Detailed Study On Data Dissemination with
Cluster-based Data Dissemination in VANET
Prashant Kumar Shrivastava, Priya Srivastava, Dr. Rachana Dubey
Abstract: Due to their gigantic potential to improve traffic security, productivity, and other included administrations, the Vehicle Ad-hoc Network (VANET) has developed as of late as the most appealing theme for specialists and car enterprises. The most testing piece of research is directing in VANET. Vehicle systems are another class of remote systems that have developed through advances in remote and car innovation. These systems are additionally known by name of VANETs, which are measured as one of genuine uses of specially appointed system, for correspondence among neighboring vehicles likewise amongst vehicles &immobile gear. Neutral of VANET systems is to put on certain notices, for example, ready message scattering, announcing a mishap between autos to diminish the probability of crash, sight and sound ongoing applications, and numerous different applications. This paper describes the dissemination of data based on the mechanism of clustering. Various studies have given that research has been done in this sector with regard to information dissemination.
Keywords: Vehicle Ad hoc NETworks, Data Dissemination, Data Dissemination Techniques, Cluster-based Data Dissemination
————————————————————
1. I
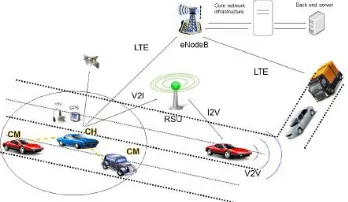
NTRODUCTIONVANETs are vehicle correspondence n/ws [3] that are shaped immediately & consequently between nearby autos without the utilization of any foundation, for example, switches, servers, & so on. Vehicles can in this manner associated with other adjacent autos, for example vehicle to-vehicle correspondence (C2C), or even some present offices (C2I, for example, roadside offices. VANETs ' essential intrigue is to create applications that guarantee to make our driving more secure, progressively powerful & increasingly agreeable. This incorporates cautioning applications alarming different vehicles, climate or traffic conditions, sight & sound documents trading between vehicles (for example music, motion pictures) & additionally some roadside units (for example Television, radio or news), & so forth. Broadcasting conventions assume a significant job in interchanges for the dispersal of data the same number of abnormal state applications & even different conventions accept that a communicate administration exists. Planning
Fig. 1. Data Dissemination in Vehicular Ad Hoc Network
Crisp successful VANET communicate calculations, be that as it may, stays open problem. In reality, significance of great conduct of broadcasting calculations leads numerous scientists to concentrate on advancing conduct of these scattering conventions, e.g., an augmenting quantity of hubs originated to & limiting both times required & system over-burden [4]. An intriguing way to deal with cluster-based vehicular interchanges can be found in [5], where correspondences are regularly communicated at the same time when conceivable, fleeting groups are made so as to establish a spine that can be utilized to help unicast interchanges. Perhaps the most grounded inspiration for the structure of group-based vehicular systems is given, where the creators demonstrate that, as indicated by reasonable portability models, VANETs normally advance to clustered setups. The upsides of clustering have likewise been abused in the domain of decentralized recognition, e.g., to decide ideal grouping & medium access control arrangements. Specifically, the creators give a general system to the calculation of the likelihood of choice mistake when a spatially consistent parallel marvel is recognized through a (perhaps) staggered sensor organize.
1.
D
ATAD
ISSEMINATION INV
EHICULARA
DH
OCN
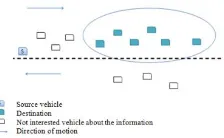
ETWORKSDisseminationof circulation data is a rule of few studymechanism, in result of way that data is constantly shared concerns traffic circumstance (for instance condition of street, state of vehicle.) so as toward encouraging development of drivers & travelers on streets, to empower them to make fitting choices to variations happening in street. Specifically data applicable to dangers & risky cases happen on streets, this data provisions prompt discharge & fast [6] to guarantee traffic wellbeing. This sort of data is generally sent to a gathering of vehicles where the open enthusiasm here is subsequently most fitting technique is communicated. In spite of the fact that there are unique situations where intrigue is disturbed particular gathering (eg: Geocast) (see Figure 2 & 3).
