HIV 1 cell to cell transmission and broadly neutralizing antibodies
Full text
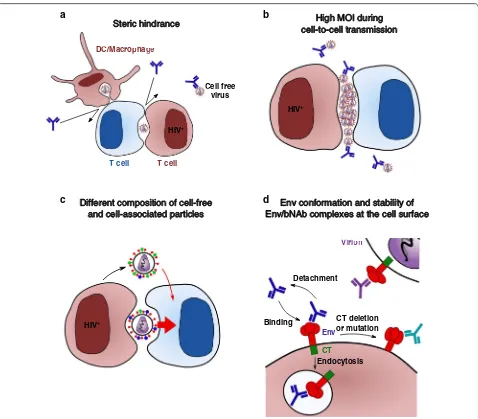
Figure

Related documents
The replication kinetics of ASFV recombinant v ⌬ E165R showed that dUTPase activity is necessary for virus growth in macrophages, the natural host cells, but not in Vero cells..
Furthermore, using our recently gen- erated conditional knockout system for the PIK3CA gene, we show that genetic ablation of the p110 ␣ isoform of PI3K abol- ished
Here, we show that KSHV infection of primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced the expression and release of Ang-2, which in turn was required for
Given that a key aim of the whole STEM Programme is to increase progression into Science and Mathematics subjects post-16, and the generally positive attitudes developed by girl
attention to these test performances in schools? In constructing a relationship between the NAPLAN and TIMMS performances to effective practices, the report suggests that
rOka was also recovered when pGlowgE or Met-gE cells were transfected with the intact cosmids, indicating that gE expression by the cell lines did not inhibit viral replication..
The design adopted for this study was Quasi experimental Pre-test and Post-test control group design to assess the effectiveness of Isometric exercises on level of