metal-organic papers
m1004
Zanget al. (C13H10BrN2)[Ni(C3S5)2]C3H6O doi:10.1107/S1600536806012207 Acta Cryst.(2006). E62, m1004–m1005
Acta Crystallographica Section E
Structure Reports
Online
ISSN 1600-5368
N
-(4-Bromobenzyl)-4-cyanopyridinium
bis(2-thioxo-1,3-dithiole-4,5-dithiolato)-nickelate(III) acetone solvate
Shuang-Quan Zang,aYang Sub and Ruo-Jie Taoa*
a
Institute of Molecular and Crystal Engineering, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, People’s Republic of China, andbCoordination Chemistry Institute, State Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence e-mail: rjtao@henu.edu.cn
Key indicators
Single-crystal X-ray study
T= 293 K
Mean(C–C) = 0.009 A˚
Rfactor = 0.055
wRfactor = 0.105
Data-to-parameter ratio = 15.8
For details of how these key indicators were automatically derived from the article, see http://journals.iucr.org/e.
Received 1 April 2006 Accepted 3 April 2006
#2006 International Union of Crystallography All rights reserved
The title compound, (C13H10BrN2)[Ni(C3S5)2]C3H6O, is a new
ionic complex in which the NiIIIatom exhibits a square-planar coordination involving four S atoms from two 2-thioxo-1,3-dithiole-4,5-dithiolate (dmit) ligands. In the crystal structure, weak S S and hydrogen-bonding interactions form a three-dimensional supramolecular network.
Comment
The syntheses and characterization of bis-dithiolate metal complexes and their analogs have been actively studied for a long time because of their properties and potential applica-tions such as in conducting or magnetic materials and non-linear optics (NLO) (Cassoux, 1999). 2-Thioxo-1,3-dithiole-4,5-dithiolate (dmit) metal complexes are well known as molecular conductors (Akutagawa & Nakamura, 2000).
In order to study the interplay of magnetic properties, the title compound, (I), was synthesized. Its structure is found to comprise three separate components (Fig. 1), namely the [NiIII(dmit)2]
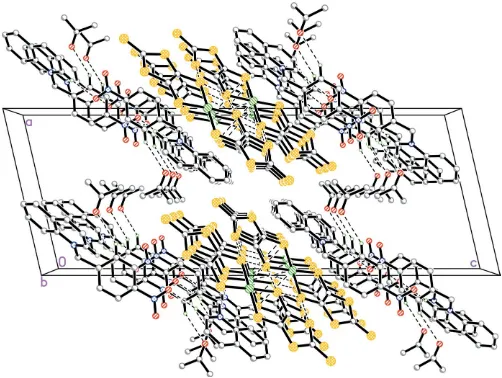
anion, the N -(4-bromobenzyl)-4-cyano-pyridinium cation and an actone solvent molecule. The NiIII ion adopts square-planar coordination involving four S atoms of two dmit ligands. All three components of the structure stack in columns down the a axis (Fig. 2). The columns are stabilized by hydrogen bonding (Table 2) and weak S N and S S interactions [S8 N2 = 3.192 (5) A˚ and S7 S7i = 3.582 (3) A˚ ; symmetry code: (i)x+ 2,-y+ 2,-z+ 1], resulting in a three-dimensional supramolecular network structure.
Experimental
4,5-Bis(thiobenzoyl)-1,3-dithiole-2-thione (812 mg, 2.0 mmol; Wang
bromide (2 mmol, 0.380 g) in methanol at an interval of approxi-mately 20 min. The solution was stirred for a further 30 min and the resulting solid collected by filtration. Single crystals of (I) were obtained by evaporation of a dilute acetone solution over 1–2 weeks at room temperature.
Crystal data
(C13H10BrN2)[Ni(C3S5)2]C3H6O
Mr= 783.66
Triclinic,P1
a= 9.197 (2) A˚
b= 10.601 (3) A˚
c= 15.714 (4) A˚
= 98.265 (5) = 92.767 (4) = 95.821 (5)
V= 1505.3 (7) A˚3
Z= 2
Dx= 1.729 Mg m 3
MoKradiation
= 2.69 mm1
T= 293 (2) K Needle, black 0.30.10.1 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
’and!scans
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000)
Tmin= 0.739,Tmax= 0.760
7546 measured reflections 5213 independent reflections 2680 reflections withI> 2(I)
Rint= 0.063
max= 25.0
Refinement
Refinement onF2
R[F2> 2(F2)] = 0.055
wR(F2) = 0.105
S= 0.99 5213 reflections 330 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
w= 1/[2(F
o2) + (0.02P)2
+ 0.04P]
whereP= (Fo2+ 2Fc2)/3
(/)max= 0.001
max= 0.55 e A˚
3
min=0.49 e A˚
3
Table 1
Selected geometric parameters (A˚ ,).
