A Bi Polar Triple Output Converter with Duty Cycle Estimation
Full text
Figure


Related documents
• Materials management fully integrated with 3D modeling • Structural dynamic analysis of modules and foundation • Design for transportation, including fatigue analysis The result is
The aim of this study was to assess the accuracy of first trimester fms-like tyro- sine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) and placental growth factor (PlGF), both alone and in combination, in
Due to the highly competitive relationship between the market rates and evaluation levels for the Teacher classification, we recommend CCSD utilize the above ranges for the
under limiting nitrogen conditions despite strongly reduced Mep2p expression levels suggested that nitrogen starvation- induced filamentous growth may not depend on the Mep2p
A mobile user wants to access the range queries like “nearest hospital”, “nearest ATM” etc., from the location based server. With untrustworthy servers, the location based
The aim of interworking is to provide a heterogeneous mobile data network such that WLAN users can seamless use 3G wireless networks.. Interworking Techniques
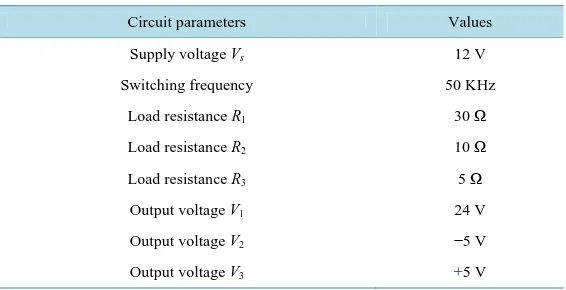
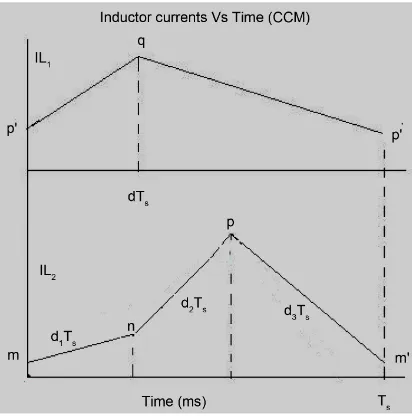
Initially the converter works in Buck-Boost converter mode to charge the battery in constant current mode by keeping the duty cycle of PWM2 constant and varying the duty cycle of
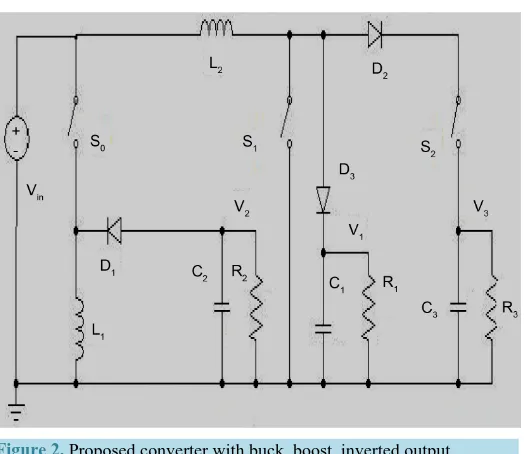
The traditional DC-DC converters such as the buck, boost, buck–boost, Cuk, single-ended primary inductor converter (SEPIC), Zeta converter, K-Y converter and Luo