________________________-
Prashant Kumar Shrivastava, Asst Prof CSE Dept, LNCTE, Bhopal (M.P), prashant.shri1@gmail.com
Priya Srivastava, M_Tech Scholar, LNCTE, Bhopal (M.P), srivastava.priya1000@gmail.com
Fig. 2. Datalectured to a precisecluster of vehicles
Fig. 3. Datatransfer to all vehicles
The principle objective is to effectively communicatea message as ofbasis to different hubs arranged in equivalent geological zone. Activelandscape& directional versatility of automobiles, conveying communicationstowardunique or entirely vehicles, speaks to noteworthy test. In addition, in light of nonattendance of the framework &developed portability of vehicles, depending messages amongst vehicles needdistribution plans. Center issue in multi-bounce broadcasting is manner by which to limit the quantity of repetitively got messages while keeping up great idleness & reachability, since rebroadcasting causes tradeoff among reachability & effectiveness below various host thicknesses[7].
A. Solutions for Data Dissemination in VANETs
Currently proposed answers for information dispersal in VANETs pursue two primary ideal models: communicate or multicast. Broadcast Communication-In communicating correspondence worldview, basis vehicle hub transfer data to the majority of its neighbor hubs. These hubs will at that point quickly forward the data to their neighbors utilizing another communicate to convey the data to the objective hubs. Communicate is progressively reasonable for vehicle wellbeing data administrations since they are postponing delicate & need to spread cautioning data in a constrained brief timeframe. To defeat this issue, a few arrangements dependent on transferring & astute sending have been proposed DV-CAST [8], AID [9] &DRIFT [10]. Multicast Communication-The principle objective of multicast correspondence in VANETs is to achieve information correspondence from source hub to a gathering of objective hubs. Geocast is particular type of multicast in which objective hubs are those situated in a predetermined geographic position (zone of pertinence), generally with respect to wellspring of communication. Meanwhile most VANET applications & administrations are usually founded on vehicles' location, geocast conventions have gotten greater part of the concentration in late proposition. Be that as it may, one of the principal challenges in VANETs is the way to build up a productive geocast convention in such a profoundly powerful topology. In this segment, we will survey probably the most outstanding geocast directing
conventions in VANETs. the absolute most understood geocast steering conventions in VANETs are DRG [11] &Mobicast[12].
1.
D
ATAD
ISSEMINATIONT
ECHNIQUESVarious information scattering methods [13] via VANETs are suggested to fit various requests. Essentially, two noteworthy applications are vigorously inquired about around there: traffic wellbeing, & travel comfort. Traffic security applications are low information rates, bound to set number of neighborhood with exacting inactivity limitations. While travel comfort applications are known as postponement tolerant applications with increasingly loosened up time imperatives, yet are relied upon to require information transmission traversing generally faraway separations. There are three fundamental models for information scattering in VANETs: Push, Pull & Hybrid. Information dispersal approaches in VANETs can be characterized in 2 primary classes [14]: Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I/I2V) & Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Data Dissemination. Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Data Dissemination: In this category, we consume protocols that needspecific sort of roadside infrastructure to do data dissemination, which may be push or pull-based. Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Data Dissemination: In this class, we consume conventions that do not needsome foundation & vehicles convey exclusively in specially appointed manner [15].
Table I. Data Dissemination Approaches
Data
Dissemination Approach
Typical
Scenario Drawback
V2I Dissemination
Push-based
Public-interest data
Not
appropriatevia non-public information
Pull-based
User-specific data
Greatinformation traffic,
interferences, collisions
V2V Dissemination
Flooding Sparse N/Ws
Not scalable, high data traffic
Relaying Dense N/Ws
Needs efficient relay collection in order toconfirm reliability
Opportunistic N/Ws partitions
Possible high overhead & delay
A. Push Model
In a push model, information is spread proactively exploitingspecial communicate. The push model is commonly favored for wellbeing informing frameworks [16], for example, impact cautioning frameworks, crisis message scattering frameworks & data frameworks determined for dangerous street conditions like ice, water or day off. By & by, different methodologies likewise exist to help different kinds of uses, for example, entry time estimation, speed desire & clog discovery.
B. Pull Model
overhead, thrufewer idleness imperatives. In draw createdprocedure, customerusuallyconductsreview to communicate site, & gets an answer communicationas of that point. In such uses, clients may endure new postponements up to reaction inevitably returns. Draw based strategies frequently target travel comfort applications, for example, administration revelation & deferral tolerant frameworks.
C. Hybrid Model
There are not many half breeds conspires that consolidate the two models together to help various applications. Alongside the push & force models that were displayed, there are not many plans that consolidate the two models so as to help various kinds of uses inside VANET situation. Data move convention for vehicular figuring "VITP" [17] bolsters the foundation of dispersed administration framework over VANETs, by indicating the language structure & the semantic of mailsamongst vehicles. VITP usestogether of data spread models. Aimed at wellbeing mails, for example, cautions around crises or perilous traffic conditions, push-based procedure is utilized, thougha destroy based system is proposed to recover data through area delicate questions distributed by vehicles on interest.
