Ultrasonic assessment of exercise-induced change in skeletal muscle glycogen content
Full text
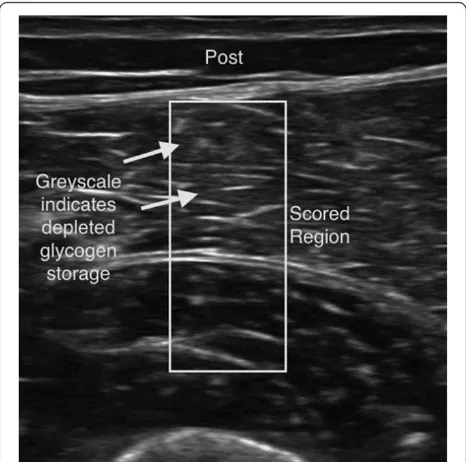
Figure


Related documents
Scandinavian welfare states and the Netherlands, with more state-intervention in the health care sector, fare considerable worse than Switzerland and show much higher levels of
(Indeed Evaluate is a public algorithm with no secrets.) It is clear that as defined above, fully homomorphic encryption can be trivially realized from any secure encryption scheme,
We have introduced the concept of total edge product cordial labeling and derive several results on it. To investigate analogous results for various graphs as well as in the context
Overall, the excess heat experiments by the Condensed Matter Nuclear Reaction Division of Tohoku University are going well, but the transmutation experiments there have yet to
Conclusion: Our data suggest that besides the high variety of different detected species, initial antibiotic treatment with a combination of systemic cefuroxime and
The findings on reasons for outsourcing addressed the research question on why organisations outsource by linking with the introduction of this paper where The
ACD: asymmetric cell division; APC/C: anaphase promoting complex/cyclo- some; aPKC: atypical Protein Kinase C; AIK: Aurora/IPL1-related kinase; ARK: Aurora-related kinase; AURK: