Antibody Binding and Neutralization of Primary and T-Cell Line-Adapted Isolates of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1
Full text
Figure

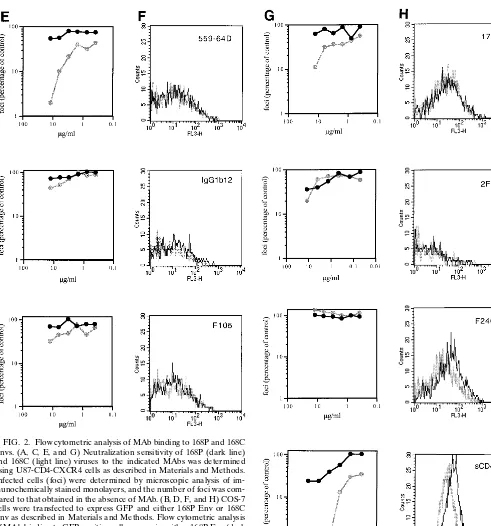

Related documents
As outlined below, transgenic mouse models of hepatitis infection in the liver indicate that direct lysis mediated by CTL granule exocytosis is a less-favor- able immune
Asenapine and its metabolite by Bioanalytical Method in human plasma using LC-MS/MS. The main objectives of the RP-HPLC-MS/MS method development to rapidly.. assay and determine
Whereas treatment of Girardenia zeylanica Dcne extract significantly declined the effect of CCl4 induced damage and it was evidenced by the decreased level of total
The adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV-2) Rep78 and Rep68 proteins are required for replication of the virus as well as its site-specific integration into a unique site, called
Aim: To compare the dentinal tubule occluding ability of Pro-Argin based dentifrice and Carbon Dioxide Laser in the treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity.. Materials and Methods:
In agreement with their inability to inhibit the morphologic changes of apoptosis, none of the clinical isolates of HSV-2 showed any inhibitory effect on caspase-3 or caspase-8
Although analysis of MP mutants LQ37D and LQ37E supports the suggestion that phosphory- lation of MP had a positive effect on the subfunction (inter- cellular localization) of
Bough ton et al (2006) conducted a study to determine whether the regular assessment of children’s pain would improve their pain management and pain would improve their