Ni1—S7 2.1545 (16) Ni1—S5 2.1547 (16)
Ni1—S4 2.1605 (16) Ni1—S6 2.1649 (16)
S7—Ni1—S5 86.20 (6) S7—Ni1—S4 178.59 (6) S5—Ni1—S4 93.18 (6)
S7—Ni1—S6 92.71 (6) S5—Ni1—S6 177.58 (7) S4—Ni1—S6 87.96 (6)
Table 2
Hydrogen-bond geometry (A˚ ,).
D—H A D—H H A D A D—H A
C15—H15 N2i
0.93 2.50 3.290 (8) 143 C14—H14 O1ii 0.93 2.55 3.135 (8) 121 C13—H13B O1ii
0.97 2.46 3.230 (9) 136
Symmetry codes: (i)x;yþ1;zþ1; (ii)x1;y;z.
All H atoms were refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.93 A˚ andUiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic H atoms, C—H = 0.97 A˚ and
Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for CH2 H atoms, and C—H = 0.96 A˚ and
Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms.
Data collection:SMART(Bruker, 2000); cell refinement:SAINT
(Bruker, 2000); data reduction:SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Bruker, 2000); program(s) used to refine structure:SHELXTL; molecular graphics:SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication:SHELXTLandPLATON(Spek, 2003).
The authors thank the Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province for financial support.
References
Akutagawa, T. & Nakamura, T. (2000).Coord. Chem. Rev.198, 297–311. Bruker (2000).SADABS,SMART(Version 5.625),SAINT(Version 6.02) and
SHELXTL(Version 6.10). Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA. Cassoux, P. (1999).Coord. Chem. Rev.185/186, 213–232.
Spek, A. L. (2003).J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
[image:2.610.312.564.75.156.2] [image:2.610.314.565.217.406.2]Wang, C. S., Batsanov, A. S., Bryce, M. R. & Howard, J. A. K. (1998).Synthesis, pp. 1615–1618.
Figure 1
The asymmetric unit of (I), showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level and H atoms are represented by circles of arbitrary size.
Figure 2
supporting information
sup-1 Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, m1004–m1005
supporting information
Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, m1004–m1005 [https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536806012207]
N
-(4-Bromobenzyl)-4-cyanopyridinium
bis(2-thioxo-1,3-dithiole-4,5-dithiol-ato)nickelate(III) acetone solvate
Shuang-Quan Zang, Yang Su and Ruo-Jie Tao
N-(4-Bromobenzyl)-4-cyanopyridinium bis(2-thioxo-1,3-dithiole-4,5-dithiolato)nickelate(III) acetone solvate
Crystal data
(C13H10BrN2)[Ni(C3S5)2]·C3H6O
Mr = 783.66
Triclinic, P1 Hall symbol: -P 1
a = 9.197 (2) Å
b = 10.601 (3) Å
c = 15.714 (4) Å
α = 98.265 (5)°
β = 92.767 (4)°
γ = 95.821 (5)°
V = 1505.3 (7) Å3
Z = 2
F(000) = 786.0
Dx = 1.729 Mg m−3
Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å Cell parameters from 804 reflections
θ = 2.5–22.4°
µ = 2.69 mm−1
T = 293 K Needle, black 0.3 × 0.1 × 0.1 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube Graphite monochromator
φ and ω scans
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2000)
Tmin = 0.739, Tmax = 0.760
7546 measured reflections 5213 independent reflections 2680 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Rint = 0.063
θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.0°
h = −10→10
k = −7→12
l = −18→18
Refinement
Refinement on F2
Least-squares matrix: full
R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.055
wR(F2) = 0.105
S = 0.99 5213 reflections 330 parameters 14 restraints
Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods
Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map
Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites
H-atom parameters constrained
w = 1/[σ2(F
o2) + (0.02P)2 + 0.04P]
where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3
(Δ/σ)max = 0.001
Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3
Special details
Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes.
Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2,
conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used
only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2
are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. Two
DFIX restraints on two bonds (C16–C19 and C21–C22). Twelve DELU restraints on the pyridine ring (N1 C14 > C18).
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
x y z Uiso*/Ueq
supporting information
sup-3 Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, m1004–m1005
H20C 0.5580 0.5018 0.8785 0.300* C21 0.6025 (10) 0.3226 (9) 0.8689 (5) 0.123 (3) C22 0.4850 (11) 0.2644 (11) 0.9124 (7) 0.302 (9) H22A 0.3941 0.2626 0.8792 0.453* H22B 0.4797 0.3133 0.9683 0.453* H22C 0.5027 0.1784 0.9186 0.453* N1 −0.0145 (5) 0.1818 (4) 0.7244 (3) 0.0591 (12) S1 0.8584 (2) 1.48341 (17) 0.12731 (12) 0.1117 (7) S2 0.6668 (2) 1.26554 (16) 0.17419 (10) 0.0865 (5) S3 0.93637 (19) 1.35129 (14) 0.27390 (10) 0.0794 (5) S4 0.58654 (17) 1.05888 (15) 0.28470 (9) 0.0774 (5) S5 0.88065 (16) 1.15543 (13) 0.39461 (9) 0.0686 (4) S6 0.52012 (16) 0.86344 (14) 0.40212 (9) 0.0690 (4) S7 0.80795 (16) 0.97166 (14) 0.51400 (9) 0.0680 (4) S8 0.47060 (17) 0.66924 (15) 0.52389 (9) 0.0760 (5) S9 0.73328 (17) 0.77180 (15) 0.62845 (9) 0.0714 (5) S10 0.5507 (2) 0.55030 (18) 0.67645 (10) 0.1042 (7) Br1 0.27186 (10) 0.17125 (9) 1.13312 (5) 0.1400 (4) N2 0.1693 (5) 0.4865 (5) 0.5061 (3) 0.0831 (15)
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
U11 U22 U33 U12 U13 U23
S1 0.160 (2) 0.0857 (14) 0.1027 (13) 0.0311 (13) 0.0248 (14) 0.0397 (11) S2 0.1004 (14) 0.0845 (12) 0.0808 (11) 0.0303 (11) −0.0023 (10) 0.0217 (9) S3 0.0958 (13) 0.0594 (10) 0.0850 (11) 0.0099 (9) 0.0074 (10) 0.0156 (9) S4 0.0698 (11) 0.0772 (11) 0.0848 (11) 0.0089 (9) −0.0098 (9) 0.0150 (9) S5 0.0662 (10) 0.0615 (10) 0.0782 (10) 0.0047 (8) −0.0075 (8) 0.0162 (8) S6 0.0540 (10) 0.0744 (11) 0.0763 (10) 0.0048 (8) −0.0068 (8) 0.0088 (8) S7 0.0607 (10) 0.0616 (10) 0.0784 (10) −0.0011 (8) −0.0099 (8) 0.0098 (8) S8 0.0700 (11) 0.0807 (12) 0.0712 (10) −0.0129 (9) 0.0093 (9) 0.0045 (9) S9 0.0760 (11) 0.0745 (11) 0.0607 (9) −0.0018 (9) 0.0017 (8) 0.0076 (8) S10 0.1355 (17) 0.1062 (15) 0.0676 (11) −0.0177 (13) 0.0177 (11) 0.0199 (10) Br1 0.1362 (8) 0.1885 (9) 0.0855 (5) −0.0509 (7) −0.0260 (5) 0.0461 (5) N2 0.075 (4) 0.083 (4) 0.103 (4) 0.011 (3) 0.026 (3) 0.043 (3)
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
