Design of a Low Power Class AB Two-Stage Op-Amp with Symmetrical Slew Rate
Full text
Figure
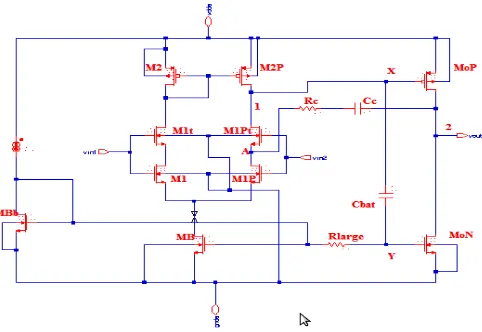
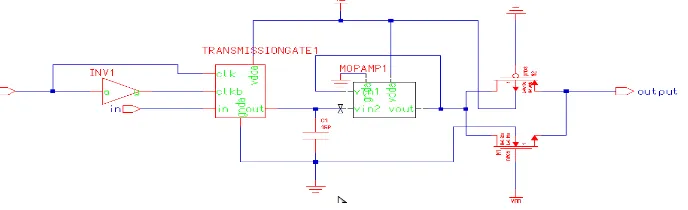
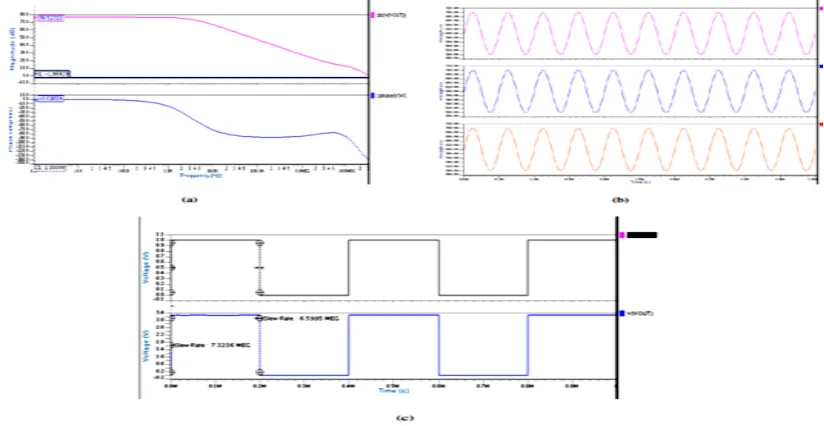
Related documents
NO reactive antibodies remained for the F1 serum in this antiserum after ab- sorption with both parental sera, hence by this test there was no evidence of a “hybrid
This working paper reports on preliminary printed circuit board measurements comparing printed circuit boards with solid and with lattice ground and supply planes, initial
(ii) Most of the Paramecium PKGs possess a molecular organization characteristic of mammalian PKGs (19, 48), including a regulatory part with two cGMP-binding domains in the
BioMed Central World Journal of Surgical Oncology ss Open AcceCase report Undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma of the liver mimicking acute appendicitis Case report and review of the
Figure 5 shows, for each type of considered vehicle and at speed of 40 km/h, the behaviour of the dynamic load, varying the road surface profile (see Fig.. ( 12 ) has made it
These results were a little bit different from those of previous studies performed by Blanco et al demonstrating that QL2 block was a super- ior analgesic technique, which can
Tensile tests on specimens taken from steel reinforcing bars extracted in-situ from concrete structural elements of the interior water pipe-supporting system of the cooling tower,
have introduced the generation of a canine MBS-model of the hind limb for the simulation of ground reaction forces during different movements and its validation with force data
