Dam management with imperfect models: bayesian model averaging and neural network control
Full text
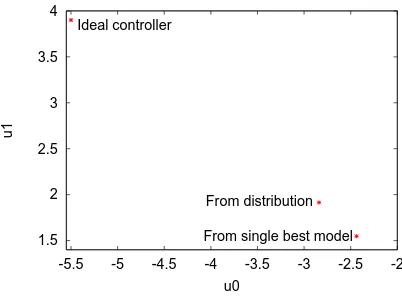
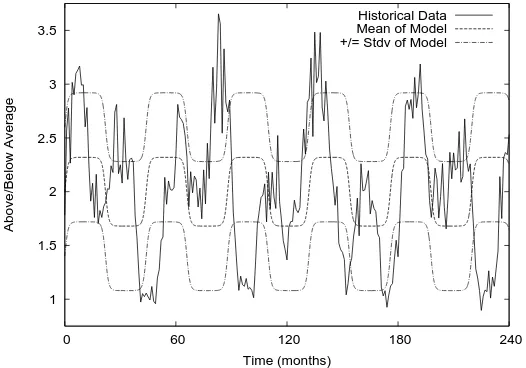
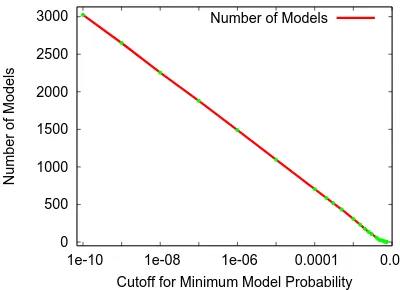
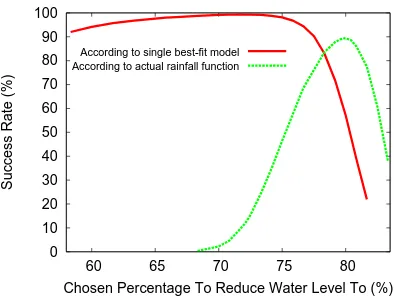
Figure

Related documents
innovation in payment systems, in particular the infrastructure used to operate payment systems, in the interests of service-users 3.. to ensure that payment systems
National Conference on Technical Vocational Education, Training and Skills Development: A Roadmap for Empowerment (Dec. 2008): Ministry of Human Resource Development, Department
When the set of α -vectors is suboptimal, which is the case most of the time, then actions selected after the second time step may be different than those selected by the policy
Given certain assumptions on the approximate driver and the approximate terminal condition, these estimates can be extended to an equivalence result between the global
The total coliform count from this study range between 25cfu/100ml in Joju and too numerous to count (TNTC) in Oju-Ore, Sango, Okede and Ijamido HH water samples as
19% serve a county. Fourteen per cent of the centers provide service for adjoining states in addition to the states in which they are located; usually these adjoining states have
occidentalis per day, and in their study the population of the prey was less than this predation rate, which allowed effective control of this species of Frankliniella
/ L, and a different adsorbent mass, is shown in Figure 5. The results obtained show that the removal rate increases quickly at first, until a time of 60 min, and