Link prediction using a probabilistic description logic
Full text
Figure

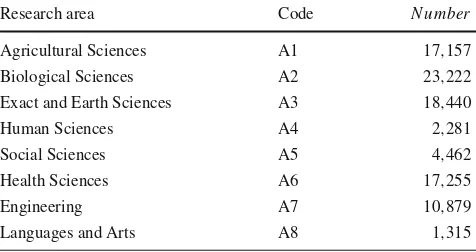


Related documents
Classifiers are able to capture important interdependence relation- ships between nodes since feature vectors are formed based on unsupervised link prediction measures that capture di
We propose to make use of active learning in this setting, and introduce ALPINE, a specific active learning approach for link prediction in such partially observed networks
A Bayesian network model is subsequently applied to deliver posterior probability distributions of key parameters as part of a discounted cash fl ow analysis.. The results illustrate
The proposed ECCPM uses an Erlang coefficient computed based on conditional probability which analyses the reputation of mobile nodes and resilience of the entire network with aid
Our own link prediction approach differs from common techniques in that we consider multiple network snapshots with temporal trends captured in the time factor matrix C, given by
The theoretical Bayesian coverage probability bias for prediction intervals is computed and compared with the plug-in method using the restricted maximum likelihood estimates of
13 Increasing link-prediction error in a messenger-app network (OAStg for 1281 nodes). Budgets are sufficient for traditional greedy to give a complete cascade in G. Since
In figure 8 the results obtained in the case of MAP value for conditional probability are more efficient than the corresponding crisp values in the case of Norm (P)



