Degree Project Course
MSc
of
Engineering,
Master
Degree
Anne Håkansson
annehak@kth.se
Director of studies for degree project
Degree project goals
•
11 goals for civil engineering programs
•
10 goals for master programs
The Higher Education Ordinance
http://www.uhr.se/sv/Information-in-English/Laws-and-regulations/The-Higher-Education-Ordinance/
Degree project goals (selected)
• be able to apply relevant knowledge and skills within a technical
area to a given problem.
• within given constraints, even with limited information, be able to
independently analyze and discuss complex problems and
handle large problems on an advanced level in a technical area.
• reflect on, evaluate, and critically review their own and others’
scientific results.
• be able to document and present their own work, for a given
audience, following strict requirements on structure, format, and
language.
• be able to identify the need for further knowledge and
continuously develop their own knowledge.
Degree project grading
Process
planning and conducting work according to an agreed time-li
ne; taking initiative; identifying and acquiring additional required
knowledge;
openness for guidance and criticism; analyzing other’s work and
phrasing questions and criticism (this aspect is know as “opposition”:
each student must oppose a degree project of some other student).
Engineering and scientific content
applying engineering-related and
scientific skills; modeling, analyzing, developing, and evaluating;
correct
choice of methods based on problem formulation; consciousness of
aspects relating to society and ethics (if applicable).
Presentation
written report where project and results shall be
presented and analyzed; language, formal aspects, meticulousness;
oral presentation
Prerequisites
To
begin
the
degree
project:
MsC of
Engineering
(Civilingenjör)
at
least
‐
210
hp of
studies
for
a
270
hp program
‐
240
hp of
studies
for
a
300
hp program.
Master:
at
least 60hp
of
studies,120
hp program.
These
requirements
are
checked
by
the
administration
before
the
student
is
registered
for
the
degree
project
course
and
Thesis course
•
Starts two times per year:
1 period (Aug/ Sept)
3 period (Jan)
Starts 3-4 months earlier with finding projects
• Write a project description (project proposal)
Before course starts (Jan)
Fall
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Finds and
Decides degree
project
Write a project
proposal and hand
in via Bilda
Deadline 15th of
December
Examiner is
assigned / accepts
Fills in registration form,
get it signed, and hand
in
Register course = Start
Student
Supervisor
Examiner
Administrator
Controls credits and
registers the student
Spring
Figure 1: Start-up phase for degree project, Fall - Spring.
Supervisor is
assigned / accepts
Examiner signs
registration form
Degree project
Find and decide degree project
- degree project fair
- companies
- web pages:
•
http://www.kth.se/samverkan/exjobb/kth-exjobbportal-1.292786
•
http://www.kth.se/student/program/examensarbete
/forslag-pa-exjobb-2013-1.412711?programme=tkomk
•
http://www.ict.kth.se/xjobb/
Information about degree project
Find more information about degree project:
https://www.kth.se/en/student/program/examensarbe
te/ict-examensarbete-2014-1.346485?programme=tkomk
http://intra.ict.kth.se/utbildning/grundutbildning-vid-ict/examensarbete-1.16410
In Bilda:
Examensarbete / Degree projects, skolan/
ICT-School 2015
Before course starts, coming spring
Course starts in period 3 (Jan):
Find Degree project – Negotiate with examiner/supervisor
Number of students per thesis:
1 student per thesis
Write Project proposal – hand in not later than 15
th
of
December
(for autumn, not later than 1
st
of June)
All students that will take the course during spring - MUST
Project proposal = Application (not registration)
Project Title
The length of this project plan shall not be longer than 2-3 pages, which is about 400
words – 600 words
Authors
Organization and Supervisor
How the project is to be organized, Name and contact information to the supervisor –
if exists
Keywords
1-6 keywords describing the degree project
Background
Short description of the area
Problem statement
Problem area, focusing on the area to work with
Problem
Project proposal , cont. (Template in Bilda)
Purpose
Purpose of the degree project, Effect goals
Goals
Goals, objectives and/or results of the degree project, Result goals
Tasks
Tasks and sub-tasks that are necessary to carry out the work
Methods
Research methods that will be used to carry out the degree project and to write
the thesis
Milestone chart (time schedule)
Project timeline
Risks, Consequences and Ethics
Potential risks with the degree project and work
Summary
Short summary of the degree project and work
Without degree project but will take the
course during spring
If Project_Title is not decided, please write “To be decided”.
If no keywords are selected, write areas of interests.
