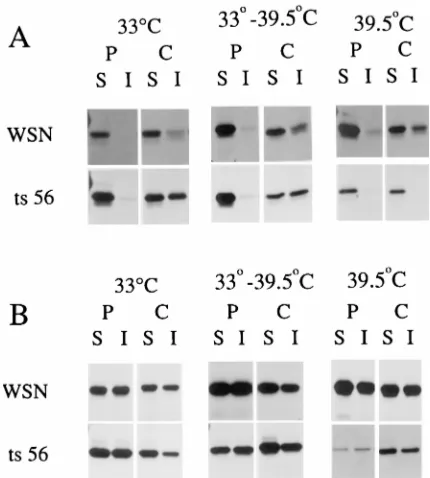
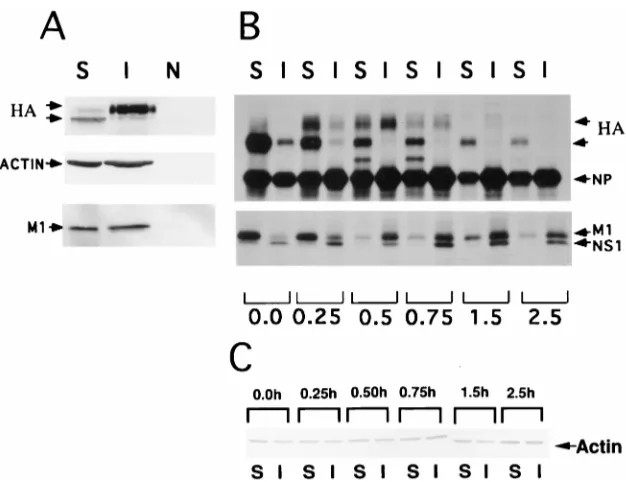
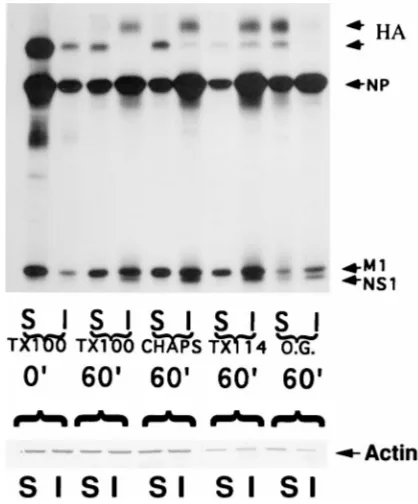
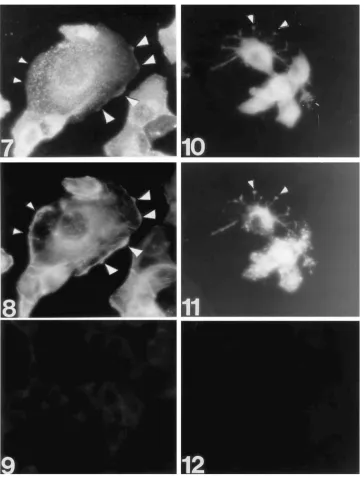
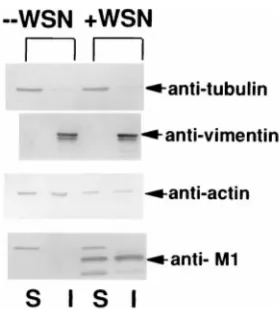
Association of influenza virus NP and M1 proteins with cellular cytoskeletal elements in influenza virus-infected cells.
Full text
Figure
Related documents
Copyright and reuse: City Research Online aims to make research outputs of City, University of London available to a wider audience.. Copyright and Moral Rights remain with
EGFP expression in human thymocytes 4 weeks after direct injection of HIV-1 vector in thy/liv implants of SCID-hu mice.. Prior to vector injection, SCID-hu thy/liv mice were
46) American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The International Classification of Sleep Disorders: Diagnostic & Coding Manual. Westchester,Ill.: American Academy of
elective caesarean section under spinal anaethesia – Anaesthesia. and analgesia July
In a previous study using a mixed leukocyte culture in which lymphocytes were stimulated in vitro with HIV-1-infected autologous blast cells, we demon- strated that immunization
These mutant E2 proteins were tested for expression, stability, and compartmentalization in cells and for sequence-specific DNA binding, as well as in functional assays
In this system, transcriptional activation mediated by the VP16 activation domain occurs if the YY1-VP16 fusion protein is tethered to the promoter either by a direct protein-
Sedimentation velocity analysis indicated that most of the newly synthesized M protein is monomeric, suggesting that the solubility of M protein in the cytosol is maintained by