Efficient Energy for Low Power VLSI Design
Full text
Figure
![Fig. 1 [2]. The average dynamic power dissipation for this network is given as: Vi the node voltage, VDD the full voltage swing, Ci is the parasitic capacitance linked with each node in the circuit ( including the output node),represents the corresponding node transition factor](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/1414336.1654372/2.595.98.488.80.281/dissipation-voltage-parasitic-capacitance-including-represents-corresponding-transition.webp)
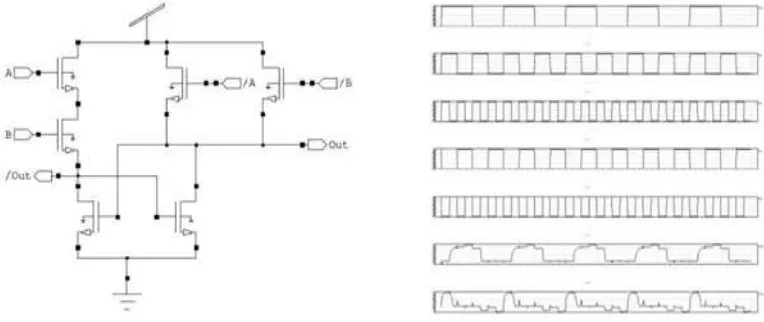
![Figure 3(a). Conventional CMOS logic gate [2] adiabatic logic gate Figure 3(b). The topology of an implementing the same function](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/1414336.1654372/3.595.113.480.465.606/figure-conventional-cmos-adiabatic-figure-topology-implementing-function.webp)

Related documents
In this project we compare a different types of logic designs like Adiabatic logic and Gate diffusion Inputs logic and finally Pass Transistor Logic to the CMOS
Design of Adiabatic Vedic multiplier using EEAL (Energy Efficient Adiabatic Logic) is proposed in literature [1].In this paper, we described low power area-efficient
So here we compare PFAL (Positive Feedback Adiabatic Logic) and ECRl (Efficient Charge – Recovery Logic) technique basic logic gates with CMOS gates.. Results gives improvement
In this paper the implementation of various CMOS logic styles such as STATIC CMOS logic, DUAL RAIL logic and PSEUDO NMOS logic in various CMOS logic gates such as AND, NAND,
Demand of low power circuits design is increasing due to the large growth in portable digital equipment. In this reference adiabatic structure are used that provides a
In this paper by considering power consumption as the major aspect, designed an 8-bit CEPAL carry select adder, this CEPAL Energy recovery circuits based on the
This can be done if the quantum cost and garbage output value of the digital circuits should be reduced which can only be possible by using reversible logic
•• Dy Dyna nam mic ic po powe wer r di diss ssip ipat atio ions ns:: whenever the logic whenever the logic level changes at different points in the circuit because of the change