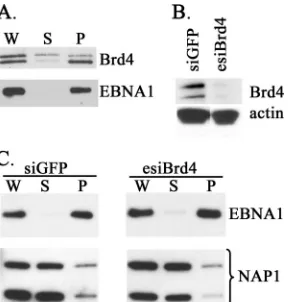
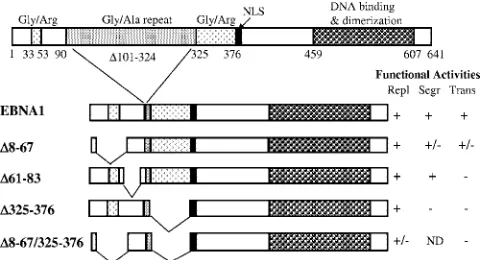
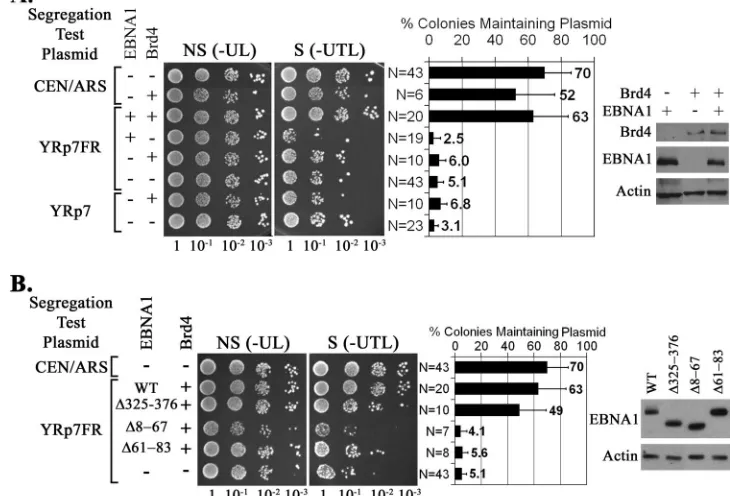
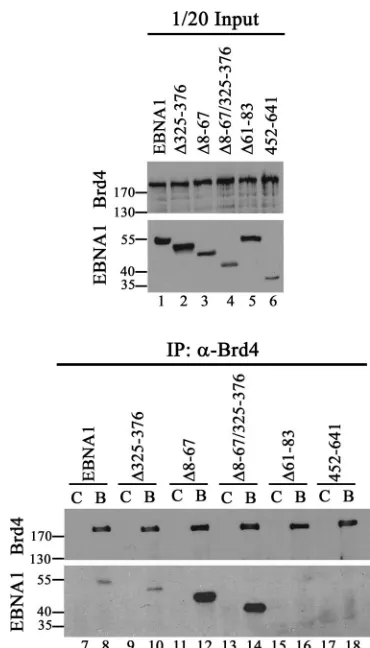
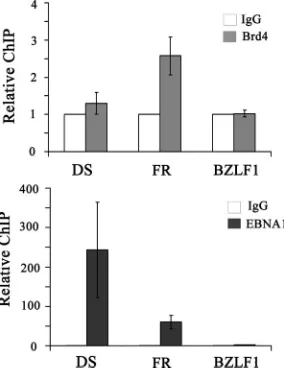
The EBNA1 Protein of Epstein-Barr Virus Functionally Interacts with Brd4
Full text
Figure
Related documents
QPID study report Y: Other training for young people (2001) Audience: national policy-makers, Learning and Skills Council Purpose: research into practice. Topics: C, D, H,
In summary, we show persistence of HIV-1-specific CD8 T-cell responses to multiple epitopes in the chronic phase of HIV-1 infection, in some cases in the presence of persistent
As retroviruses such as Moloney murine leukemia virus (MLV) and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) bud from infected cells, they coencapsidate two copies of viral genomic
SENTHIL AAKASH carrying out a study on the topic: CLINICAL PROFILE AND OUTCOME OF PANCREATITIS IN CHILDREN AGED LESS THAN 15 YEARS – DESCRIPTIVE( RETROSPECTIVE AND
To investigate whether the differential trafficking routes selected by Ad5-GFP and Ad5/35L-GFP vectors affect the efficiency of gene transfer, we analyzed reporter (GFP) gene
Trust, within the context of virtual communities involved in OSS projects, is a complex, multidimensional and dynamic concept that exists within different spheres/levels of open
Treatment of human osteosarcoma cells, expressing CD4 and various chemokine receptors, with the glu- cosylceramide synthase
We have optimized the induction of antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) in rhesus macaques by a lipo- peptide vaccine containing seven peptides from simian immunodeficiency