organic papers
Acta Cryst.(2006). E62, o3189–o3190 doi:10.1107/S1600536806022082 Luet al. C
12H10N8O2S
o3189
Acta Crystallographica Section E Structure Reports
Online
ISSN 1600-5368
4-(2-Nitrobenzylideneamino)-3-(1
H
-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1
H
-1,2,4-triazole-5(4
H
)-thione
Xiao-Lan Lu,aWen-Zhao Bi,b Yu-Qing Shang,bLiang-Zhong Xub* and Guan-Ping Yub
aCollege of Chemistry and Chemical
Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, People’s Republic of China, andbCollege of Chemistry and Molecular
Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266042, People’s Republic of China
Correspondence e-mail: qknhs@yahoo.com.cn
Key indicators Single-crystal X-ray study T= 294 K
Mean(C–C) = 0.004 A˚ Rfactor = 0.043 wRfactor = 0.112
Data-to-parameter ratio = 14.1
For details of how these key indicators were automatically derived from the article, see http://journals.iucr.org/e.
Received 23 May 2006 Accepted 9 June 2006
#2006 International Union of Crystallography All rights reserved
In the title compound, C12H10N8O2S, the thione-substituted
triazole ring forms dihedral angles of 79.86 (2) and 9.86 (3), respectively, with the other triazole ring and the benzene ring. Intermolecular N—H N hydrogen bonds link the molecules into chains extended along the [101] direction. The crystal packing is further stabilized by van der Waals forces.
Comment
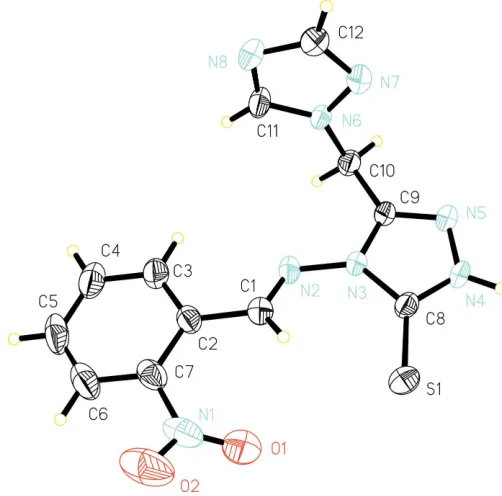
Recently, compounds containing the 1H-1,2,4-triazole group have attracted much interest because they have good plant-growth regulatory activity for a wide variety of crops (Xuet al., 2002). In addition, amine- and thione-substituted triazoles have been studied as anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agents (Eweisset al., 1986; Awadet al., 1991). In a search for new triazole compounds with better biological activity, the title compound, (I), was synthesized. We report here the crystal structure of (I) (Fig. 1).
Bond lengths and angles in the triazole rings in (I) are in agreement with those in previous reports (Liet al., 2005; Xuet al., 2005). The molecule exists in the thione tautomeric form, with an S=C distance of 1.672 (2) A˚ , indicating substantial double-bond character (Escobar-Valderramaet al., 1989). The mean planes C10–C12/N6/N7/N8 and C1–C7/N1 make dihe-dral angles of 79.86 (2) and 9.86 (3), respectively, with the thione-substituted triazole plane C8–C10/N3/N4/N5/S1.
Intermolecular N—H N hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules into chains extended along the [101] direction. The crystal packing (Fig. 2) is further stabilized by van der Waals forces.
Experimental
10–20 min in glacial acetic acid. The mixture was then filtered and crystallized from ethanol to afford the title compound (yield: 1.55 g, 93.7%). Single crystals suitable for X-ray measurements were obtained by recrystallization from ethanol at room temperature.
