Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing for High-Dimensional Regression
Full text
Figure
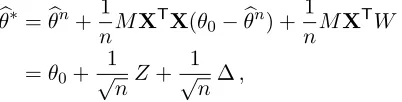
Related documents
Formulating a hypothesis test Interpreting a hypothesis test Common types of hypothesis test Power calculations Hypothesis tests and confidence intervals..
As a confidence interval extends from the sample mean minus the half- width to the sample mean plus the half-width, the function CONFIDENCE.NORM can be used to obtain a
South African policy exhibits attitudes contradictory to the values of Southern African Development Community (SADC) - to promote a unified Southern Africa.. Existing policies need
alias exec c configure terminal alias exec p4 show ip interface brief alias exec p6 show ipv6 interface brief alias exec r show run | section router rip alias exec b show run
depends on alternative hypothesis and selected level of type I error not equal - two-tail test, 50% of area in each tail of the distribution greater or less than - one-tail test,
Larger samples allow us to detect even small differences between sample statistics and true6.
zero mean, unit variance uniformly distributed