organic papers
Acta Cryst.(2005). E61, o2191–o2192 doi:10.1107/S160053680501843X Ho¨rgeret al. C
14H17N7O7S
o2191
Acta Crystallographica Section E
Structure Reports Online
ISSN 1600-5368
(3
R
,6
S
,7
R
,8
R
,9
S
,9a
S
)-Methyl
6,9-diacetoxy-7,8-diazidoperhydro-5-oxothiazolo[3,2-
a
]azepine-3-carboxylate
Rolf Ho¨rger, Michael Marsch, Armin Geyer and Klaus Harms*
Fachbereich Chemie der Philipps-Universita¨t, Hans-Meerwein-Strasse, D-35032 Marburg, Germany
Correspondence e-mail: harms@chemie.uni-marburg.de
Key indicators
Single-crystal X-ray study T= 193 K
Mean(C–C) = 0.002 A˚ Rfactor = 0.023 wRfactor = 0.057
Data-to-parameter ratio = 12.6
For details of how these key indicators were automatically derived from the article, see http://journals.iucr.org/e.
#2005 International Union of Crystallography Printed in Great Britain – all rights reserved
The absolute configuration has been determined for the bicyclic title compound, C14H17N7O7S, an intermediate in the
synthesis of fixed chiral bis(1,2-aminohydroxy) compounds. In the crystal structure, the chair conformation of the seven-membered lactam ring exhibits four axial heteroatom substituents. The fused five-membered thiazolidine ring prevents inversion of the seven-membered iduronic acid ring derivative to the thermodynamically more favourable chair conformation with four equatorial substitutions.
Comment
1,2-Amino alcohols find application as chiral auxiliaries, where the heteroatoms form a complex with a metal reaction centre (Ager et al., 1996). Two vicinal amino alcohol units are the starting material in the syntheses of bis(oxazolines), which provide high enantioselectivities in a number of transforma-tions (Gant & Meyers, 1994). We present a precursor of a bis(1,2-amino alcohol), a novel class of ligands with two amino alcohol units attached to a seven-membered lactam ring.
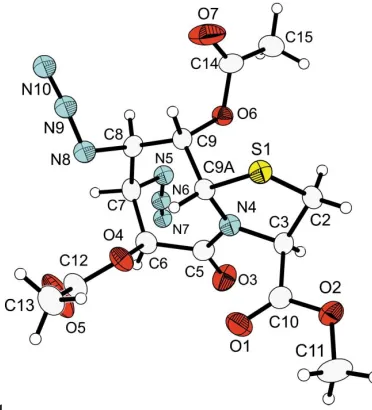
The title compound, (I) (Fig. 1), was prepared from the starting material (3R,6S,7S,8S,9S,9aS)-methyl octahydro-6,7,8,9-tetrahydroxy-5-oxothiazolo[3,2-a ]azepine-3-carboxyl-ate, which is obtained by condensation of d-
-mannur-onolactone with the methyl ester of l-cysteine (Tremmel &
Geyer, 2002). The bond lengths and angles (Table 1) are within normal ranges. Activation and subsequent substitution of NaN3 for the two hydroxy groups in positions 7 and 8
inserts the N-termini in the molecule. Finally, the acetylation of the remaining hydroxy groups was performed with acetic acid anhydride.
In contrast to the conformation observed in the crystalline state, the seven-membered lactam ring shows dynamics between a chair and a twist–boat conformation in solution. The coupling constants between the protons 6, 7 and 8 represent the typical values for dynamic systems of about 5– 8 Hz. The NOE experiments also indicate a more flexible structure of (I) in solution.
Experimental
The reaction of (3R,6S,7R,8R,9S,9aS)-methyl 6,9-dihydroxy-7,8-diazidooctahydro-5-oxothiazolo[3,2-a]azepine-3-carboxylate (1.88 g, 5.48 mmol) with an excess of acetic acid anhydride (4 ml) was carried out in dry pyridine (30 ml) overnight at room temperature. After removal of the solvent, colourless crystals were obtained by recrys-tallization from ethyl acetate (yield 2.2 g, 5.26 mmol, 95%).1H NMR
(600 MHz, CDCl3):5.60 (d, 3
J9aH,9H= 1.23 Hz, 1H, 9a-H), 5.53 (d, 3J
6H,7H = 7.41 Hz, 1H, 6-H), 5.32 (dd, 3J3H,20H = 6.93 Hz, 3J3H,2H =
2.40 Hz, 1H, 3-H), 5.13 (dd,3J9H,9aH= 1.23 Hz, 3
J9H,8H= 3.57 Hz, 1H,
9-H), 4.23 (dd,3J7H,6H= 7.41 Hz, 3
J7H,8H= 6.17 Hz, 1H, 7-H), 3.91 (dd, 3
J8H,7H= 6.24 Hz, 3
J8H,9H= 3.64 Hz, 1H, 8-H), 3.78 (s, 3H, CO2CH3),
3.35 (dd,3J20H,3H= 6.93 Hz,2J20H,2H= 11.53 Hz, 1H, 20-H), 3.14 (dd,
2J
2H,20H= 11.60 Hz,3J2H,3H= 2.47 Hz, 1H, 2-H), 2.23 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.18
(s, 3H, CH3). 13
C NMR (150 MHz, CDCl3): 169.61 (CO), 169.49
(CO), 169.29 (CO), 164.43 (5-C), 74.86 (9-C), 73.84 (6-C), 64.89 (3-C), 63.09 (8-C), 59.33 (7-C), 58.90 (9a-C), 53.22 (CH3), 31.44 (2-C), 21.07,
20.85 (CH3). Crystal data
C14H17N7O7S
Mr= 427.41
Orthorhombic,P212121
a= 8.6418 (4) A˚
b= 11.8765 (6) A˚
c= 18.2755 (12) A˚
V= 1875.69 (18) A˚3
Z= 4
Dx= 1.514 Mg m 3
MoKradiation
Cell parameters from 26411 reflections
= 2–26
= 0.23 mm1
T= 193 (2) K Block, colourless 0.60.30.2 mm
Data collection
Stoe IPDS-II diffractometer
!scans
Absorption correction: none 27463 measured reflections 3765 independent reflections 3473 reflections withI> 2(I)
Rint= 0.031 max= 26.2
h=10!10
k=14!14
l=22!22
Refinement
Refinement onF2 R[F2> 2(F2)] = 0.023
wR(F2) = 0.057
S= 1.03 3765 reflections 298 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
w= 1/[2
(Fo2) + (0.0405P)2]
whereP= (Fo2+ 2Fc2)/3
(/)max= 0.001 max= 0.18 e A˚
3 min=0.15 e A˚3
Extinction correction:SHELXL97
Extinction coefficient: 0.0035 (8) Absolute structure: Flack (1983),
[image:2.610.75.261.72.277.2]with 1222 Friedel pairs Flack parameter:0.02 (5)
Table 1
Selected geometric parameters (A˚ ,).
S1—C2 1.8038 (15)
S1—C9A 1.8228 (13)
C2—C3 1.517 (2)
C3—N4 1.4577 (17)
N4—C5 1.3559 (18)
N4—C9A 1.4766 (17)
C5—C6 1.526 (2)
C6—C7 1.527 (2)
C7—C8 1.527 (2)
C8—C9 1.5374 (19)
C9—C9A 1.5202 (19)
C2—S1—C9A 92.81 (6)
C3—C2—S1 103.49 (9)
N4—C3—C2 106.24 (11)
C5—N4—C3 118.59 (11)
C5—N4—C9A 124.36 (11)
C3—N4—C9A 114.48 (10)
N4—C5—C6 118.50 (12)
C5—C6—C7 114.79 (12)
C8—C7—C6 117.34 (12)
C7—C8—C9 119.82 (12)
C9A—C9—C8 116.94 (11)
N4—C9A—S1 105.54 (9)
C9—C9A—S1 110.99 (9)
N4—C5—C6—O4 58.52 (15)
C5—C6—C7—N5 47.00 (15)
O4—C6—C7—C8 47.55 (16)
C6—C7—C8—N8 76.07 (15)
N5—C7—C8—C9 75.46 (15)
C7—C8—C9—O6 78.73 (15)
N8—C8—C9—C9A 75.08 (14) O6—C9—C9A—N4 52.54 (14)
Methyl groups were refined with idealized geometry [C—H = 0.98 A˚ , H—C—H = 109.5 and U
iso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C)], with torsion
angles refined to fit the electron density. All other H atoms were located and refined isotropically. The resulting C—H bond lengths are in the range 0.941 (17)–1.034 (17) A˚ .