The file can, then, look like:
“author1–To_be_decided–distributed_systems,embedded_systems–
141130.pdf”
Date is the date when handing in the project plan and has the format:
Year-Month-Day
Author
Supervisor / Examiner
•
Supervisor and Examiner at KTH
•
Supervisor (Company)
•
Find examiner and supervisor
Help from Director of Studies – from beginning
Contact possible Examiner and/or Supervisor
Contact PA (program directors)
Bilda – support if both supervisor and examiner are missing
*
Examiner
handles the registration form
Program Directors
http://www.kth.se/en/ict/kontakt/programansvariga-1.33074
Master of Science in engineering
Information Technology -
Robert Rönngren
Master's programs
Nanoelectronics/Nanotechnology -
Mattias Hammar
Software Engineering of distributed Systems -
Mihhail Matskin
System on chip Design -
Johnny Öberg
Communication Systems -
Markus Hidell
Embedded Systems -
Johnny Öberg
EIT ICT Labs -
Konrad Tollmar
Erasmus Mundus programs
European Master in Distributed Computing-
Johan Montelius
Program directors
Older programs with no admission
Mechatronics and industrial IT
-Electronics and communication -
Bengt Molin
IT Business Systems/Information Systems
-Microelectronics -
Mattias Hammar
Business engineering -
Anders Sjögren
Applied IT -
Anders Västberg
Design and Implementation of ICT Products and Systems -
Mark T. Smith
Engineering and management of Information systems -
Paul Johannesson
Information and communication Systems Security
-Photonics -
Urban Westergren
ICT Entrepreneurship -
Markus Hidell
Internetworking -
Markus Hidell
Work Phase, 20 weeks
Supervision, 20 weeks
Checkpoints / Mandatory seminars
Several checkpoints and compulsory seminars for master
thesis:
Summary, Abstract, and Outline
Introduction
Research Methodology
Main thesis
Conclusions
Presentation seminar
Opposition seminar
Supervisor
-
Examiner
w 1 - Summary, Abstract, Outline
/Table of Contents
w 5 - Introduction
w 8 - Research Methodology
w 13 - Main thesis
w 16 – Conclusions
w 20 Presentation seminar/
Opposition seminar
w 8 - Proposal seminar
w 18 – Preliminary thesis
w 20 - Presentation
seminar/Opposition seminar
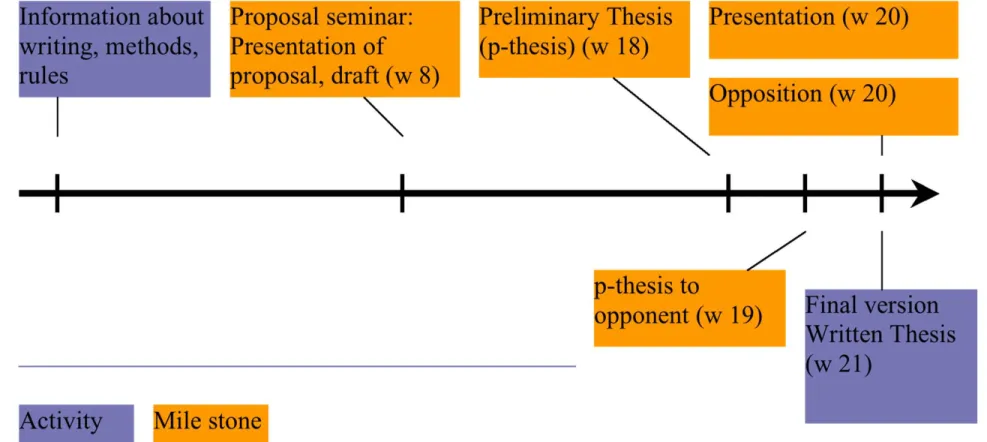
Student activities /seminars
w 0 – Registration form (fill-in, signatures, hand in)
w 1 – Summary, Abstract, Outline /Table of Contents
w 5 – Introduction
w 8 – Research Methodology
w 8 – Proposal seminar
w 13 – Main thesis
w 16 – Conclusions
w 18 – Preliminary thesis
w 19 – Thesis to opponent
w 20 – Presentation seminar/ Opposition seminar
Alterations in process
The guidelines should be followed closely
and the
dates for the milestones should be attained.
If there is a need to deviate from the original plan,
then the student must request approval from the
examiner (and supervisor, if applicable) well before
modifying the original plan.
Any unplanned and non-negotiated deviation
reduces the process’ grade.
Lectures
Coming lectures, Period 1:
Structure and Contents
Introduction
Research Methodology /Methodologies
Conclusions
Questions
Study Abroad
http://prezi.com/k8ne2er6xv-0/exjobb-utomlands-35-2013/
exchange@ict.kth.se