Turing learning: a metric-free approach to inferring behavior and its application to swarms
Full text
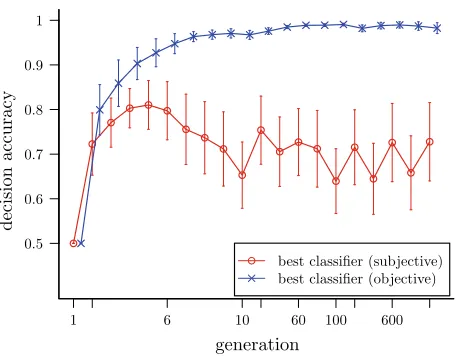
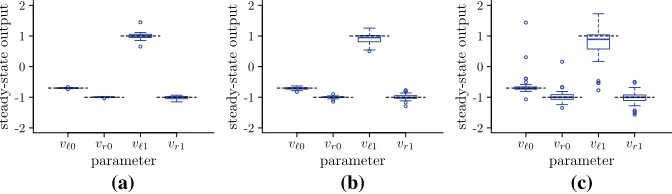
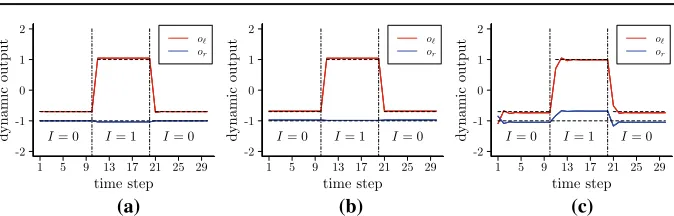
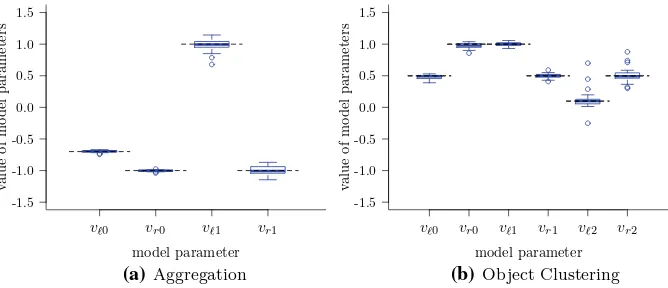
Figure



Related documents
More than an office building Imagine a modern and comfortable office building, built with use of green technologies, located in the very center of Wrocław, close to the
The instrument contained 13 attitudinal statements related to the newsletter received, measured on a seven-point Likert scale: reactions to the site (newsletter frequency, drop
Synthetic biology unites multidisciplinary efforts directed at the design of complex biologi- cal systems to obtain useful novel properties and activities based on the
Dependent variable, in this study, was tax morale where the variables of religiosity, national pride, and importance of religion, importance of politics,
With sdmpredictors we aim to complement these R packages by providing an easy to use interface for the acquisition of uniform and compatible terrestrial and marine
likely to be handicapped than a child of like birth weight born to a mother without. such
After successfully supporting the development of the wind power technology, an approach is needed to include the owners of wind turbines in the task of realizing other ways, other