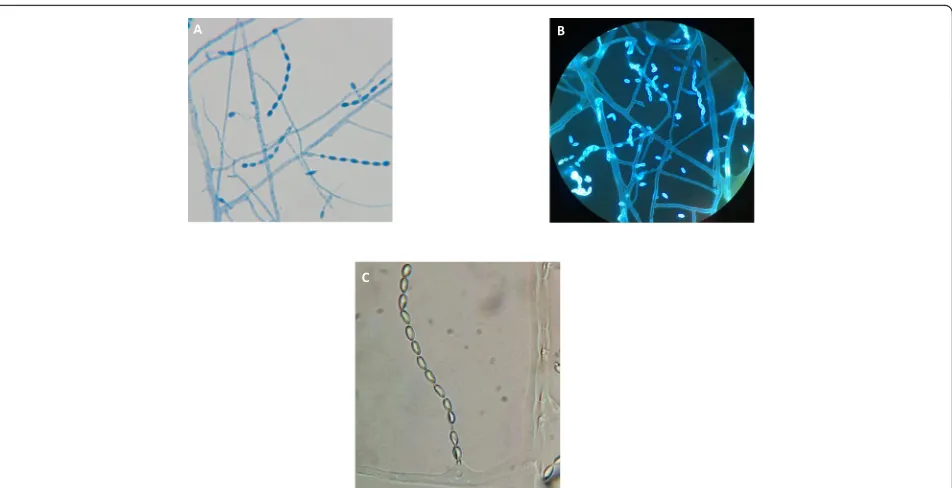
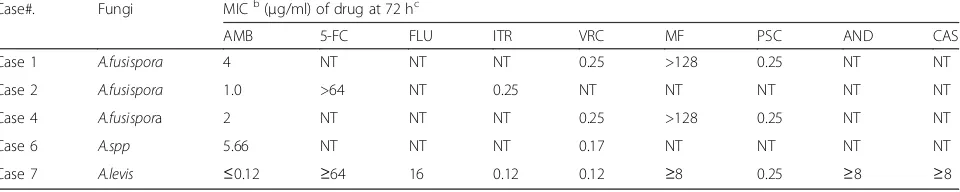
The first case of Acrophialophora levis induced severe pneumonia: a case report and literature review
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Comparison of human metapneumovirus, respiratory syncytial virus and influenza A virus lower respiratory tract infections in hospitalized young children.. Mansbach JM, McAdam AJ,
In order to investigate the synergistic effect on growth of human growth hormone (hGH) and an anabolic agent, fluoxymesterone, 28 children with hypo- pituitarism received the
ABSTRACT: This qualitative multiple case study utilizes a Black feminist ethic of caring (Collins, 2009; Thompson, 1998) to explore how three African American women
In making this last comparison, note that differences can arise from three sources: First, the mixing parameters could be close to boundary values, leading to biased
[17] The higher occurrence of WSLs after 6 months of orthodontic therapy confirms that demineralization can speedily become a concern with fixed appliances when the
A study assessing the growth, lipid peroxidation and activity of antioxidative enzymes in sorghum seedlings grown under salt stress from artificially aged and primed seeds showed that
contribution of Lucban specialty foods to its tourism industry in terms of social and economic.. benefits and proposed a plan of action to promote Lucban as a
Table 2 for post sonication chemical oxygen demand % reduction with sonication time for all concentrations of sample.. 1 time of sonication vs % COD reduced