On the Electrochemical Investigations of Substituted LiNiVO4 for Lithium Battery cathodes
Full text
Figure


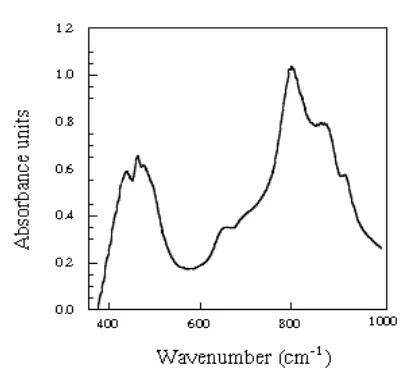
Related documents
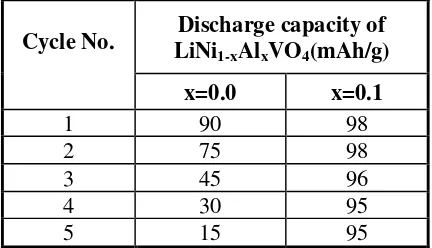
Constant current charge-discharge, cyclic voltammetry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy tests show that samples annealed at 800°C for 12h exhibit an increased
7 shows initial discharge charge and cycling stability curves of CoO nanorods @ N doped carbon composite obtained with different pyrrole contents.. It can be found
7 shows initial discharge charge and cycling stability curves of CoO nanorods @ N doped carbon composite obtained with different pyrrole contents.. It can be found
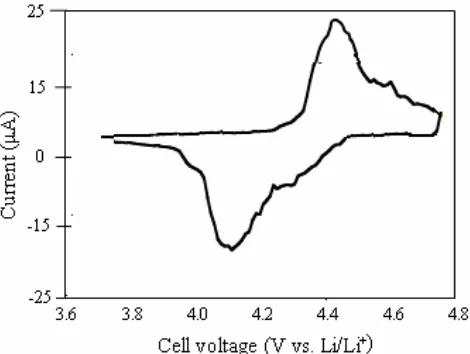
The electrochemical properties were measured using cyclic voltammetry (CV) method, and the CV data is shown in Figure 2. This area indicates that the charge/discharge response for
The cycling and rate performance of the sample (4wt% CNTs) are also investigated at different rates in Fig.5.The material charge-discharge specific capacity has any
Film-forming additives relatively suppressed change in the surface morphology of Si thick-film electrode after charge-discharge cycling; disintegration of Si electrode
Clearly, the LiMn2O4/graphene sample can suppress the charge transfer resistance, which is contributed to a higher discharge capacity and high rate capability
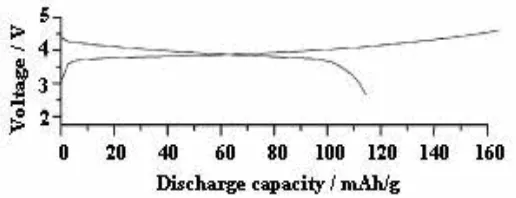
charge/discharge cycling in the voltage range of 3.0 – 4.4 V at 0.1 C (1 C = 148 mAh/g). 7a, there are two distinct voltage plateaus at 4.1 and 4.0 V, respectively, cor- responding