Turbulence and wake effects in tidal stream turbine arrays
Full text
Figure




Related documents
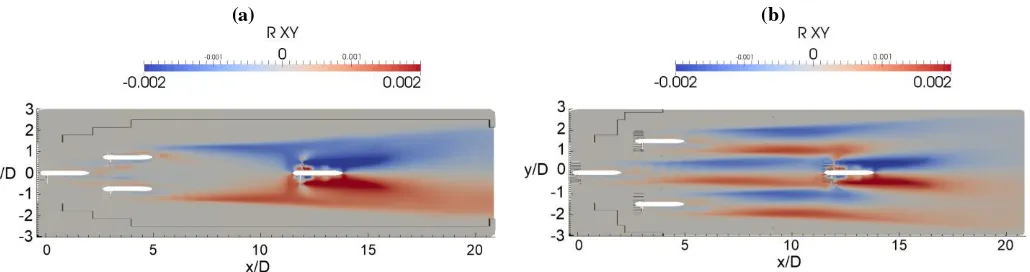
In the case of the Tandem array, the turbulence intensity in Figure 18 shows the highest I values to be in the near wake, with values peaking at about 70% then recovering
Turbomachinery, mixed-flow pump, CFD, turbulence model, velocity field, off-design flow- rate, unsteady flow, numerical methods
The wind turbine model also caused increased turbulence levels in the upper part of the wake, while both the mean shear and the turbulence intensity in the lower part were
Such differences would indicate that simplified methods to model the wake characteristics of tidal stream turbines, such as the absorption disc approach [3, 2, 4], may
The velocity field and thermal characteristics for isothermal and uniform heat flux surfaces in the presence of wall jet flow have been predicted using different turbulence models
Velocity deficit at 180.95 m downstream computed using lidar data, the Gaussian wake model, multi-zone wake model, and the Jensen wake model under different turbulence
mean flow velocity ( Callitriche ) or turbulence ( Groenlandia ), but Total Kinetic Energy (Total KE) was 337. the single best descriptor of uptake rates for both species (Figure
In Figure 19 is possible to see the velocity profiles obtained for the 95N, 5 m/s and 2% free stream turbulence intensity case (mild favorable pressure gradient and low flow