Ni1—S7 2.1545 (16) C10—H10 0.9300 Ni1—S5 2.1547 (16) C11—C12 1.363 (6) Ni1—S4 2.1605 (16) C11—H11 0.9300 Ni1—S6 2.1649 (16) C12—C13 1.487 (6) C1—S1 1.638 (6) C13—N1 1.477 (6) C1—S3 1.709 (6) C13—H13A 0.9700 C1—S2 1.730 (6) C13—H13B 0.9700 C2—C3 1.347 (7) C14—N1 1.323 (6) C2—S4 1.719 (6) C14—C15 1.371 (7) C2—S2 1.751 (5) C14—H14 0.9300 C3—S5 1.722 (6) C15—C16 1.384 (7) C3—S3 1.722 (6) C15—H15 0.9300 C4—C5 1.353 (6) C16—C17 1.365 (7) C4—S6 1.711 (5) C16—C19 1.367 (7) C4—S8 1.730 (5) C17—C18 1.384 (7) C5—S7 1.702 (5) C17—H17 0.9300 C5—S9 1.742 (5) C18—N1 1.308 (6) C6—S10 1.640 (6) C18—H18 0.9300 C6—S8 1.719 (5) C19—N2 1.146 (6) C6—S9 1.724 (5) O1—C21 1.165 (8) C7—C12 1.352 (7) C20—C21 1.430 (10) C7—C8 1.374 (7) C20—H20A 0.9600 C7—H7 0.9300 C20—H20B 0.9600 C8—C9 1.358 (8) C20—H20C 0.9600 C8—H8 0.9300 C21—C22 1.440 (14) C9—C10 1.325 (8) C22—H22A 0.9600 C9—Br1 1.876 (7) C22—H22B 0.9600 C10—C11 1.389 (7) C22—H22C 0.9600
supporting information
sup-5 Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, m1004–m1005
S5—Ni1—S6 177.58 (7) N1—C14—H14 119.1 S4—Ni1—S6 87.96 (6) C15—C14—H14 119.1 S1—C1—S3 124.3 (4) C16—C15—C14 119.6 (6) S1—C1—S2 123.1 (4) C16—C15—H15 120.2 S3—C1—S2 112.6 (3) C14—C15—H15 120.2 C3—C2—S4 122.4 (5) C17—C16—C15 116.8 (5) C3—C2—S2 115.2 (5) C17—C16—C19 121.9 (6) S4—C2—S2 122.4 (4) C15—C16—C19 121.3 (6) C2—C3—S5 120.2 (5) C16—C17—C18 121.1 (6) C2—C3—S3 116.5 (5) C16—C17—H17 119.5 S5—C3—S3 123.2 (4) C18—C17—H17 119.5 C5—C4—S6 120.7 (4) N1—C18—C17 120.4 (6) C5—C4—S8 116.5 (4) N1—C18—H18 119.8 S6—C4—S8 122.9 (3) C17—C18—H18 119.8 C4—C5—S7 121.9 (4) N2—C19—C16 178.5 (7) C4—C5—S9 115.7 (4) C21—C20—H20A 109.5 S7—C5—S9 122.4 (3) C21—C20—H20B 109.5 S10—C6—S8 123.6 (3) H20A—C20—H20B 109.5 S10—C6—S9 122.9 (3) C21—C20—H20C 109.5 S8—C6—S9 113.5 (3) H20A—C20—H20C 109.5 C12—C7—C8 122.5 (6) H20B—C20—H20C 109.5 C12—C7—H7 118.7 O1—C21—C22 120.5 (10) C8—C7—H7 118.7 O1—C21—C20 122.8 (9) C9—C8—C7 118.6 (7) C22—C21—C20 116.2 (9) C9—C8—H8 120.7 C21—C22—H22A 109.5 C7—C8—H8 120.7 C21—C22—H22B 109.5 C10—C9—C8 120.6 (7) H22A—C22—H22B 109.5 C10—C9—Br1 119.8 (7) C21—C22—H22C 109.5 C8—C9—Br1 119.6 (6) H22A—C22—H22C 109.5 C9—C10—C11 120.2 (6) H22B—C22—H22C 109.5 C9—C10—H10 119.9 C18—N1—C14 120.3 (5) C11—C10—H10 119.9 C18—N1—C13 118.9 (5) C12—C11—C10 120.7 (6) C14—N1—C13 120.7 (5) C12—C11—H11 119.6 C1—S2—C2 97.4 (3) C10—C11—H11 119.6 C1—S3—C3 98.3 (3) C7—C12—C11 117.3 (6) C2—S4—Ni1 101.6 (2) C7—C12—C13 121.1 (6) C3—S5—Ni1 102.5 (2) C11—C12—C13 121.7 (6) C4—S6—Ni1 102.33 (18) N1—C13—C12 113.1 (4) C5—S7—Ni1 102.37 (18) N1—C13—H13A 109.0 C6—S8—C4 97.3 (3) C12—C13—H13A 109.0 C6—S9—C5 97.1 (3)
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
D—H···A D—H H···A D···A D—H···A
C14—H14···O1ii 0.93 2.55 3.135 (8) 121
C13—H13B···O1ii 0.97 2.46 3.230 (9) 136