Inhibition of Latent Membrane Protein 1 Impairs the Growth and Tumorigenesis of Latency II Epstein-Barr Virus-Transformed T Cells
Full text
Figure
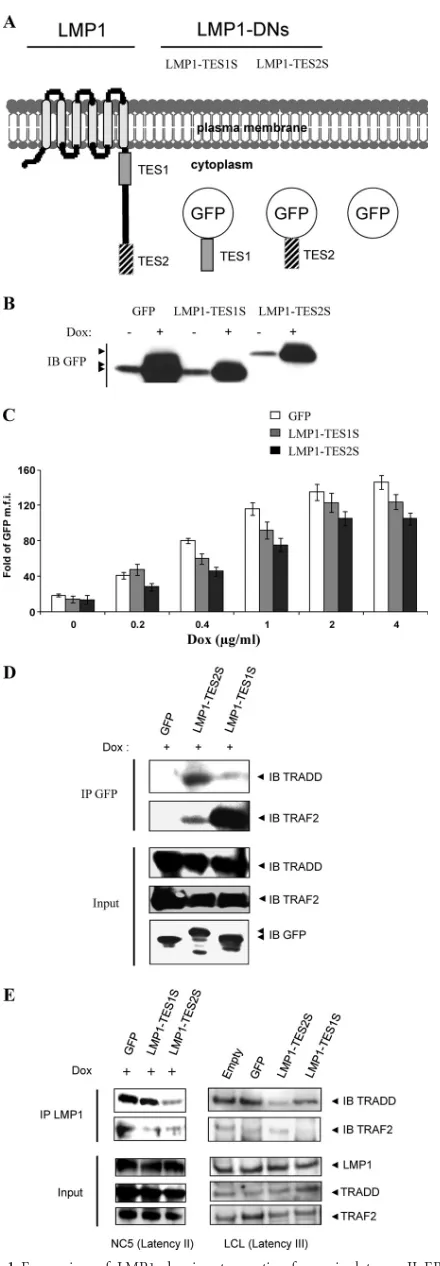
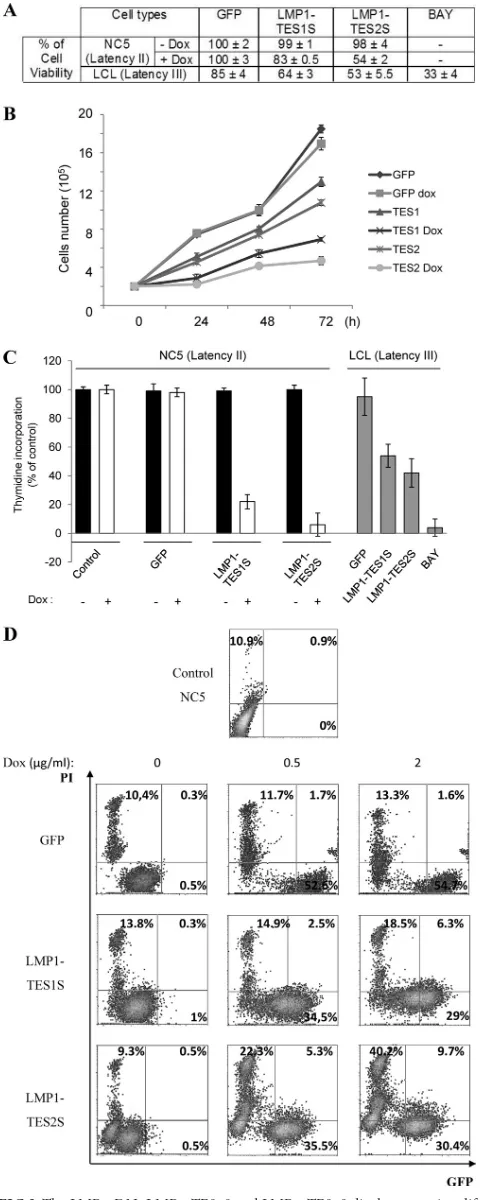

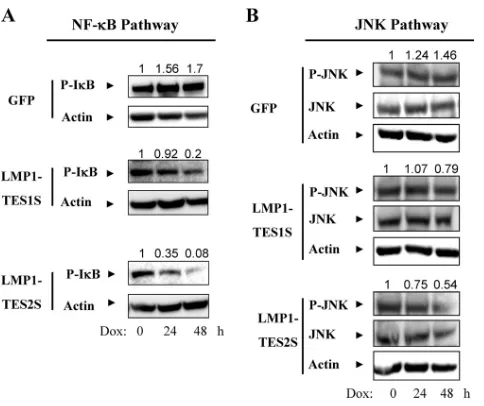
Related documents
any one test positive was more sensitive and less specific than the combination of both tests and Anti CCP test alone and more sensitive. but equally specific when
A. Specificity of HCMV binding to the 34- and 32-kDa receptor proteins. Cold competition analyses were performed to demonstrate the specificity of binding of HCMV to the 34- and
We have analyzed LCMV isolates derived from purified CD4+ T cells and macrophages of congenitally infected carrier mice and shown that three types of variants are present in
Infection of baby hamster kidney cells with vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) results in the accumulation of immature Ul and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) that
I here declare that this dissertation entitled “ “COMPARITIVE STUDY BETWEEN EFFICACY OF ORAL MISOPROSTOL & VAGINAL MISOPROSTOL & FOLEY BULB WITH OXYTOCIN
Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus expressing respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) glyco- proteins: RSV fusion protein can mediate infection and cell fusion. Recombinant
(A) BALB/c/SCID mice were challenged with the indicated doses of wild-type Lister (WT-L), defective Lister (dVV-L), recombinant de- fective Lister expressing p53 (dVV-L-p53),
The aim of the current project was to examine organisational and individual factors considered likely to impact on medication administration performance in the hospital