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2003; cell refinement:
X-AREA; data reduction: X-AREA; program(s) used to solve structure:SHELXS97(Sheldrick, 1997); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997); molecular graphics:
DIAMOND(Brandenburg, 2004); software used to prepare material for publication:WinGX(Farrugia, 1999).
References
Ager, D. J., Prakash, I. & Schaad, D. R. (1996). Chem. Rev. 96, 835– 875.
Brandenburg, K. (2004).DIAMOND. Version 3.0a. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
Farrugia, L. J. (1999).J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838. Flack, H. D. (1983).Acta Cryst.A39, 876–881.
Gant, T. G. & Meyers, A. I. (1994).Tetrahedron, pp. 2297–2360.
Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97. University of Go¨ttingen, Germany.
Stoe & Cie (2003).X-AREA. Version 1.20. Stoe & Cie., Darmstadt, Germany. Tremmel, P. & Geyer, A. (2002).J. Am. Chem. Soc.124, 8548–8549.
Figure 1
[image:2.610.314.565.228.404.2]supporting information
sup-1 Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, o2191–o2192
supporting information
Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, o2191–o2192 [https://doi.org/10.1107/S160053680501843X]
(3
R
,6
S
,7
R
,8
R
,9
S
,9a
S
)-Methyl
6,9-diacetoxy-7,8-diazidoperhydro-5-oxothia-zolo[3,2-
a
]azepine-3-carboxylate
Rolf H
ö
rger, Michael Marsch, Armin Geyer and Klaus Harms
(3R,6S,7R,8R,9S,9aS)-Methyl 6,9-diacetoxy-7,8-diazidoperhydro- 5-oxothiazolo[3,2-a]azepine-3-carboxylate
Crystal data C14H17N7O7S Mr = 427.41
Orthorhombic, P212121 Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab a = 8.6418 (4) Å b = 11.8765 (6) Å c = 18.2755 (12) Å V = 1875.69 (18) Å3 Z = 4
F(000) = 888 Dx = 1.514 Mg m−3
Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å Cell parameters from 26411 reflections θ = 2–26°
µ = 0.23 mm−1 T = 193 K Plate, colourless 0.6 × 0.3 × 0.2 mm
Data collection STOE IPDS-II diffractometer ω scans
27463 measured reflections 3765 independent reflections 3473 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Rint = 0.031
θmax = 26.2°, θmin = 2.1° h = −10→10
k = −14→14 l = −22→22
Refinement Refinement on F2 Least-squares matrix: full R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.023 wR(F2) = 0.057 S = 1.03 3765 reflections 298 parameters 0 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
w = 1/[σ2(F
