Compressive sensing in distributed radar sensor networks using pulse compression waveforms
Full text
Figure

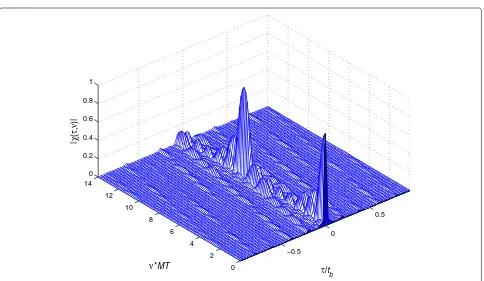
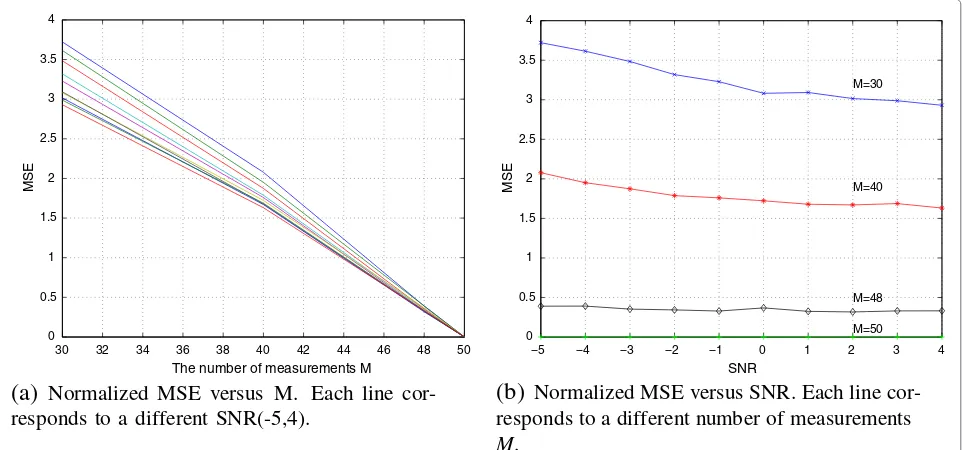

Related documents
For Benjamin, this takes the form of irruptions of messianic time which connect moments of different time-series together, rupturing the continuum of homogeneous empty time
HLF will continue to support the urgent repair needs of faith buildings as before (including cathedrals in Scotland and Northern Ireland), but will also extend the scope of
Hayek’s thought, notably in her 1994 book Arguments for a New Left.
Further, electromagnetic brain responses to acoustically widely deviant and contextually novel sounds have been well studied in adults (Escera et al., 2000; Friedman et al.,
In this case, the perceived high cost and poor value of ‘healthy’ food (particularly for students from poorer communities) provided in rushed, over-crowded canteen environments,
99 This does not imply that reactions to political and economic news in such markets are necessarily appropriate (i.e. without volatility), simply that such
The familiarity of the actors to the British public surely contributed to Queer as Folk's popularity and wide success; and it was one of the programme’s
This research explores the beliefs and experiences of mental health clinicians working with people who are subject to a Community Treatment Order (CTO).. Previous research