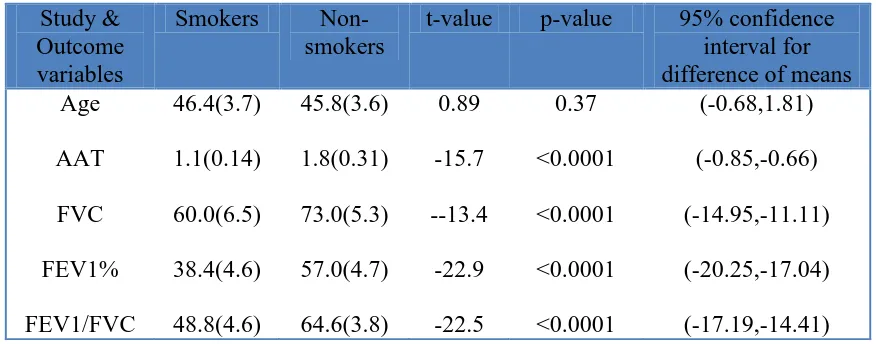
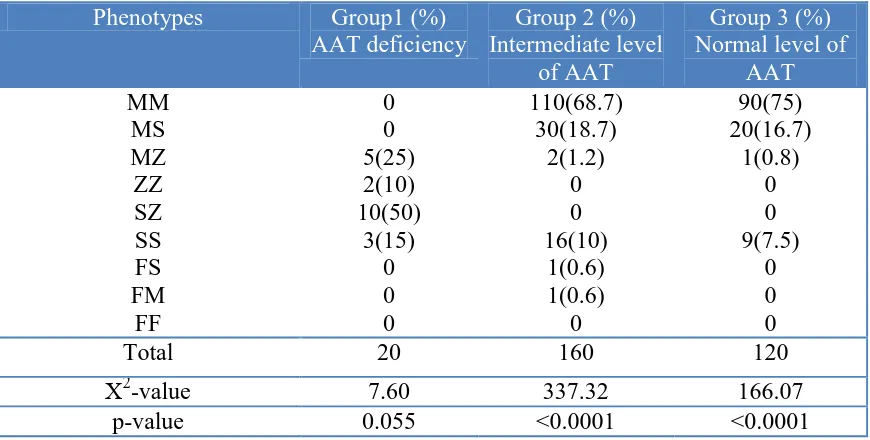
The Efficiency of Alpha1-antitrypsin Deficiency Detection by Isoelectric Focusing Phenotypes in Relation to Serum Protein Concentrations in COPD Patients
Full text
Figure


Related documents
Finding showed no significant difference between two study groups in belief in regard to more beauty and at- tractiveness because of drug use; but a significant dif- ference was
However, it was the more experienced teachers who selected more groups of children/students as having low chances, than the teachers with lower seniority (respectively:
A descriptive model is commonly applied, in order to display and characterize the logic of a system [34, 35]. Next, explanatory models are used to explain
Data Warehouse Information Flows.. Processes associated with the extraction , cleaning , and loading. of the data from the source systems into the
AAE: Acquired angioedema; ACEI: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; APP: Aminopeptidase P; ARB: Angiotensin receptor blocker; C1-INH: C1 esterase inhibitor; FFP: Fresh
For example, Borg and colleagues (2011) found that relative to young adult control participants, both older individuals without dementia and older adults with dementia
The prevalence of anxiety, somatization disorder, alcohol abuse and eating disorders was greater in Guasca than Guatavita with a prevalence of 32.5% and 25.7% for an- xiety, 73.8%
Basal active TGF- β serum levels of T2DM patients treated with metformin and sulfonylurea (S+M), insulin glargine (G+M) or a DPP-4 inhibitor (D+M) as well as of non-diabetic