o2) + (0.0405P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 (Δ/σ)max = 0.001
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Extinction correction: SHELXL97, Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 Extinction coefficient: 0.0035 (8)
Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1222 Friedel pairs
Absolute structure parameter: −0.02 (5)
Special details
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
x y z Uiso*/Ueq
S1 0.93658 (4) 0.78105 (3) 0.932394 (19) 0.02993 (9) O1 0.72097 (14) 1.02073 (9) 0.84038 (6) 0.0422 (3) O2 0.77775 (13) 1.07408 (9) 0.95457 (6) 0.0387 (3) C2 0.79249 (18) 0.84106 (13) 0.99221 (7) 0.0303 (3) O3 0.41574 (12) 0.87437 (10) 0.85470 (7) 0.0445 (3) C3 0.67490 (16) 0.89081 (11) 0.93976 (8) 0.0274 (3) O4 0.65824 (11) 0.79216 (9) 0.72530 (5) 0.0343 (2) N4 0.65314 (13) 0.80757 (9) 0.88205 (6) 0.0257 (2) O5 0.52800 (18) 0.79360 (19) 0.62079 (7) 0.0835 (6) C5 0.52719 (16) 0.81647 (12) 0.83818 (8) 0.0297 (3) N5 0.40742 (14) 0.59176 (12) 0.82761 (7) 0.0356 (3) O6 0.69789 (10) 0.58136 (8) 0.92982 (5) 0.0274 (2) N6 0.27310 (15) 0.61778 (11) 0.81167 (7) 0.0363 (3) C6 0.52657 (15) 0.75261 (12) 0.76574 (8) 0.0302 (3) O7 0.88241 (16) 0.45006 (11) 0.94269 (9) 0.0635 (4) C7 0.52604 (15) 0.62456 (12) 0.77305 (8) 0.0286 (3) N7 0.14630 (16) 0.63567 (16) 0.80547 (9) 0.0527 (4) N8 0.78018 (14) 0.56883 (11) 0.73145 (7) 0.0349 (3) C8 0.67658 (16) 0.56820 (12) 0.79691 (8) 0.0286 (3) N9 0.86548 (15) 0.48517 (13) 0.72995 (7) 0.0415 (3) C9 0.76799 (15) 0.61597 (11) 0.86206 (7) 0.0251 (3) C9A 0.79345 (14) 0.74260 (11) 0.86352 (7) 0.0246 (3) C10 0.72686 (15) 1.00102 (12) 0.90444 (8) 0.0295 (3) N10 0.9475 (2) 0.41203 (16) 0.72358 (9) 0.0617 (4) C11 0.8232 (2) 1.18381 (13) 0.92716 (12) 0.0501 (4)
H11A 0.8943 1.1744 0.8858 0.075*
H11B 0.8748 1.2262 0.9662 0.075*
H11C 0.7311 1.225 0.911 0.075*
C12 0.6455 (2) 0.80834 (14) 0.65298 (8) 0.0389 (4) C13 0.7961 (2) 0.84535 (16) 0.62221 (9) 0.0455 (4)
H13A 0.8478 0.7812 0.599 0.068*
H13B 0.8615 0.8749 0.6616 0.068*
H13C 0.7784 0.9044 0.5857 0.068*
C14 0.76862 (17) 0.49567 (12) 0.96557 (8) 0.0326 (3) C15 0.6889 (2) 0.46680 (14) 1.03475 (9) 0.0422 (4)
H15A 0.744 0.405 1.059 0.063*
H15B 0.5825 0.4435 1.0241 0.063*
H15C 0.6876 0.5328 1.067 0.063*
supporting information
sup-3 Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, o2191–o2192
