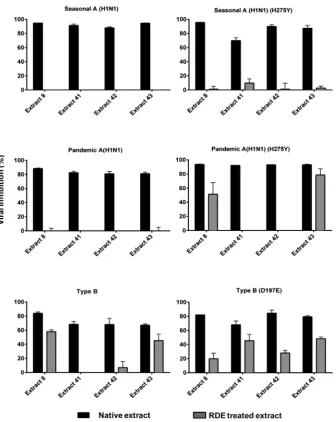
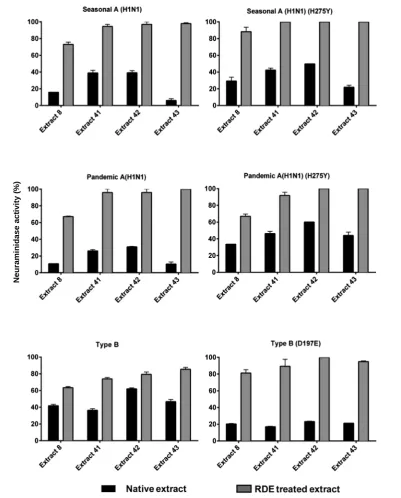
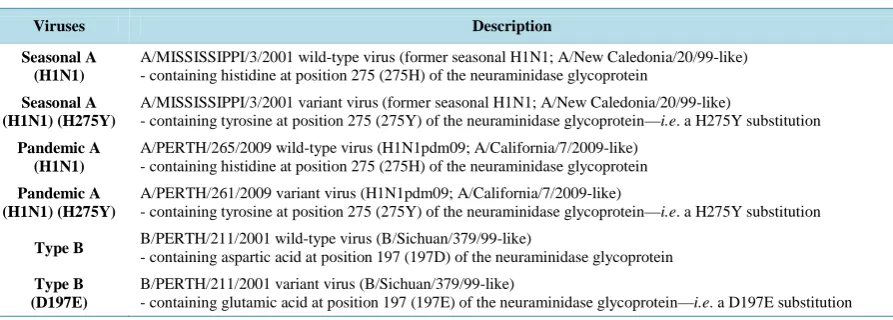
Evidence of Synergistic Activity of Medicinal Plant Extracts against Neuraminidase Inhibitor Resistant Strains of Influenza Viruses
Full text
Figure



Related documents
The aim of this study is presenting the structure and fundamental characteristics of a Mixed Experience Program Training and Employment whose overall objective was
Second, it is to develop a conceptual framework which included the independent variables such as usefulness, ease of use, relative advantage, perceived risk, perceived
Idempotent procedures (those that have no additional effects if called more than once) are easily handled, but enough difficulties remain that code to call remote
A system of major characteristics indicators for rural household energy consumption includes effective heat consumption/or livelihood per capita per day (EHC), the share
AD: Alzheimer’s disease; ADAS13: Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment—Cogni- tive 13-item scale; ADNI: Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; APOE : apolipoprotein E gene;
Hospital admission is considered a risk (especially for older patients), which increases with age [1]. Among 70- year olds who are admitted in the hospital, 35% show functional loss
CC: collagenous colitis; FAC: focal active colitis; IBS: irritable bowel syndrome; LC: lymphocytic colitis; MC: microscopic colitis.. Author
HSIL-micro: High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion cannot exclude microinvasion; PR: Prevalence ratio; HSIL: High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; CI: Confidence