Crystal data
C12H10N8O2S
Mr= 330.34 Monoclinic,P21=n
a= 11.421 (2) A˚
b= 8.1070 (14) A˚
c= 16.446 (3) A˚
= 105.345 (3) V= 1468.5 (5) A˚3
Z= 4
Dx= 1.494 Mg m3 MoKradiation
= 0.25 mm1
T= 294 (2) K Block, yellow 0.180.100.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
’and!scans
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996)
Tmin= 0.950,Tmax= 0.985
8026 measured reflections 2991 independent reflections 1894 reflections withI> 2(I)
Rint= 0.038
max= 26.4
Refinement
Refinement onF2
R[F2> 2(F2)] = 0.043
wR(F2) = 0.112
S= 1.03 2991 reflections 212 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
w= 1/[2(F
o2) + (0.0393P)2
+ 0.548P]
whereP= (Fo2+ 2Fc2)/3
(/)max< 0.001
max= 0.26 e A˚
3
min=0.24 e A˚
3
Table 1
Hydrogen-bond geometry (A˚ ,).
D—H A D—H H A D A D—H A
N4—H4A N8i 0.88 (3) 1.97 (3) 2.838 (3) 171 (2)
Symmetry code: (i)xþ1
2;yþ32;zþ12.
The positional and isotropic displacement parameters of the H atoms attached to N4 were refined freely. All other H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C—H = 0.93 or 0.97 A˚ , and refined using a riding model, withUiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Data collection:SMART(Bruker, 1998); cell refinement:SAINT
(Bruker, 1999); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97(Sheldrick, 1997); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997); molecular graphics:
SHELXTL (Bruker, 1999); software used to prepare material for publication:SHELXTL.
References
Awad, I., Abdel-Rahman, A. & Bakite, E. (1991). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol.51, 483–486.
Bruker (1998).SMART. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA. Bruker (1999). SAINT and SHELXTL. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison,
Wisconsin, USA.
Escobar-Valderrama, J. L., Garcia-Tapia, J. H., Ramirez-Ortiz, J., Rosales, M. J., Toscano, R. A. & Valdes-Martinez, J. (1989).Can. J. Chem.67, 198–201. Eweiss, N., Bahajaj, A. & Elsherbini, E. (1986).J. Heterocycl. Chem.23, 1451–
1458.
Li, W.-H., Yu, G.-P., Liu, F.-Q., Hou, B.-R. & Yu, Z.-G. (2005).Acta Cryst.E61, o2058–o2060.
Sheldrick, G. M. (1996).SADABS. University of Go¨ttingen, Germany. Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97. University of
Go¨ttingen, Germany.
Xu, L.-Z., Yu, G.-P., Xu, F.-L. & Li, W.-H. (2005).Acta Cryst.E61, o2061– o2062.
[image:2.610.311.562.72.320.2] [image:2.610.313.563.375.514.2]Xu, L.-Z., Zhang, S.-S., Li, H.-J. & Jiao, K. (2002).J. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ.18, 284–286.
Figure 1
View of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 40% probability level.
Figure 2
A packing diagram, viewed down thebaxis. Hydrogen bonds are shown
supporting information
sup-1
Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, o3189–o3190
supporting information
Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, o3189–o3190 [https://doi.org/10.1107/S1600536806022082]
4-(2-Nitrobenzylideneamino)-3-(1
H
-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1
H
-1,2,4-triazole-5(4
H
)-thione
Xiao-Lan Lu, Wen-Zhao Bi, Yu-Qing Shang, Liang-Zhong Xu and Guan-Ping Yu
4-(2-Nitrobenzylideneamino)-3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole- 5(4H)-thione
Crystal data
C12H10N8O2S Mr = 330.34 Monoclinic, P21/n
Hall symbol: -P 2yn
a = 11.421 (2) Å
b = 8.1070 (14) Å
c = 16.446 (3) Å
β = 105.345 (3)°
V = 1468.5 (5) Å3
Z = 4
F(000) = 680
Dx = 1.494 Mg m−3
Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å
Cell parameters from 1979 reflections
θ = 2.5–25.9°
µ = 0.25 mm−1
T = 294 K
Block, yellow
0.18 × 0.10 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube Graphite monochromator
φ and ω scans
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996)
Tmin = 0.950, Tmax = 0.985
8026 measured reflections 2991 independent reflections 1894 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
Rint = 0.038
θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.0°
h = −14→13
k = −10→4
l = −20→20
Refinement
Refinement on F2
Least-squares matrix: full
R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 wR(F2) = 0.112
S = 1.03
2991 reflections 212 parameters 0 restraints
Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods
Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map
Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0393P)2 + 0.548P]
where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3
(Δ/σ)max < 0.001
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Special details
Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes.
Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2,
conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used
only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2
are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger.
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
x y z Uiso*/Ueq
S1 0.59893 (6) 0.69127 (10) 0.62340 (4) 0.0568 (2)
O1 0.7180 (2) 0.6319 (3) 0.45292 (16) 0.0877 (8)
O2 0.7361 (2) 0.4553 (3) 0.35946 (18) 0.1013 (9)
N1 0.6874 (2) 0.5739 (3) 0.3820 (2) 0.0661 (7)
N2 0.40527 (17) 0.8406 (2) 0.44138 (11) 0.0400 (5)
N3 0.39256 (16) 0.8451 (2) 0.52331 (11) 0.0335 (5)
N4 0.41264 (18) 0.8584 (3) 0.65536 (12) 0.0412 (5)
H4A 0.438 (2) 0.842 (3) 0.7099 (17) 0.056 (8)*
N5 0.30740 (17) 0.9419 (2) 0.61942 (11) 0.0404 (5)
N6 0.11614 (16) 0.8818 (3) 0.42617 (11) 0.0375 (5)
N7 0.05211 (19) 0.7839 (3) 0.46600 (13) 0.0536 (6)
N8 0.0092 (2) 0.7219 (3) 0.32815 (13) 0.0553 (6)
C1 0.4790 (2) 0.7390 (3) 0.42440 (15) 0.0425 (6)
H1 0.5218 0.6659 0.4651 0.051*
C2 0.4954 (2) 0.7389 (3) 0.33855 (15) 0.0416 (6)
C3 0.4123 (2) 0.8181 (4) 0.27341 (15) 0.0526 (7)
H3 0.3455 0.8698 0.2845 0.063*
C4 0.4263 (3) 0.8221 (4) 0.19243 (17) 0.0651 (9)
H4 0.3697 0.8766 0.1498 0.078*
C5 0.5252 (3) 0.7444 (4) 0.1750 (2) 0.0729 (10)
H5 0.5356 0.7484 0.1208 0.087*
C6 0.6067 (3) 0.6626 (4) 0.2370 (2) 0.0687 (9)
H6 0.6720 0.6086 0.2249 0.082*
C7 0.5927 (2) 0.6597 (3) 0.31775 (18) 0.0513 (7)
C8 0.4685 (2) 0.7967 (3) 0.60077 (14) 0.0370 (6)
C9 0.29860 (19) 0.9337 (3) 0.53949 (13) 0.0333 (5)
C10 0.1982 (2) 1.0076 (3) 0.47272 (14) 0.0394 (6)
H10A 0.1530 1.0837 0.4984 0.047*
H10B 0.2321 1.0696 0.4339 0.047*
C11 0.0892 (2) 0.8421 (3) 0.34524 (15) 0.0489 (7)
H11 0.1225 0.8925 0.3057 0.059*
C12 −0.0098 (2) 0.6914 (4) 0.40393 (16) 0.0559 (7)
supporting information
sup-3
Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, o3189–o3190 Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
U11 U22 U33 U12 U13 U23
S1 0.0446 (4) 0.0770 (6) 0.0449 (4) 0.0168 (4) 0.0050 (3) 0.0145 (4)
O1 0.0668 (15) 0.115 (2) 0.0797 (17) 0.0251 (14) 0.0167 (13) −0.0072 (15)
O2 0.0695 (15) 0.0721 (17) 0.167 (3) 0.0103 (13) 0.0388 (16) −0.0375 (17)