H9A 0.8322 (17) 0.7637 (12) 0.8156 (8) 0.021 (3)*
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
U11 U22 U33 U12 U13 U23
S1 0.02403 (16) 0.03384 (18) 0.03193 (16) −0.00140 (14) −0.00650 (14) −0.00153 (14) O1 0.0503 (7) 0.0405 (6) 0.0359 (6) −0.0046 (5) −0.0076 (5) 0.0092 (5) O2 0.0464 (6) 0.0277 (5) 0.0419 (6) −0.0049 (5) −0.0049 (5) −0.0047 (4) C2 0.0331 (8) 0.0327 (8) 0.0250 (6) −0.0040 (6) −0.0030 (6) 0.0005 (6) O3 0.0287 (6) 0.0514 (7) 0.0534 (7) 0.0124 (5) −0.0087 (5) −0.0144 (5) C3 0.0264 (7) 0.0295 (7) 0.0264 (7) −0.0006 (5) 0.0022 (6) −0.0028 (5) O4 0.0280 (5) 0.0451 (6) 0.0297 (5) −0.0064 (4) −0.0024 (4) 0.0082 (5) N4 0.0231 (5) 0.0257 (6) 0.0282 (6) 0.0001 (4) −0.0023 (4) −0.0028 (4) O5 0.0585 (8) 0.1550 (17) 0.0369 (7) −0.0463 (10) −0.0175 (6) 0.0212 (9) C5 0.0236 (6) 0.0303 (7) 0.0352 (7) 0.0005 (5) −0.0019 (5) 0.0000 (6) N5 0.0229 (6) 0.0473 (8) 0.0365 (6) −0.0038 (5) 0.0019 (5) 0.0012 (6) O6 0.0258 (5) 0.0289 (5) 0.0276 (5) 0.0015 (4) 0.0029 (4) 0.0038 (4) N6 0.0294 (7) 0.0430 (8) 0.0364 (7) −0.0074 (5) 0.0044 (5) −0.0056 (6) C6 0.0201 (6) 0.0388 (8) 0.0318 (7) −0.0010 (5) −0.0042 (5) 0.0008 (6) O7 0.0610 (8) 0.0524 (8) 0.0771 (9) 0.0306 (6) 0.0298 (7) 0.0284 (7) C7 0.0220 (6) 0.0371 (8) 0.0267 (6) −0.0062 (5) 0.0013 (5) −0.0028 (6) N7 0.0256 (7) 0.0708 (11) 0.0616 (9) 0.0009 (7) 0.0050 (7) −0.0050 (8) N8 0.0313 (6) 0.0421 (7) 0.0313 (6) 0.0027 (6) 0.0054 (5) −0.0080 (5) C8 0.0262 (7) 0.0293 (7) 0.0305 (7) −0.0016 (6) 0.0033 (5) −0.0041 (6) N9 0.0350 (7) 0.0543 (9) 0.0353 (7) 0.0035 (7) 0.0020 (6) −0.0142 (6) C9 0.0208 (6) 0.0292 (7) 0.0252 (6) 0.0000 (5) 0.0032 (5) −0.0008 (5) C9A 0.0199 (6) 0.0287 (7) 0.0252 (6) −0.0012 (5) −0.0004 (5) 0.0011 (5) C10 0.0241 (6) 0.0296 (7) 0.0347 (7) 0.0018 (6) −0.0017 (6) −0.0016 (6) N10 0.0537 (9) 0.0721 (11) 0.0593 (9) 0.0247 (9) 0.0065 (8) −0.0198 (8) C11 0.0485 (10) 0.0265 (7) 0.0754 (12) −0.0043 (7) −0.0123 (9) 0.0046 (8) C12 0.0421 (8) 0.0453 (9) 0.0292 (7) −0.0085 (7) −0.0059 (6) 0.0042 (6) C13 0.0463 (10) 0.0534 (10) 0.0369 (8) −0.0097 (8) 0.0040 (7) 0.0048 (7) C14 0.0325 (8) 0.0240 (7) 0.0412 (8) 0.0005 (6) 0.0007 (6) 0.0044 (6) C15 0.0478 (9) 0.0384 (9) 0.0406 (8) 0.0041 (7) 0.0048 (7) 0.0105 (7)
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
S1—C2 1.8038 (15) C6—H6 0.954 (16)
S1—C9A 1.8228 (13) O7—C14 1.1980 (19)
O1—C10 1.1950 (18) C7—C8 1.527 (2)
O2—C10 1.3362 (18) C7—H7 1.034 (17)
