UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
DESIGN OF AUTOMATIC TOOL CHANGER FOR WELDING
GUN TIP
This report submitted in accordance with requirement of the Universiti Teknikal Malaysia
Melaka (UTeM) for the Bachelor Degree of Manufacturing Engineering (Robotic &
Automation) with Honours.
By
MUHAMAD AZIM BIN AZAMI
Alamat Tetap:
18-01-18, Pangsapuri Cheras 4E,
56100, Cheras Kuala lumpur
Tarikh: _________________________
Cop Rasmi:
Tarikh: _______________________
** Jika Laporan PSM ini SULIT atau TERHAD, sila lampirkan surat daripada pihak berkuasa/organisasi berkenaan dengan menyatakan sekali sebab dan tempoh laporan PSM ini perlu dikelaskan sebagai
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
BORANG PENGESAHAN STATUS LAPORAN PROJEK SARJANA MUDA
TAJUK: Design of Automatic Tool Changer for Welding Gun Tip
SESI PENGAJIAN: 2008/09 Semester 2
Saya MUHAMAD AZIM BIN AZAMI
mengaku membenarkan Laporan PSM ini disimpan di Perpustakaan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) dengan syarat-syarat kegunaan seperti berikut:
1. Laporan PSM adalah hak milik Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka dan penulis. 2. Perpustakaan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka dibenarkan membuat salinan
untuk tujuan pengajian sahaja dengan izin penulis.
3. Perpustakaan dibenarkan membuat salinan laporan PSM ini sebagai bahan pertukaran antara institusi pengajian tinggi.
4. **Sila tandakan (√)
SULIT
TERHAD
TIDAK TERHAD
(Mengandungi maklumat yang berdarjah keselamatan atau kepentingan Malaysia yang termaktub di dalam AKTA RAHSIA RASMI 1972)
(Mengandungi maklumat TERHAD yang telah ditentukan oleh organisasi/badan di mana penyelidikan dijalankan)
Disahkan oleh:
DECLARATION
I hereby, declared this report entitled “Design of Automatic Tool Changer for Welding Gun Tip” is the result of my own research except as cited in references.
APPROVAL
This report is submitted to the Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering of UTEM as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Manufacturing Engineering (Manufacturing Process) with Honours. The member of the supervisory committee is as follow:
ABSTRACT
ABSTRAK
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
First of all I would like to thank Allah the Almighty for His blessing which have help me to complete the project report and giving me the strength to work along the project period which one of the requirement for the Bachelor Degree of Manufacturing Engineering (Robotic & Automation) course.
I would like to give by deepest gratitude to my supervisor, En. Arfauz Bin A. Rahman and Pn Syamimi Bt Shamsuddin that always being helpful in guiding me through the whole project period. With the knowledge and experiences that he have, he shares it by giving brilliant advices that are useful in order to finish up the project. With the project related activities managed by him shows the full support given in order for his student to succeed.
I also love to thank my entire family members that continuously giving support and love which increase my spirit to do the best in what I do. I would like thank to all of my friends and lecturers that also give some contribution to my project.
TABLE OF CONTENT
Abstract i
Abstrak ii
Acknowledgment iii
Table of Content iv
List of Tables vii
List of Figures vii
1. CHAPTER 1 : INTRODUCTION 1
1.1 Objective 2
1.2 Scope 2
2. CHAPTER 2 : LITERATURE REVIEW 4
2.1 Welding 4
2.1.1 Method Of Welding 4 2.1.2 Advantages Of Welding 7
2.2 Welding Gun 8
2.2.1 Type Of Welding Gun 8 2.2.2 Anatomy Of Welding Gun 11 2.2.3 Application Of Welding Gun 12 2.2.3.1Manual Welding Gun 13 2.2.3.2Robotic Welding Gun 13
2.3 Welding Gun Tip 14
2.6.1 Benefit Of Automating Welding Process 22 2.7 Computer Aided Design (CAD) 24
2.7.1 Benefit of CAD 25
2.7.2 CAD Software 26
2.7.2.1SolidWorks 26
2.7.2.2Automation Studio 29
2.7.2.3Autodesk AutoCAD 30
2.7.2.4Autodesk Inventor 31
2.7.2.5CATIA 33
2.7.2.6Working Model 34
3. CHAPTER 3 : METHODOLOGY 35
3.1 Overall Completion Planning 35 3.1.1 Project Objectives and Scopes 35 3.1.2 Literature Review Research 36 3.1.3 Design Software Selection 37
3.1.4 Design Selection 37
3.1.5 Design Development 37 3.1.6 Simulating and Analysis of Design 37 3.2 Literature Review Research Methods 38
