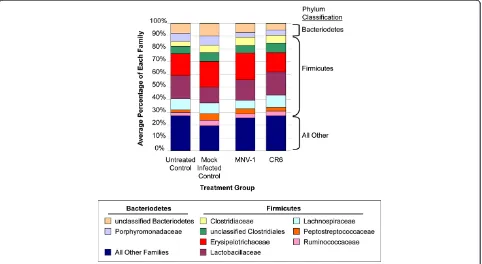
Murine norovirus infection does not cause major disruptions in the murine intestinal microbiota
Full text
Figure


Related documents
“Representin’ in cyberspace: Sexual scripts, self-definition, and hip hop culture in Black American adolescent girls’ home pages.” Culture, Health & Sexuality 9, no.
Most estab- lished risk factors for breast cancer in humans are thought to influence risk through hormone-related pathways [1], increased concentrations of endogenous oestrogens
The combined re- sults from gene discovery, protein expression and distribution profiling (especially the “surprising” presence under the nematode cuticle), and recombinant
(b) By analyzing the result , we can conclude that besides different parameters like feed , depth of cut, cutting speed , the flank wear contributes a lot in order to control the
USEAC trade specialists provide global business solutions by (1) identifying the best markets for their clients’ products; (2) developing effective market-entry strategies based
We have been careful to assert that land value maximization leads, under the stipulated conditions, to an efficient level of supply of public goods; the equilibrium may still not
Therefore, rather than considering the processes taking place in the Earth’s core as the result of a superposition of oscillations (i.e. stationary mechanisms) occurring on a dis-
The SEMQ mutation allowed the production of infectious reporter virus in cells cotransfected with rhA3G, and in replication- competent HIV-1, it allowed productive replication in