N1 0.0440 (14) 0.0640 (18) 0.097 (2) −0.0020 (13) 0.0308 (15) −0.0169 (16)
N2 0.0445 (11) 0.0504 (14) 0.0263 (10) 0.0030 (10) 0.0114 (9) 0.0014 (9)
N3 0.0335 (10) 0.0415 (12) 0.0245 (9) 0.0016 (8) 0.0059 (8) 0.0008 (8)
N4 0.0414 (11) 0.0583 (14) 0.0204 (10) 0.0004 (10) 0.0022 (9) 0.0040 (10)
N5 0.0404 (11) 0.0526 (14) 0.0264 (10) −0.0002 (10) 0.0054 (8) −0.0028 (9)
N6 0.0344 (10) 0.0521 (13) 0.0238 (10) 0.0053 (9) 0.0037 (8) −0.0022 (9)
N7 0.0491 (13) 0.0778 (17) 0.0344 (12) −0.0106 (12) 0.0121 (10) −0.0089 (11)
N8 0.0537 (14) 0.0737 (17) 0.0339 (12) −0.0055 (12) 0.0036 (10) −0.0126 (11)
C1 0.0418 (14) 0.0500 (16) 0.0360 (14) 0.0026 (12) 0.0107 (11) −0.0004 (11)
C2 0.0413 (13) 0.0475 (16) 0.0399 (14) −0.0107 (11) 0.0178 (11) −0.0097 (12)
C3 0.0525 (16) 0.068 (2) 0.0392 (15) −0.0100 (14) 0.0160 (12) −0.0050 (14)
C4 0.075 (2) 0.083 (2) 0.0381 (16) −0.0315 (18) 0.0156 (15) −0.0065 (15)
C5 0.088 (2) 0.095 (3) 0.0501 (19) −0.047 (2) 0.0439 (19) −0.0278 (18)
C6 0.066 (2) 0.081 (2) 0.074 (2) −0.0292 (18) 0.0446 (18) −0.0351 (19)
C7 0.0457 (15) 0.0532 (18) 0.0616 (18) −0.0143 (13) 0.0259 (13) −0.0182 (14)
C8 0.0363 (12) 0.0431 (15) 0.0287 (12) −0.0052 (11) 0.0037 (10) 0.0047 (11)
C9 0.0343 (12) 0.0383 (14) 0.0263 (12) −0.0023 (10) 0.0062 (9) −0.0043 (10)
C10 0.0405 (13) 0.0446 (15) 0.0309 (13) 0.0069 (11) 0.0057 (10) −0.0037 (11)
C11 0.0533 (16) 0.0658 (19) 0.0255 (12) 0.0045 (14) 0.0069 (11) −0.0030 (12)
C12 0.0470 (15) 0.075 (2) 0.0448 (16) −0.0132 (14) 0.0114 (13) −0.0128 (15)
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
S1—C8 1.672 (2) C1—C2 1.473 (3)
O1—N1 1.220 (3) C1—H1 0.9300
O2—N1 1.216 (3) C2—C3 1.387 (4)
N1—C7 1.472 (4) C2—C7 1.402 (3)
N2—C1 1.261 (3) C3—C4 1.383 (3)
N2—N3 1.393 (2) C3—H3 0.9300
N3—C9 1.375 (3) C4—C5 1.387 (5)
N3—C8 1.394 (3) C4—H4 0.9300
N4—C8 1.329 (3) C5—C6 1.357 (5)
N4—N5 1.370 (3) C5—H5 0.9300
N4—H4A 0.88 (3) C6—C7 1.380 (4)
N5—C9 1.293 (3) C6—H6 0.9300
N6—C11 1.324 (3) C9—C10 1.487 (3)
N6—N7 1.359 (3) C10—H10A 0.9700
N6—C10 1.458 (3) C10—H10B 0.9700
N7—C12 1.312 (3) C11—H11 0.9300
N8—C11 1.314 (3) C12—H12 0.9300
O2—N1—O1 123.9 (3) C6—C5—C4 120.1 (3)