3.2.1 Key words 39
3.2.2 Correct data 39
3.2.3 Collect Data 39
3.2.4 Source Profile Register 39 3.3 Designing Procedures 40
3.3.1 Sketch Design 40
3.3.2 Select Design 41
3.3.3 Integrate and Analyze Design 41
3.3.4 Finalize Design 41
3.5 Design Software Selection Methods 43 3.5.1 Software Capability 44 3.5.2 Human – Computer Interaction 44 3.5.3 Ease of Understanding 44
3.5.4 Easy to Use 44
3.6 Design Analysis Methods 45 3.7 Using Design Software 45 3.7.1 SolidWorks 2005 45 3.7.2 Working Model 6.0 48
4. CHAPTER 4 : DESIGN 51
4.1 Basic Design Sketch/Drawing 52
4.1.1 Design 1 52
4.1.2 Design 2 53
4.1.3 Design 3 54
4.2 Design Selection 55
4.3 Design Development 57 4.3.1 Operation Principles 58 4.3.2 Design Placing Location 58 4.3.3 Design Dimension 59
4.3.4 Design Shape 60
4.4 Finalize Design 61
4.5 Robot Design 63
4.6 Design Details 66
4.6.1 Materials and Devices 69 4.6.2 Design dimension 70 4.6.3 Workspace details 71
5. CHAPTER 5 : SIMULATION ANALYSIS AND DISCUSSION 74
5.1 The Benchmark 74
5.2 Rotator Speed 77
5.3 Electrode Tip Change Speed 82 5.4 Electrode Tip Alignment 86
5.5.1 Interpretation of factor of safety (FOS) values 91 5.6 Simulation of Changing Operation 92
6. CHAPTER 6 : CONCLUSION 96
6.1 Future Improvement 97
REFERENCES 98
APPENDICES 101
A Design Details B Stepper Motor
LIST OF TABLES
4.1 Different and Similarity between Designs 56 4.2 Pugh Method of Selecting the Design 57 4.3 Material of the Tool Changer 70
5.1 Manual Method of Changing the Welding Gun Tip 74
LIST OF FIGURES
2.1 Fusion Welding 5
2.2 Resistance Spot Welding 6 2.3 Brazing and Soldering 6 2.4 Most Common Welding Methods 7 2.5 SMAW Electrode Holder 8
2.6 MIG Welding 9
2.7 TIG Welding 9
2.8 Two Usual Type of Resistance Welding Mechanism; 10 (A) C – Type and (B) X – Type
2.10 MIG Gun Parts 11 2.11 TIG Welding Torch Parts 12 2.12 Spot Welding Parts 12 2.13 A Man Manually Using SMAW Welding 13 2.14 Spot Welding Gun That Attached To An Arm Robot 14 2.15 Welding Gun Tip/Contact-Tube Location In MIG Welding 14 2.16 Varieties Of Electrode Tip 15 2.17 Wore And Deformed Electrode Tip 16 2.18 Hand Held Electrode Dresser 17
2.19 Automatic Tip Dresser 18
2.20 Steam Power Textile Machine 19 2.21 Fully Automated Production Line 20 2.22 One Of The Product Of CAD 23
2.23 Solidworks Logo 26
2.24 Design Using Solidworks 27 2.25 Design Stress Analysis Using Solidworks 27 2.26 An Assembly Of Drive Shaft 28 2.27 Automation Studio 29 2.28 The Application Of Automation Studio 29
2.29 Autodesk Autocad 30
2.30 Autocad Application In Designing A Model 30 2.31 Autocad’s Drawing Imported Into CNC Machine 31 2.32 Autodesk Inventor 31 2.33 A Part Of Model Consist Several Individual 32 2.34 Part That Is Created Using Autodesk Inventor 32
2.35 CATIA 33
2.36 TOYOTA F1 Model Using CATIA 33 2.37 Human 3D Model For Testing Human View For Inside A Car 34 2.38 Simulation Of Car Crash Using Working Model Software 34
3.1 Flow Chart of Overall Project Planning 36 3.2 A Couple of Internet Search Engine, (A) Google.Com And 38
(B) Yahoo.Com
3.4 Design Procedures 40 3.5 Method of Design Selecting 42 3.6 Important Aspect in Design Software Selection 43 3.7 Solidworks Icon Is Selected and Clicked 46 3.8 Solidworks Window 46 3.9 Method of Opening New Workspace or Document; (A) Clicking Menu 47
FILE>NEW, (B) Click the NEW Icon, (C) Click The Menu NEW DOCUMENT
3.10 New Solidworks Document 47 3.11 Solidworks Workspace 48 3.12 Working Model Icon 49 3.13 Working Model Window 49 3.14 How to Edit Properties 49 3.15 Simulator’s Run Button 50
4.1 Location Of Electrode Tip And Tip Holder 51 4.2 View Of Design 1; (A) All Electrodes Widens, And 52
(B) Four Electrode Retract To Give the Versatility When Welding
4.4 Basic Concept of Design 1 That Is Attached To The End Of 53 Welding Gun Arm
4.5 View of Design 2 with Turret Concept 53 4.6 Design 2 That Is Attached To the Welding Gun 54 4.7 The Basic View of Electrode Gripping Part Of Design 3 54 4.8 Design 3 Basic View 55 4.9 Potential Risk of Human Worker That Could Occur In Regarding Robot 59 4.10 The Working Envelope of A Robot 59 4.11 Suggested Location of the Tool Changer 60 4.12 The Changes in the Design Looks 61 4.13a Automatic Tool Changer For Welding Gun Tip 62 4.13b Design in the Solidworks Work Space 62