1.
C
LUSTER-
BASED DATA DISSEMINATIONVehicular impromptu systems are imagined with their exceptional & remarkable intercommunication frameworks to give security in canny transportation frameworks & backing large‐size systems. Because of thick & scanty traffic conditions, directing is constantly a provoking err& to set up dependable & successful correspondence among vehicle hubs in the exceptionally transportable condition. A few sorts of directing conventions have been suggested to deal with great versatility & dynamic topologies with topology‐based steering, position & geocast directing, & cluster‐based directing conventions. Cluster‐based steering is achievable answers for vehicular systems because of its sensible & increasingly feasible environment. In cluster‐based conventions, system is separated in numerous clusters & each group chooses a cluster head for information spread [18]. In cluster-based steering a gathering of hubs distinguishes themselves to be a piece of group & a hub is assigned as group head will communicate the parcel to group. This convention is proposed for an expressway situation where vehicles are isolated into clusters & a vehicle hub is chosen as a head of group. The cluster-based routing protocol (CBRP) was presented by Jiang. In CBRP the hubs of a remote system are separated into a few disjoint or covering groups. Each group chooses one hub as the supposed cluster head [19]. These uncommon hubs are in charge of the directing procedure. Neighbors of cluster heads can't be group heads too. Be that as it may, CH can speak with one another by utilizing portal hubs. A door is a hub that has at least two cluster heads as its neighbors or when the groups are disjoint at any rate one cluster head & another passage hub. The directing procedure itself is executed as source steering by flooding the system with a course solicitation message [20]. The principle point of grouping is to choose ideal vehicle hubs with comparative versatility examples to join a similar cluster. Cluster‐based directing conventions additionally help to decrease the channel conflict & give reasonable
channel access to the hubs. These conventions are likewise viable to diminish the impact of handoff idleness & limit the bundle dropping issues [21].
1.
L
ITERATURES
URVEYnormally grasp most sensible dispersal contrive in order to fit notice message transport technique to every specific situation. Our framework uses as data parameters vehicular thickness & topological physiognomies of earth wherever vehicles are arranged, in order to pick which dissipating plan to usage. We balance our recommendation with reverence 2 static dispersing plans (eMDR& NJL), &3 flexible spread systems (UV-CAST, FDPD, & DV-CAST). Reenactment results display that our strategy through and through improves these plans, having the choice to help progressively powerful advised message dispersing in all conditions going on low densities with complex maps, to high densities in essential circumstances. In specific, RTAD recovers existing strategies to the extent level of vehicles taught, while on a very basic level decreasing the number of messages sent, thusly easing impart storms [26]. [26]. Omar Chakroun & SoumayaCherkaoui [2014] present dispersal & clog shirking plan for security communicationsended IEEE 802.11p VANETs. So as toward guarantee great conveyance rates past 300 m, methodology engenders data more than two bounces while staying away from the subsequent blockage by utilizing a completely circulated Hilter kilter transmit control alteration system. The plan utilizes double cross ward improvement under-limitation procedures to choose finest vehicle to go about hand-off aimed at information sending. Planmay appraise likelihood of probability of reception rate (PRR), & change sending separation to meet base prerequisites of PRR & conveyance separation to fit explicit security application necessities. The proposed arrangement, in contrast to past scattering methods, works all the while on decreasing clog due to multi-bounce handing-off & on guaranteeing low start to finish delay. Recreation results affirm the adequacy of the proposed adjustment & handing-off plan & its worthwhile system execution contrasted with others, under different traffic imperatives [27]. Kakkasageri et al. [2014] Propose an intellectual specialist based basic data collection & scattering in VANETs by utilizing relapse component. Relapse based subjective specialist approach productively totals the gathered basic data & limits repetitive information dispersal. Suggested plan mechanism over clustered vehicles via utilizing a lot of static & versatile operators. plan works in accompanying advances: (1) approval & sifting of gathered basic data; (2) age of convictions dependent on substantial & separated basic data; (3) totaling convictions to create want utilizing relapse system; (4) correction of want for better nature of total; (5) concluding goal dependent on overhauled want; (6) scattering accumulated data to adjacent groups. We approve suggested plan by recreation. Plan performs improved when contrasted with ESSMD (Event Suppression for Safety Message Dissemination) plot as far as basic data procurement delay, collection delay, start to finish delay, scattering deferral & transfer speed usage [28]. Fogue et al. [2012] current improved Message Dissemination dependent on Roadmaps(e-MDR), a new plan exceptionally intended to expand level of educated vehicles & decrease notice time; simultaneously, it mitigates communicate storm issue in genuine urban situations. We assess effect that our plan has on execution after connected toward VANET situations dependent on genuine city maps, & outcomes demonstrate that it beats past plans in entire circumstances [29]. Schwartz et al.