O2—C11 1.450 (2) N8—N9 1.2375 (19)
C2—C3 1.517 (2) N8—C8 1.4941 (18)
C2—H21 0.957 (18) C8—C9 1.5374 (19)
C2—H22 0.955 (17) C8—H81 0.986 (16)
O3—C5 1.2213 (17) N9—N10 1.127 (2)
C3—N4 1.4577 (17) C9—C9A 1.5202 (19)
C3—H3 0.941 (17) C9A—H9A 0.971 (15)
O4—C12 1.3401 (18) C11—H11A 0.98
O4—C6 1.4359 (17) C11—H11B 0.98
N4—C5 1.3559 (18) C11—H11C 0.98
N4—C9A 1.4766 (17) C12—C13 1.484 (2)
O5—C12 1.187 (2) C13—H13A 0.98
C5—C6 1.526 (2) C13—H13B 0.98
N5—N6 1.2361 (18) C13—H13C 0.98
N5—C7 1.4822 (18) C14—C15 1.480 (2)
O6—C14 1.3550 (17) C15—H15A 0.98
O6—C9 1.4386 (16) C15—H15B 0.98
N6—N7 1.1219 (19) C15—H15C 0.98
C6—C7 1.527 (2)
C2—S1—C9A 92.81 (6) C9—C8—H81 107.0 (9)
C10—O2—C11 115.84 (13) N10—N9—N8 174.66 (19)
C3—C2—S1 103.49 (9) O6—C9—C9A 109.17 (10)
C3—C2—H21 114.4 (10) O6—C9—C8 110.18 (11)
S1—C2—H21 107.0 (10) C9A—C9—C8 116.94 (11)
C3—C2—H22 111.1 (10) O6—C9—H9 107.0 (9)
S1—C2—H22 112.2 (10) C9A—C9—H9 106.7 (9)
H21—C2—H22 108.5 (13) C8—C9—H9 106.3 (9)
N4—C3—C2 106.24 (11) N4—C9A—C9 113.72 (10)
N4—C3—C10 108.27 (11) N4—C9A—S1 105.54 (9)
C2—C3—C10 113.83 (12) C9—C9A—S1 110.99 (9)
N4—C3—H3 109.6 (10) N4—C9A—H9A 110.8 (9)
C2—C3—H3 112.3 (10) C9—C9A—H9A 106.8 (9)
C10—C3—H3 106.5 (10) S1—C9A—H9A 108.9 (8)
C12—O4—C6 119.31 (11) O1—C10—O2 123.95 (14)
C5—N4—C3 118.59 (11) O1—C10—C3 124.71 (13)
C5—N4—C9A 124.36 (11) O2—C10—C3 111.33 (12)
C3—N4—C9A 114.48 (10) O2—C11—H11A 109.5
O3—C5—N4 122.06 (13) O2—C11—H11B 109.5
O3—C5—C6 119.44 (13) H11A—C11—H11B 109.5
N4—C5—C6 118.50 (12) O2—C11—H11C 109.5
N6—N5—C7 115.16 (13) H11A—C11—H11C 109.5
C14—O6—C9 116.08 (10) H11B—C11—H11C 109.5
N7—N6—N5 171.25 (17) O5—C12—O4 122.56 (15)
O4—C6—C5 106.33 (11) O5—C12—C13 127.31 (15) O4—C6—C7 111.92 (11) O4—C12—C13 110.13 (13)
C5—C6—C7 114.79 (12) C12—C13—H13A 109.5
O4—C6—H6 109.1 (9) C12—C13—H13B 109.5
C5—C6—H6 106.0 (9) H13A—C13—H13B 109.5
C7—C6—H6 108.5 (10) C12—C13—H13C 109.5
N5—C7—C8 106.37 (11) H13A—C13—H13C 109.5
N5—C7—C6 108.83 (12) H13B—C13—H13C 109.5
C8—C7—C6 117.34 (12) O7—C14—O6 122.79 (14)
supporting information
sup-5 Acta Cryst. (2005). E61, o2191–o2192
C8—C7—H7 107.4 (9) O6—C14—C15 112.09 (12)
C6—C7—H7 106.6 (10) C14—C15—H15A 109.5
N9—N8—C8 111.76 (13) C14—C15—H15B 109.5
N8—C8—C7 106.25 (11) H15A—C15—H15B 109.5
N8—C8—C9 108.08 (11) C14—C15—H15C 109.5
C7—C8—C9 119.82 (12) H15A—C15—H15C 109.5
N8—C8—H81 108.8 (9) H15B—C15—H15C 109.5
C7—C8—H81 106.5 (9)