4.14a Robot Design 64
4.17 The Minimum and the Maximum Opening Of Welding Gun 66 4.18 Tool Changer for Welding Gun Tip 67 4.19 Steps of Changing the Welding Gun Tips 68 4.20 Inside the Changer 69 4.21 Exploded View of Tool Changer Parts 69 4.22 Tool Changer Dimension 71 4.23 One of the Comment Production Line Involving Robot 72 4.24 Production Line in Real-Life 72 4.25 Layout of Tool Location 73 4.26 A Solidworks View of the Tool Changer Location to The 73
Welding Robot
5.1 Manual Welding Gun Tip Changing Method 76
5.2 Tips Alignment 76
5.3 Rotator Set 77
5.4 Rotator Radius 78
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
Welding gun is one of the important components in welding process. It is used as a guidance or pointer for an accurate welding. On top of that, it is also acts as a path way for the electricity to flow from the transformer to the welded metal. Welding gun is usually handled manually by human. Nowadays it usually attached to a robotic arm. The usage of welding gun to assist human in welding process is increasing whether manually or using robot. With the high increment rate of welding gun usage in industry, the frequency of maintenance is also increasing. One of the important parts of welding gun that need to be maintained is the tip. The tip is directly exposed to high temperature and perhaps high pressure, and may need to be maintained frequently. Usually maintenance of the tips is done by changing the damaged tip with the new one. Currently, the maintenance procedure is done manually by human and it is not the best method to be used. Due to limited energy of human, the method result to longer idle time of production and higher risk of the human safety.
1.1 Objectives
The aim of this project is to design an automatic tool changer for welding gun tip. This aim is achieved through these objectives:-
(a) To study, analyze, and suggest an automated method of changing the welding gun tip for an industrial robot
(b) To design an automatic tool changer for welding gun tip using Solidworks software
(c) To simulate and analyze the potential utilization of automated tool changer of welding gun tip
1.2 Scope of project
5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 Gant chart of PSM1 for Semester 1
Task \ Week 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Introduction
Literature review
Methodology
Propose Design
Design Sketch
CAD Design
Task \ Week 1 2 3 4 1 1 1 1 1 BREAK 5 1 1 1 13 14
Introduction
Literature review
Methodology
Design Process
CAD Design
Design Development
Simulation
Discussion
Conclusion
CHAPTER 2
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Welding
Joining process plays important role in the manufacturing industries, especially in the assembly sector. The term for joining process is widely in range, covering many aspects of process that may includes brazing, soldering, adhesive bonding, mechanical fastening, and welding. Welding is a joining process which involves metal parts. This process includes melting and joining parts of metal together to form new item or product.
Balchin (1991) defines welding as uniting pieces of metal part at joint faces. The faces are melted by heating it with additional similar composition filler metal. Later, the melted faces which are put close together will stick when it cooled. O’con (2000) extend the definition by saying that welding is not just sticking metals together, but it is a total science and the main method of construction and manufacturing used world wide.
2.1.1 Method of welding
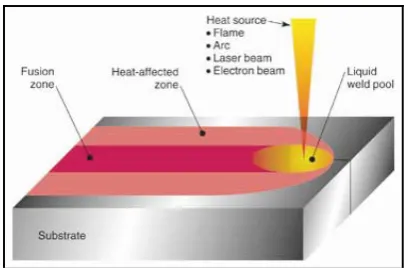
When heat alone is used the process is called fusion welding. Referring to Houldcroft (2001), the metal to be weld is melt to form a bridge between the combining parts and will united after it solidifies. Adapted from his book, Figure 2.1 shows that the metal which is melted can come exclusively from the parts to be joined. In other hand extra metal know as filler metal may also included if welded metal is too thick. The name ‘fusion welding’ is used due to the metal workpiece that has to be melted to make joint.
Figure 2.1: Fusion welding (courtesy of www.llnl.gov)
.