[2011] present a straightforward & hearty dispersal convention that proficiently manages information spread in both thick & scanty vehicular systems. We will probably address parkway situations wherever vehicles furnished bydevices identify an occasion, e.g., peril & communicate an occasion communication to a particular course of intrigue. So as to manage to communicate correspondence under various system densities, we structure a spread convention so that: (I) it avoids purported communicate storm issue in thick organizes by utilizing an upgraded communicate concealment method; & (ii) it productively manages disengaged arranges by depending on store-convey advancing correspondence model. A curiosity of convention lies in its straightforwardness & heartiness. Straightforwardness is accomplished by just thinking about 2 states (i.e., group tail & non-tail) via vehicles. Besides, vehicles in two bearings support scattering communications is consistently way, deprived of turning to various activity mannersvia every heading. Power is accomplished by doling out communication conveyance obligation to numerous vehicles in inadequate systems. Our recreation results demonstrate that our convention accomplishes higher conveyance proportion & higher strength when contrasted & DV-CAST under assorted street situations [30].
1.
C
ONCLUSIONVANET is a developing innovation for future shrewd transportation frameworks (ITSs). Vehicular impromptu systems are imagined with their extraordinary & exceptional intercommunication frameworks to give wellbeing in wise transportation frameworks & backing large‐ size systems. As of late, VANETs have drawn more prominent consideration of analysts just as academicians because of their noteworthy appealing highlights, for example, dynamic network, self-sorting out & no brought together organization. Be that as it may, because of the amazingly high portability of vehicles, topology changes oftentimes. Thus may cause a high correspondence overhead for trading & refreshing the topology data. The most widely recognized arrangement embraced for this issue is the clustering. Many grouping based conventions have been proposed which mastermind vehicles into clusters & just the cluster heads need to speak with group individuals & neighboring clusters. Cluster‐based Routing for Sparse & Dense Networks is essentially founded on clustering where convention embraces well perceive steering measurements for CH race including vehicle thickness, signal quality, & heading.
R
EFERENCES[1] Fiore M, Harri J, Filali F, Bonnet C. Vehicular mobility simulation for VANETs, anss. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Simulation Symposium (ANSS’07); 2007. p. 301– 309.
[2] DarK, Bakhouya M, Gaber J, Wack M, Lorenz P. Wireless communication technologies for ITS applications. IEEE Communications Magazine 2010;48(5):156–62.
[3] Ruiz, P., Dorronsoro, B., Bouvry, P., & Tardón, L. (2012). Information dissemination in VANETs based upon a tree topology. Ad Hoc Networks, 10(1), 111–127.
Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, 2008.
[5] Gorrieri, A., Martalò, M., Busanelli, S., & Ferrari, G. (2016). Clustering & sensing with decentralized detection in vehicular ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Networks, 36, 450–464. [6] Ouafa Mahma & Ahmed Korichi, ―TOWARDS A NEW
APPROACH OF DATA DISSEMINATION IN VANETS NETWORKS‖, David C. Wyld et al. (Eds): CCSEA, CLOUD, DKMP, SEA, SIPRO - 2016 pp. 13–23, CS & IT-CSCP 2016. [7] Bakhouya, M., Gaber, J., & Lorenz, P. (2011). An adaptive approach for information dissemination in Vehicular Ad hoc Networks. Journal of Network & Computer Applications, 34(6), 1971–1978.
[8] O. K. Tonguz, N. Wisitpongphan, & F. Bai, ―DV-CAST: A Distributed Vehicular Broadcast Protocol for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks,‖ IEEE Wireless Communications, vol. 17, pp. 47–56, April 2010.
[9] M. Bakhouya, J. Gaber, & P. Lorenz, ―An Adaptive Approach for Information Dissemination in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks,‖ Journal of Network & Computer Applications, 2011.