O2—N1—C7 117.6 (3) C6—C5—H5 120.0
O1—N1—C7 118.3 (2) C4—C5—H5 120.0
C1—N2—N3 118.5 (2) C5—C6—C7 120.0 (3)
C9—N3—N2 119.14 (17) C5—C6—H6 120.0
C9—N3—C8 107.40 (18) C7—C6—H6 120.0
N2—N3—C8 132.64 (19) C6—C7—C2 121.9 (3)
C8—N4—N5 114.70 (18) C6—C7—N1 116.7 (3)
C8—N4—H4A 123.3 (17) C2—C7—N1 121.4 (2)
N5—N4—H4A 121.9 (17) N4—C8—N3 102.6 (2)
C9—N5—N4 103.68 (18) N4—C8—S1 126.92 (17)
C11—N6—N7 109.3 (2) N3—C8—S1 130.51 (18)
C11—N6—C10 130.1 (2) N5—C9—N3 111.64 (19)
N7—N6—C10 120.58 (18) N5—C9—C10 124.5 (2)
C12—N7—N6 101.9 (2) N3—C9—C10 123.80 (19)
C11—N8—C12 102.3 (2) N6—C10—C9 111.64 (19)
N2—C1—C2 118.3 (2) N6—C10—H10A 109.3
N2—C1—H1 120.8 C9—C10—H10A 109.3
C2—C1—H1 120.8 N6—C10—H10B 109.3
C3—C2—C7 116.6 (2) C9—C10—H10B 109.3
C3—C2—C1 120.3 (2) H10A—C10—H10B 108.0
C7—C2—C1 123.0 (2) N8—C11—N6 111.0 (2)
C4—C3—C2 121.7 (3) N8—C11—H11 124.5
C4—C3—H3 119.2 N6—C11—H11 124.5
C2—C3—H3 119.2 N7—C12—N8 115.5 (3)
C3—C4—C5 119.7 (3) N7—C12—H12 122.3
C3—C4—H4 120.1 N8—C12—H12 122.3
C5—C4—H4 120.1
C1—N2—N3—C9 −168.9 (2) O1—N1—C7—C2 −35.4 (4)
C1—N2—N3—C8 22.9 (4) N5—N4—C8—N3 0.1 (3)
C8—N4—N5—C9 −0.9 (3) N5—N4—C8—S1 179.03 (17)
C11—N6—N7—C12 −0.2 (3) C9—N3—C8—N4 0.8 (2)
C10—N6—N7—C12 179.4 (2) N2—N3—C8—N4 170.0 (2)
N3—N2—C1—C2 −177.79 (19) C9—N3—C8—S1 −178.13 (19)
N2—C1—C2—C3 −15.5 (4) N2—N3—C8—S1 −8.9 (4)
N2—C1—C2—C7 165.2 (2) N4—N5—C9—N3 1.4 (2)
C7—C2—C3—C4 −1.5 (4) N4—N5—C9—C10 −179.8 (2)
C1—C2—C3—C4 179.1 (2) N2—N3—C9—N5 −172.38 (19)
C2—C3—C4—C5 0.4 (4) C8—N3—C9—N5 −1.5 (3)
C3—C4—C5—C6 1.1 (4) N2—N3—C9—C10 8.8 (3)
C4—C5—C6—C7 −1.4 (4) C8—N3—C9—C10 179.7 (2)
C5—C6—C7—C2 0.2 (4) C11—N6—C10—C9 −118.1 (3)
C5—C6—C7—N1 −177.7 (3) N7—N6—C10—C9 62.4 (3)
C3—C2—C7—C6 1.2 (4) N5—C9—C10—N6 −107.2 (3)
C1—C2—C7—C6 −179.4 (2) N3—C9—C10—N6 71.4 (3)
C3—C2—C7—N1 179.0 (2) C12—N8—C11—N6 −0.3 (3)
supporting information
sup-5
Acta Cryst. (2006). E62, o3189–o3190
O2—N1—C7—C6 −32.7 (4) C10—N6—C11—N8 −179.2 (2)
O1—N1—C7—C6 142.5 (3) N6—N7—C12—N8 0.0 (3)
O2—N1—C7—C2 149.3 (3) C11—N8—C12—N7 0.2 (3)
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
D—H···A D—H H···A D···A D—H···A
N4—H4A···N8i 0.88 (3) 1.97 (3) 2.838 (3) 171 (2)