Microcirculatory alterations in ischemia–reperfusion injury and sepsis: effects of activated protein C and thrombin inhibition
Full text
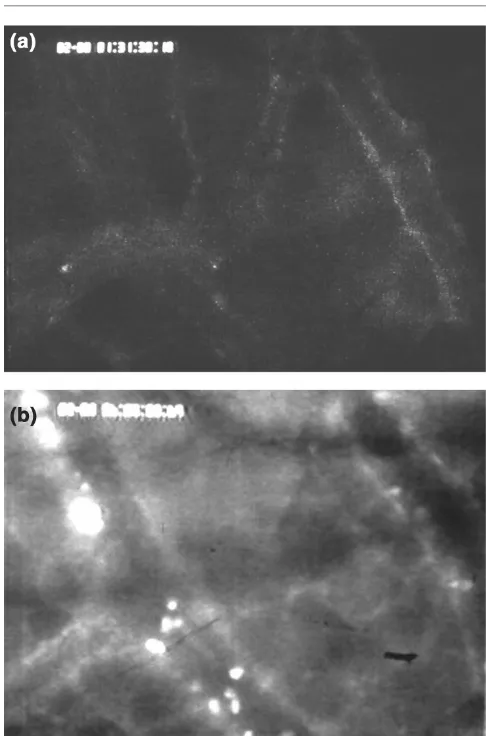
Figure

Related documents
Bounameaux H, Miron MJ, Blanchard J, de Moerloose P, Hoffmeyer P, Leyvraz PF: Measurement of plasma D-dimer is not useful in the prediction or diagnosis of postoperative deep
In order to assess whether collective treatment improves the social support for post-stroke patients, the original treatment protocol was modified (individual therapy for six
The advantage of adding a decoupled read port is that it eliminates the tradeoff between the read stability and the write ability in the SRAM array to which
Specifically, it was tested whether the pathway responsible for biosynthesis of the low-salt tetrasac- charide could decorate Asn-498 in cells grown in medium con- taining 3.4 M
An educational experiment was designed which included: (a) a pretest to assess the study population's knowledge and attitudes regarding smoking, (b) a lecture
Regulations for water quality in Australia are based on anticipating potential public health and environmental risks and preventing them from arising through the risk management
Taking a commonly-used and commonly-available trade policy model as our starting point, we examine the long-run effects of large-scale structural change with and without international
Keywords: Garcina kola shell; Activated Carbons (ACs); chemical activation; iodine number; burn-off;