Figure 2.2: Resistance spot welding (courtesy of www.substech.com)
According to Kalpakjian and Schmid (2006) which defined, Brazing and Soldering can considered as welding and these types of joining require lower temperature than welding. Filler metals are placed in the joint and are melted using external source of heat. When it is solidified, a strong joint is obtained. Figure 2.3 is an example of the two joining process. Both brazing and soldering are different in the temperature used, where needed temperature and joint strength of soldering is lower then brazing.
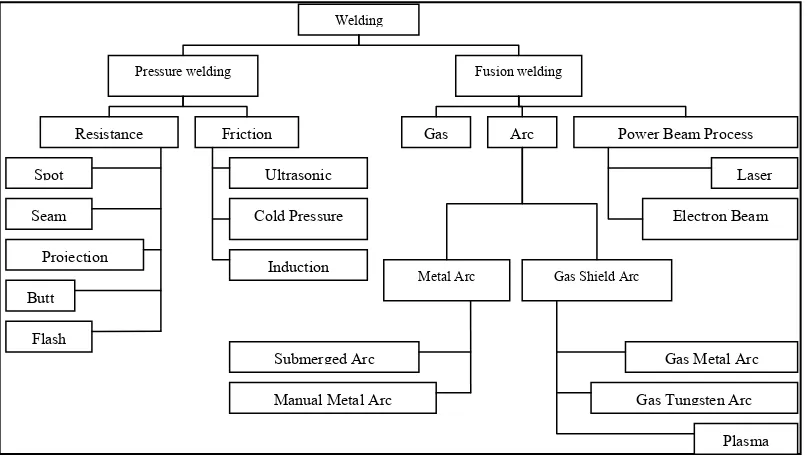
[image:21.595.192.447.449.673.2]Weman (2003) has provided a schematic presentation of the most common welding method used world wide shown in the Figure 2.4 below. In this figure, brazing and soldering is not listed.
Pressure welding Fusion welding
Resistance Friction
Spot Seam Projection Butt Ultrasonic Cold Pressure Induction
Gas Arc Power Beam Process
Laser
Electron Beam
Metal Arc Gas Shield Arc
Manual Metal Arc
Submerged Arc Gas Metal Arc
Gas Tungsten Arc
Plasma Flash
Welding
Figure 2.4: Most common welding methods
2.1.2 Advantages of Welding
[image:22.595.114.518.153.381.2]2.2 Welding Gun
Generally, welding gun is the equipment or tool that acts as a holder for welders to perform welds. Houldcroft and John (2001) defined that welding torch or gun, which later being the British standard preferred term, is a device that held by welder for weld. The term ‘gun’ is use by the International Welding Thesaurus is for a device that filler wire is feed through it. In another point of view, Weman (2003) defined that welding gun is an important part of the welding equipment. It brings the shielding gas, electrode, and welding current to the weld spot.
2.2.1 Type of Welding Gun
The common welding use in fusion welding is the Shielded Metal Arc welding or SMAW, MIG welding and TIG welding. Each of the welding is different in operating to perform weld. Thus, different welding gun is needed in order the weld to be done.
[image:23.595.257.380.627.752.2]For the Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), it uses a welding gun known as electrode holder. This is because SMAW uses an electrode which is made from filler metal that is coated with flux. The electrode is clipped to the electrode holder which acts as a holder. It also has the function of electrical connector that will let the current flow through the electrode to the workpiece to perform weld. Davis (2003) defined that welding gun for SMAW is also known as electrode holder. It is held by the operator and firmly grips the electrode, carrying the welding current to it. Figure 2.5 show the common electrode holder used for SMAW
The Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) or also known as MIG uses a different type of welding gun than the SMAW. The MIG operate by feeding automatically wire like filler metal from a wire coil to be weld. John (2001) defined that the gun has the function of directing the electrode wire and conveying to its welding current, as well as covering both wire and molted pool with the shielding gas. Figure 2.6 shows the welding gun used in MIG welding.
Figure 2.6: MIG welding (courtesy of www.mkprod.com)
In Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) or the TIG welding, the gun used to weld is called welding torch. The TIG works by supplying electric arc between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece. The electric arc produced melts the two workpiece and combine them when the weld solidified. The tungsten electrode is hold by collet which works as adjuster for the in and out of the electrode. The gun also has a ceramic cup that used to direct the shielding gas. Finch (1997) defined that the TIG welding torch work by producing electric arc instead of flame that occurs between the tungsten and workpiece. A collect clamps the tungsten so it can be adjusted in and out of the torch. Due to the intense of heat, the ceramic cup is used to direct the shielding gas to the area of weld. Figure 2.7 shows the welding gun used in TIG.
[image:24.595.252.384.616.743.2]