[10]L. Villas, T. de &rade, & N. da Fonseca, ―An efficient & robust protocol to disseminate data in highway environments with different traffic conditions,‖ in Computers & Communication (ISCC), 2014 IEEE Symposium on, June 2014, pp. 1–6. [11]H. P. Joshi, M. L. Sichitiu, & M. Kihl, ―Distributed robust
geocast multicast routing for inter-vehicle communication,‖ in First WEIRD Workshop on WiMAX, Wireless & Mobility, 2007, pp. 1–12.
[12]Y.-S. Chen, Y.-W. Lin, & S.-L. Lee, ―A mobicast routing protocol in vehicular ad-hoc networks,‖ in Proceedings of the 28th IEEE conference on Global telecommunications, ser. GLOBECOM’09. Piscataway, NJ, USA: IEEE Press, 2009, pp. 2296–2301.
[13]Chaqfeh, M., Lakas, A., & Jawhar, I. (2014). A survey on data dissemination in vehicular ad hoc networks. Vehicular Communications, 1(4), 214–225.
[14]Aparecido, L. (2015). Data dissemination in vehicular networks: Challenges, solutions, & future perspectives. 2015 7th International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility & Security (NTMS).
[15]M. Bakhouya, J. Gaber, & P. Lorenz, ―An Adaptive Approach for Information Dissemination in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks,‖ Journal of Network & Computer Applications, 2011.
[16]T. Nadeem, P. Shankar, L. Iftode, A comparative study of data dissemination models for VANETs, in The 3rd Annual International Conference on Mobile & Ubiquitous Systems – Workshops, 2006, pp. 1–10.
[17]M.D. Dikaiakos, S. Iqbal, T. Nadeem, L. Iftode, VITP: an information transfer protocol for vehicular computing, in Proceedings of the 2nd ACM International Workshop on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks, 2005, pp. 30–39.
[18]Qureshi, K. N., Abdullah, A. H., Bashir, F., Iqbal, S., & Awan, K. M. (2018). Cluster-based data dissemination, cluster head formation under sparse, & dense traffic conditions for vehicular ad hoc networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 31(8).
[19]Shou-Chih Lo, Yi-Jen Lin, & Jhih-Siao Gao, ―A Multi-Head Clustering Algorithm in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks‖, International Journal of Computer Theory & Engineering, Vol. 5, No. 2, April 2013.
[20]Garima Dhawan & Shilpa Nagpal, ―Cluster Based Data Dissemination Protocol In VANET‖, International Journal Of Engineering & Computer Science (IJECS), Volume 5, Issue 09, September, 2016, Page No.18115-18119.
[21]Zhang Z, Boukerche A, Pazzi R. A novel multi‐hop clustering scheme for vehicular ad‐hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Symposium on Mobility Management & Wireless access; 2011:19‐26.
[22]Rehman, O., & Ould-Khaoua, M. (2018). A hybrid relay node selection scheme for message dissemination in VANETs. Future Generation Computer Systems, Volume 93, April 2019, Pages 1-17.
[23]Brik, B., Lagraa, N., Lakas, A., & Cheddad, A. (2016). DDGP: Distributed Data Gathering Protocol for vehicular networks. Vehicular Communications, 4, 15–29.
[24]Wenjie, W., & Tao, L. (2015). Quality of forwarding-based data disseminating strategy in urban VANET. The Journal of China Universities of Posts & Telecommunications, 22(6), 1– 50.
[25]Rayeni, M. S., Hafid, A., & Sahu, P. K. (2015). Dynamic spatial partition density-based emergency message dissemination in VANETs. Vehicular Communications, 2(4), 208–222.
[26]Sanguesa, J. A., Fogue, M., Garrido, P., Martinez, F. J., Cano, J.-C., Calafate, C. T., & Manzoni, P. (2015). RTAD: A real-time adaptive dissemination system for VANETs. Computer Communications, 60, 53–70.
[27]Chakroun, O., & Cherkaoui, S. (2014). Overhead-free congestion control & data dissemination for 802.11p VANETs. Vehicular Communications, 1(3), 123–133. [28]Kakkasageri, M. S., & Manvi, S. S. (2014). Regression based
critical information aggregation & dissemination in VANETs: A cognitive agent approach. Vehicular Communications, 1(4), 168–180.
[29]Fogue, M., Garrido, P., Martinez, F. J., Cano, J.-C., Calafate, C. T., & Manzoni, P. (2012). Evaluating the impact of a novel message dissemination scheme for vehicular networks using real maps. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 25, 61–80.